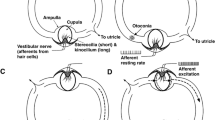
Abstract
Purpose of the review
To define the best up-to-date practical approach to treat benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV).
Recent findings
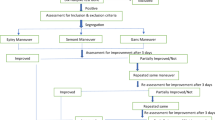
Both posterior and horizontal canal BPPV canalith repositioning maneuvers (Semont, Epley, and Gufoni’s maneuvers) are level 1 evidence treatment for evidence-based medicine. The choice of maneuver (since their efficacy is comparable) is up to the clinician’s preferences, failure of the previous maneuver, or movement restrictions of the patient. Maneuvers for controversial variants, such as anterior canal and apogeotropic posterior canal BPPV, have weaker evidence of efficacy. Despite this, these variants are increasingly diagnosed and treated. Maneuvers also play a role in the differential diagnosis with central vestibular disorders. Chair-assisted treatment may be of help if available while surgical canal plugging should be indicated in selected same-canal, same-side intractable severe BPPV.
Summary
The primary evidence-based treatment strategy for BPPV should be physical therapy through maneuvers. Despite the high success rate of liberatory maneuvers, there is a low percentage of subjects who have unsatisfactory outcomes. These patients need to be investigated to identify recurrences, multiple canal involvement, associated comorbidities (migraine, persistent postural perceptual dizziness), or risk factors for recurrences (low vitamin D serum level). Future research should also identify the optimum maneuvers for variants whose diagnosis and treatment are still a matter of some debate.






Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Neuhauser HK. The epidemiology of dizziness and vertigo. Handb Clin Neurol. 2016;137:67–82.
von Brevern M, Radtke A, Lezius F, et al. Epidemiology of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a population based study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2007;78:710–5.
Lindell E, Finizia C, Johansson M, Karlsson T, Nilson J, Magnusson M. Asking about dizziness when turning in bed predicts examination findings for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J Vestib Res. 2018;28(3–4):339–47.
Feil K, Feuerecker R, Goldschagg N, et al. Predictive capability of an iPad-based medical device (medx) for the diagnosis of vertigo and dizziness. Front Neurol. 2018;9:29.
•• Nuti D, Masini M, Mandala M. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo and its variants. In: Furman JM, Lempert T, editors. Handb Clin Neurol 2016;137:241–56. A complete overview of physipathology, diagnosis and treatment of BPPV.
• Kao WT, Parnes LS, Chole RA. Otoconia and otolithic membrane fragments within the posterior semicircular canal in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Laryngoscope. 2017;127:709–14. In vivo demonstration of detached otoconia in humans.
Meghji S, Murphy D, Nunney I, Phillips JS. The seasonal variation of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otol Neurotol. 2017;38:1315–8.
Caruso G, Nuti D. Epidemiological data from 2.270 PPV patients. Audiol Med. 2005;3:7–11.
von Brevern M, Bertholon P, Brandt T, et al. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: diagnostic criteria. J Vestib Res. 2015;25:105–17.
Anagnostou E, Kouzi I, Spengos K. Diagnosis and treatment of anterior-canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a systematic review. J Clin Neurol. 2015;11:262–7.
Vannucchi P, Pecci R, Giannoni B, Di GF, Santimone R, Mengucci A. Apogeotropic posterior semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: some clinical and therapeutic considerations. Audiol Res. 2015;5:130.
Jung JY, Kim SH. Comparison between objective and subjective benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: clinical features and outcomes. Acta Otolaryngol. 2016;136:1267–72.
Büki B, Mandalà M, Nuti D. Typical and atypical benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: literature review and new theoretical considerations. J Vestib Res. 2014;24:415–23.
•• Bhattacharyya N, Gubbels SP, Schwartz SR, et al. Clinical practice guideline: benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (update). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017;156:S1–S47. Recent clinical guidelines for BPVV.
Jumani K, Powell J. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: management and its impact on falls. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2017;126:602–5.
Schuknecht HF. Cupulolithiasis. Arch Otolaryngol. 1969;90:765–78.
Brandt T, Daroff RBG. Physical therapy for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Arch Otolaryngol. 1980;106:484–505.
Semont A, Freyss G, Vitte E. Curing the BPPV with a liberatory maneuver. Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 1988;42:290–3.
Epley JM. The canalith repositioning procedure: for treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1992;107:399–404.
Parnes LS, Price-Jones RG. Particle repositioning maneuver for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1993;102:325–31.
Herdman SJ, Tusa RJ, Zee DS, Proctor LR, Mattox DE. Single treatment approaches to benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1993;119:450–4.
Gold DR, Morris L, Kheradmand A, Schubert MC. Repositioning maneuvers for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2014;16:307.
Chen CC, Cho HS, Lee HH, Hu CJ. Efficacy of repositioning therapy in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo and preexisting central neurologic disorders. Front Neurol. 2018;9:486.
Mandalà M, Santoro GP, AsprellaLibonati G, et al. Double-blind randomized trial on short-term efficacy of Sémont maneuver for treatment of posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J Neurol. 2012;259:882–5.
Faldon ME, Bronstein AM. Head accelerations during particle repositioning manoeuvres. Audiol Neurootol. 2008;13:345–56.
Epley JM. Human experience with canalith repositioning maneuvers. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;942:179–91.
Fyrmpas G, Barkoulas E, Haidich AB, Tsalighopoulos M. Vertigo during the Epley maneuver and success rate in patients with BPPV. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013;270:2621–5.
Califano L, Capparuccia PG, Di Maria D, Melillo MG, Villari D. Treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo of posterior semicircular canal by “Quick Liberatory Rotation Manoeuvre”. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2003;23:161–7.
Michael P, Muñoz D, Tuma A, Gárate M, Barraza C, Nuñez M, et al. A chair-based abbreviated repositioning maneuver (ChARM) for fast treatment of posterior BPPV. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2019;276:2191–8.
Anagnostou E, Stamboulis E, Kararizou E. Canal conversion after repositioning procedures: comparison of Semont and Epley maneuver. J Neurol. 2014;261:866–9.
Cambi J, Astore S, Mandalà M, Trabalzini F, Nuti D. Natural course of positional down-beating nystagmus of peripheral origin. J Neurol. 2013;260:1489–96.
Giommetti G, Lapenna R, Panichi R, Mobaraki PD, Longari F, Ricci G, et al. Residual dizziness after successful repositioning maneuver for idiopathic benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a review. Audiol Res. 2017;7:178.
Nuti D, Nati C, Passali D. Treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: no need for postmaneuver restrictions. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2000;122:440–4.
Kim JS, Zee DS. Clinical practice. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. N Engl J Med. 2014;20:1138–47.
Soto Varela A, Bartual Magro J, Santos Pérez S, Vélez Regueiro M, Lechuga García R, Pérez-Carro Ríos A, et al. Benign paroxysmal vertigo: a comparative prospective study of the efficacy of Brandt and Daroff exercises, Semont and Epley maneuver. Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol (Bord). 2001;122:179–83.
Büki B. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo—toward new definitions. Otol Neurotol. 2014;35:323–8.
Choi JY, Glasauer S, Kim JH, Zee DS, Kim JS. Characteristics and mechanism of apogeotropic central positional nystagmus. Brain. 2018;141(3):762–75.
Beh SC. Horizontal direction-changing positional nystagmus and vertigo: a case of vestibular migraine masquerading as horizontal canal BPPV. Headache. 2018;58:1113–7.
Choi S, Choi HR, Nahm H, Han K, Shin JE, Kim CH. Utility of the bow and lean test in predicting subtype of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Laryngoscope. 2018;128(11):2600–4.
McClure A. Lateral canal BPV. Am J Otolaryngol. 1985;14:30–5.
Baloh RW, Jacobson K, Honrubia V. Lateral semicircular canal variant of benign positional vertigo. Neurology. 1993;43:2542–9.
Nuti D, Vannucchi P, Pagnini P. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo of the horizontal canal: a form of canalolithiasis with variable clinical features. J Vestib Res. 1996;6:173–84.
Lempert T, Tiel-Wilck K. A positional maneuver for treatment of horizontal-canal benign positional vertigo. Laryngoscope. 1996;106:476–8.
Nuti D, Agus G, Barbieri MT, et al. The management of horizontal-canal paroxysmal positional vertigo. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh). 1998;118:455–60.
Kim JS, Oh S-Y, Lee S-H, et al. Randomized clinical trial for geotropic horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Neurology. 2012;79:700–7.
Gufoni M, Mastrosimone L, Di Nasso F. Repositioning maneuver in benign paroxysmal vertigo of horizontal semicircular canal. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 1988;18:363–7.
Mandalà M, Pepponi E, Santoro GP, et al. Double-blind randomized trial on the efficacy of the Gufoni maneuver for treatment of lateral canal BPPV. Laryngoscope. 2013;123:1782–6.
Vannucchi P, Giannoni B, Pagnini P. Treatment of horizontal semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J Vestib Res. 1997;7:1–6.
Vannucchi P, Asprella Libonati G, Gufoni M. The physical treatment of lateral semicircular canal canalolithiasis. Audiol Med. 2005;3:52–6.
Ichijo H. Affected-ear-up 120° maneuver for treatment of lateral semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017;274:3351–7.
Li J, Zou S, Tian S. A prospective randomized controlled study of Li quick repositioning maneuver for geotropic horizontal canal BPPV. Acta Otolaryngol. 2018;138:779–84.
Califano L, Melillo MG, Mazzone S, Vassallo A. Converting apogeotropic into geotropic lateral canalolithiasis by head-pitching manoeuvre in the sitting position. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2008;28:287–91.
Kim JS, Oh SY, Lee SH, et al. Randomized clinical trial for apogeotropic horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Neurology. 2012;78:159–66.
• Zuma e Maia F. New treatment strategy for apogeotropic horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Audiol Res. 2016;6:163. A new maneuver for apogeotropic hcBPPV.
Kim HA, Park SW, Kim J, et al. Efficacy of mastoid oscillation and the Gufoni maneuver for treating apogeotropic horizontal benign positional vertigo: a randomized controlled study. J Neurol. 2017;264:848–55.
Califano L, Salafia F, Mazzone S, Melillo MG, Califano M. Anterior canal BPPV and apogeotropic posterior canal BPPV: two rare forms of vertical canalolithiasis. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2014;34:189–97.
Korres S, Riga M, Sandris V, et al. Canalithiasis of the anterior semicircular canal (ASC): treatment options based on the possible underlying pathogenetic mechanisms. Int J Audiol. 2010;49:606–12.
Honrubia V, Baloh RW, Harris MR, Jacobson KM. Paroxysmal positional vertigo syndrome. Am J Otolaryngol. 1999;20(4):465–70.
Yacovino DA, Hain TC, Gualtieri F. New therapeutic maneuver for anterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J Neurol. 2009;256:1851–5.
Ling X, Li KZ, Shen B, Si LH, Hong Y, Yang X. Diagnosis and treatment of canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Int J Audiol. 2018;57:673–80.
• Yang X, Ling X, Shen B, Hong Y, Li K, Si L, et al. Diagnosis strategy and Yacovino maneuver for anterior canal-benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J Neurol. 2019;266:1674–84. Increased evidence of efficacy of Yacovino’s maneuver for acBPPV.
Vannucchi P, Pecci R, Giannoni B. Posterior semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo presenting with torsional downbeating nystagmus: an apogeotropic variant. Int J Otolaryngol. 2012;2012:413603.
• Helminski JO. Peripheral downbeat positional nystagmus: apogeotropic posterior canal or anterior canal BPPV. J Neurol Phys Ther. 2019 Apr;43(Suppl 2 Supplement, Special Supplement: International Conference on Vestibular Rehabilitation):S8–S13. Differential diagnosis and treatment between acBPPV and apogeotropic pcBPPV.
Oh EH, Lee JH, Kim HJ, Choi SY, Choi KD, Choi JH. Incidence and clinical significance of positional downbeat nystagmus in posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J Clin Neurol. 2019;15(2):143–8.
Huebner AC, Lytle SR, Doettl SM, Plyler PN, Thelin JT. Treatment of objective and subjective benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J Am Acad Audiol. 2013;24:600–6.
Balatsouras DG, Korres SG. Subjective benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012;146:98–103.
•• Kim HJ, Kim JS. The patterns of recurrences in idiopathic benign paroxysmal positional vertigo and self-treatment evaluation. Front Neurol. 2017;8:690. Pattern of recurrences for BPPV.
Wei W, Sayyid ZN, Ma X, Wang T, Dong Y. Presence of anxiety and depression symptoms affects the first time treatment efficacy and recurrence of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Front Neurol. 2018;9:178.
Vaduva C, Esteban-Sanchez J, Sanz-Fernandez R, Martin-Sanz E. Prevalence and management of post-BPPV residual symptoms. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2018;275:1429–37.
AlGarni MA, Mirza AA, Althobaiti AA, Al-Nemari HH, Bakhsh LS. Association of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo with vitamin D deficiency: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2018;275:2705–11.
•• Jeong SH, Kim JS. Impaired calcium metabolism in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a topical review. J Neurol Phys Ther. 2019;43(Suppl 2 Supplement, Special Supplement: International Conference on Vestibular Rehabilitation):S37–41. Increased evidence of correlation between calcium metabolism and BPPV.
Rhim GI. Serum vitamin D and long-term outcomes of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2019;12:273–8.
Nakada T, Sugiura S, Uchida Y, Suzuki H, Teranishi M, Sone M. Difference in serum levels of vitamin D between canalolithiasis and cupulolithiasis of the horizontal semicircular canal in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Front Neurol. 2019;10:176.
Kim SK, Hong SM, Park IS, Choi HG. Association between migraine and benign paroxysmal positional vertigo among adults in South Korea. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019 Jan 24. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoto.2018.4016 [Epub ahead of print].
Staab JP, Eckhardt-Henn A, Horii A, Jacob R, Strupp M, Brandt T, et al. Diagnostic criteria for persistent postural-perceptual dizziness (PPPD): consensus document of the Committee for the Classification of Vestibular Disorders of the Bárány Society. J Vestib Res. 2017;27:191–208.
Luryi AL, Lawrence J, LaRouere M, et al. Treatment of patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo and severe immobility using the particle repositioning chair: a retrospective cohort study. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2018;127:390–4.
West N, Bloch SL, Moller MN, Hansen S, Klokker M. Reposition chair treatment improves subjective outcomes in refractory benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J Int Adv Otol. 2019;15:146–50.
Beyea JA, Agrawal SK, Parnes LS. Transmastoid semicircular canal occlusion: a safe and highly effective treatment for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo and superior canal dehiscence. Laryngoscope. 2012;122:1862–6.
Corvera Behar G, García de la Cruz MA. Surgical treatment for recurrent benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017;21:191–4.
Kelkar A, Johnson I. A novel use of intratympanic dexamethasone for intractable posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: report of two cases. J Laryngol Otol. 2018;132:1147–9.
Mandalà M, Colletti L, Carner M, Barillari M, Cerini R, Mucelli RP, et al. Pneumolabyrinth and positional vertigo after stapedectomy. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2011;38:547–50.
Guerra-Jimenez G, Domenech-Vadillo E, Alvarez-Morujo de Sande MG, et al. Healing criteria: how should an episode of benign paroxistic positional vertigo of posterior semicircular canal’s resolution be defined? Prospective observational study. Clin Otolaryngol. 2019;44:219–26.
Sim E, Tan D, Hill K. Poor treatment outcomes following repositioning maneuvers in younger and older adults with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2019;20:224.e1–224.e23.
You P, Instrum R, Parnes L. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2018;4:116–23.
Acknowledgments
The scientific illustrator Stefano Ricci, Department of Physical, Earth and the Environmental sciences, R.U. of Prehistory and Anthropology, University of Siena realized the figures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Marco Mandalà declares that he has no conflict of interest. Lorenzo Salerni declares that he has no conflict of interest. Daniele Nuti declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Neurologic Ophthalmology and Otology
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mandalà, M., Salerni, L. & Nuti, D. Benign Positional Paroxysmal Vertigo Treatment: a Practical Update. Curr Treat Options Neurol 21, 66 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-019-0606-x
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-019-0606-x