Abstract
Purpose of review
The aim of this article was to review the options and particularities of the treatment of restless legs syndrome (RLS) in Parkinson’s disease (PD).
Recent findings
RLS is more frequent in PD than in the general population. Even if these two disorders share some specificity (dopa-sensitivity), they also differ in many features (iron load, genetic profile, dopaminergic cell count), resulting in different adaptations of the treatment. Only one study has specifically explored and demonstrated the efficacy of a treatment (rotigotine) in RLS with PD, constraining us to treat RLS with PD by analogy as idiopathic RLS in the other cases. However, arrangements linked to the peculiar population and pathology of PD are required.
Summary
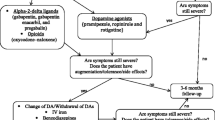
The treatment of RLS in PD consists in adaptation of dopaminergic treatment and introduction of alpha-2-delta ligands and, in refractory cases, of opioids or deep brain stimulation. Iron deficiency should probably not be compensated.

Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Allen RP, Picchietti DL, Garcia-Borreguero D, Ondo WG, Walters AS, Winkelman JW, et al. Restless legs syndrome/Willis-Ekbom disease diagnostic criteria: Updated International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group (IRLSSG) consensus criteria - history, rationale, description, and significance. Sleep Med. 2014;15:860–73.
Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1992;55:181–4.
Fereshtehnejad SM, Shafieesabet M, Shahidi GA, Delbari A, Lökk J. Restless legs syndrome in patients with Parkinson’s disease: a comparative study on prevalence, clinical characteristics, quality of life and nutritional status. Acta Neurol Scand. 2015;13:211–8.
Bhalsing K, Suresh K, Muthane UB, Pal PK. Prevalence and profile of restless legs syndrome in Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders: a case-control study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2013;19:426–30.
Rijsman RM, Schoolderman LF, Rundervoort R, Louter M. Restless legs syndrome in Parkinson’s disease. Park Relat Disord. 2014;20:S5–9.
Peralta CM, Frauscher B, Seppi K, Wolf E, Wenning GK, Högl B, et al. Restless legs syndrome in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2009;24:2076–80.
Garcia-Borreguero D, Egatz R, Winkelmann J, Berger K. Epidemiology of restless legs syndrome: the current status. Sleep Med Rev. 2006;10:153–67.
Allen RP, Walters AS, Montplaisir J, Hening W, Myers A, Bell TJ, et al. Restless legs syndrome prevalence and impact: REST general population study. Arch Intern Med. 2005;13:1286–92.
Trenkwalder C, Allen R, Hogl B, Paulus W, Winkelmann J. Restless legs syndrome associated with major diseases a systematic review and new concept. Neurology. 2016;86:1336–43.
Wetter TC, Collado-Seidel V, Pollmächer T, Yassouridis A, Trenkwalder C. Sleep and periodic leg movement patterns in drug-free patients with Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Sleep. 2000;23:361–7.
Montplaisir J, Boucher S, Poirier G, Lavigne G, Lapierre O, Lespérance P. Clinical, polysomnographic, and genetic characteristics of restless legs syndrome: a study of 133 patients diagnosed with new standard criteria. Mov Disord. 1997;12:61–5.
Pittock SJ, Parrett T, Adler CH, Parisi JE, Dickson DW, Ahlskog JE. Neuropathology of primary restless leg syndrome: absence of specific tau- and alpha-synuclein pathology. Mov Disord. 2004;19:695–9.
Earley CJ, Connor J, Garcia-Borreguero D, Jenner P, Winkelman J, Zee PC, et al. Altered brain iron homeostasis and dopaminergic function in restless legs syndrome (Willis-Ekbom disease). Sleep Med. 2014;15:1288–301.
Connor JR, Wang XS, Allen RP, Beard JL, Wiesinger JA, Felt BT, et al. Altered dopaminergic profile in the putamen and substantia nigra in restless leg syndrome. Brain. 2009;132:2403–12.
Connor JR, Wang XS, Patton SM, Menzies SL, Troncoso JC, Earley CJ, et al. Decreased transferrin receptor expression by neuromelanin cells in restless legs syndrome. Neurology. 2004;11:1563–7.
Connor JR, Boyer PJ, Menzies SL, Dellinger B, Allen RP, Ondo WG, et al. Neuropathological examination suggests impaired brain iron acquisition in restless legs syndrome. Neurology. 2003;16:304–9.
Gan-Or Z, Alcalay RN, Bar-Shira A, Leblond CS, Postuma RB, Ben-Shachar S, et al. Genetic markers of restless legs syndrome in Parkinson disease. Park Relat Disord. 2015;21:582–5.
Vilariño-Güell C, Soto AI, Young JE, Lin SC, Uitti RJ, Wszolek ZK, et al. Susceptibility genes for restless legs syndrome are not associated with Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2008;71:222–3.
Walters AS, LeBrocq C, Dhar A, Hening W, Rosen R, Allen RP, et al. Validation of the International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group rating scale for restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med. 2003;4:121–32.
Trenkwalder C, Kohnen R, Högl B, Metta V, Sixel-Döring F, Frauscher B, et al. Parkinson’s disease sleep scale-validation of the revised version PDSS-2. Mov Disord. 2011;26:644–52.
De Cock VC, Bayard S, Yu H, Grini M, Carlander B, Postuma R, et al. Suggested immobilization test for diagnosis of restless legs syndrome in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2012;27:743–9.
Perez-Lloret S, Rey M, Bondon-Guitton E, Rascol O, Montastruc JL. Drugs associated with restless legs syndrome: a case/noncase study in the French pharmacovigilance database. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2012;32:824–7.
Loddo G, Calandra-Buonaura G, Sambati L, Giannini G, Cecere A, Cortelli P, et al. The treatment of sleep disorders in Parkinson’s disease: from research to clinical practice. Front Neurol. 2017;16:42.
Garcia-Borreguero D, Silber M, Winkelman JW, Hogl B, Bainbridge J, Buchfuhrer M. Guidelines for the first-line treatment of restless legs syndrome/Willis-Ekbom disease, prevention and treatment of dopaminergic augmentation: a combined task force of the IRLSSG, EURLSSG, and the RLS-foundation. Sleep Med. 2016;21:1–11.
Grolez G, Moreau C, Sablonnière B, Garçon G, Devedjian JC, Meguig S, et al. Ceruloplasmin activity and iron chelation treatment of patients with Parkinson’s disease. BMC Neurol. 2015;15:74.
•• Winkelmann J, Allen RP, Högl B, Inoue Y, Oertel W, Salminen AV, et al. Treatment of restless legs syndrome: evidence-based review and implications for clinical practice (revised 2017). Mov Disord. 2018;33:1077–91. The newest evidence-based review on the treatment of idiopathic RLS.
Perez-Perez J, Pascual-Sedano B, Campolongo A, Kulisevsky J. Duodopa for the treatment of severe restless legs syndrome. Mov Disord. 2016;31:S304Poster953.
Pagonabarraga J, Piñol G, Cardozo A, Sanz P, Puente V, Otermín P, et al. Transdermal rotigotine improves sleep fragmentation in parkinson’s disease: results of the multicenter, prospective SLEEP-FRAM study. Parkinsons Dis. 2015;2015:1315–8.
Kim J, Chung S, Kim J, Jeon B, Singh P, Thierfelder S, et al. Rotigotine transdermal system as add-on to oral dopamine agonist in advanced Parkinson’s disease: an open-label study. BMC Neurol. 2015;15:17.
Vallderiola F, Compta Y, Aparicio J, Tarradellas J, Salazar G, Oliver J, et al. Effects of night-time use of rotigotine on nocturnal symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsons Dis. 2015;2015:475630.
Wang Y, Yang YC, Lan DM, Wu HJ, Zhao ZX. An observational clinical and video-polysomnographic study of the effects of rotigotine in sleep disorder in Parkinson’s disease. Sleep Breath. 2017;21:319–25.
Trenkwalder C, Kies B, Rudzinska M, Fine J, Nikl J, Honczarenko K, et al. Rotigotine effects on early morning motor function and sleep in Parkinson’s disease: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study (RECOVER). Mov Disord. 2011;26:90–9 The only randomized double blind study on the efficacy of a treatment in RLS with PD.
Reuter I, Ellis CM, Chaudhuri KR. Nocturnal subcutaneous apomorphine infusion in Parkinson’s disease and restless legs syndrome. Acta Neurol Scand. 2009;100:163–7.
Priano L, Albani G, Brioschi A, Guastamacchia G, Calderoni S, Lopiano L, et al. Nocturnal anomalous movement reduction and sleep microstructure analysis in parkinsonian patients during 1-night transdermal apomorphine treatment. Neurol Sci. 2003;24:207–8.
Iftikhar IH, Alghothani L, Trotti LM. Gabapentin enacarbil, pregabalin and rotigotine are equally effective in restless legs syndrome: a comparative meta-analysis. Eur J Neurol. 2017;24:1446–56.
Parsons B, Argoff CE, Clair A, Emir B. Improvement in pain severity category in clinical trials of pregabalin. J Pain Res. 2016;9:779–85.
Jost WH, Buhmann C. The challenge of pain in the pharmacological management of Parkinson’s disease. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2019;10:1–8.
Cochen De Cock V, Bayard S, Jaussent I, Charif M, Grini M, Croisier Langenier M, et al. Daytime sleepiness in Parkinson’s disease: a reappraisal. PLoS One. 2014;9:e107278.
Garcia-Borreguero D, Larrosa O, De la Llave Y, Verger K, Masramon X, Hernandez G. Treatment of restless legs syndrome with gabapentin: a double-blind, cross-over study. Neurology. 2002;48:82–6.
Allen RP, Chen C, Garcia-Borreguero D, Polo O, DuBrava S, Miceli J, et al. Comparison of pregabalin with pramipexole for restless legs syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:621–31.
Allen R, Chen C, Soaita A, Wohlberg C, Knapp L, Peterson BT, et al. A randomized, double-blind, 6-week, dose-ranging study of pregabalin in patients with restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med. 2010;11:512–9.
Garcia-Borreguero D, Larrosa O, Williams AM, Albares J, Pascual M, Palacios JC, et al. Treatment of restless legs syndrome with pregabalin: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Neurology. 2010;74:1897–904.
Perez Lloret S, Amaya M, Merello M. Pregabalin-induced parkinsonism: a case report. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2009;32:353–4.
Erol C, Ozben S, Ozer F, Cetin S, Tiras R. Bilateral ballism induced by gabapentin in idiopatic Parkinson’s disease. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2009;111:397.
Raju PM, Walker RW, Lee MA. Dyskinesia induced by gabapentin in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2007;15:288–9.
Inoue Y, Hirata K, Uchimura N, Kuroda K, Hattori N, Takeuchi M. Gabapentin enacarbil in Japanese patients with restless legs syndrome: a 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study. Curr Med Res Opin. 2013;29:13–21.
Lal R, Ellenbogen A, Chen D, Zomorodi K, Atluri H, Luo W, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-response study to assess the pharmacokinetics, efficacy, and safety of gabapentin enacarbil in subjects with restless legs syndrome. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2012;35:165–73.
Lee D, Ziman R, Perkins A, Poceta J, Walters A, Barrett R. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to assess the efficacy and tolerability of gabapentin enacarbil in subjects with restless legs syndrome. J Clin Sleep Med. 2011;7:282–92.
Walters AS, Ondo WG, Kushida CA, Becker PM, Ellenbogen AL, Canafax DM, et al. Gabapentin enacarbil in restless legs syndrome: a phase 2b, 2-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2009;32:311–20.
Kushida CA, Walters AS, Becker P, Thein SG, Perkins AT, Roth T, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study of XP13512/GSK1838262 in the treatment of patients with primary restless legs syndrome. Sleep. 2009;32:159–68.
Kushida C, Becker P, Ellenbogen A, Canafax D, Barrett R. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of XP13512/GSK1838262 in patients with RLS. Neurology. 2009;72:439–49.
Bogan R, Bornemann M, Kushida C, Tran P, Barrett R. Long-term maintenance treatment of restless legs syndrome with gabapentin enacarbil: a randomized controlled study. Mayo Clin Proc. 2010;85:512–21.
Fujishiro H. Effects of gabapentin enacarbil on restless legs syndrome and leg pain in dementia with Lewy bodies. Psychogeriatrics. 2014;14:132–4.
Walters AS, Wagner ML, Hening WA, Grasing K, Mills R, Chokroverty S, et al. Successful treatment of the idiopathic restless legs syndrome in a randomized double-blind trial of oxycodone versus placebo. Sleep. 1993;16:327–32.
Trenkwalder C, Beneš H, Grote L, García-Borreguero D, Högl B, Hopp M, et al. Prolonged release oxycodone-naloxone for treatment of severe restless legs syndrome after failure of previous treatment: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial with an open-label extension. Lancet Neurol. 2013;12:1141–50.
Trenkwalder C, Chaudhuri KR, Martinez-Martin P, Rascol O, Ehret R, Vališ M, et al. Prolonged-release oxycodone-naloxone for treatment of severe pain in patients with Parkinson’s disease (PANDA): a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14:1161–70.
Silber MH, Becker PM, Buchfuhrer MJ, Earley CJ, Ondo WG, Walters AS, et al. The appropriate use of opioids in the treatment of refractory restless legs syndrome. Mayo Clin Proc. 2018;93:59–67.
Earley CJ, Allen RP. Restless legs syndrome augmentation associated with tramadol. Sleep Med. 2006;7:592–3.
Vetrugno R, La Morgia C, D’Angelo R, Loi D, Provini F, Plazzi G, et al. Augmentation of restless legs syndrome with long-term tramadol treatment. Mov Disord. 2007;22:424–7.
Chokroverty S. Opioid-induced hyperalgesia and dopamine-induced augmentation in an intractable and refractory case of RLS. Sleep Med. 2015;16:1304.
Carlos K, Prado GF, Teixeira CDM, Conti C, de Oliveira MM, Prado LBF, et al. Benzodiazepines for restless legs syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;3:CD006939.
Shpirer I, Miniovitz A, Klein C, Goldstein R, Prokhorov T, Theitler J, et al. Excessive daytime sleepiness in patients with parkinson’s disease: a polysomnography study. Mov Disord. 2006;21:1432–8.
Benabid AL, Chabardes S, Mitrofanis J, Pollak P. Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol [Internet]. 2009;8:67–81.Available from:. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(08)70291-6.
Chahine LM, Ahmed A, Sun Z. Effects of STN DBS for Parkinson’s disease on restless legs syndrome and other sleep-related measures. Park Relat Disord. 2011;17:208–11.
Driver-Dunckley E, Evidenter VGH, Adler CH, Hillman R, Hernandez J, Fletcher G, et al. Restless legs syndrome in Parkinson’s disease patients may improve with subthalamic stimulation. Mov Disord. 2006;21:1287–9.
Klepitskaya O, Liu Y, Tsai J. Deep brain stimulation (DBS) of the subthalamic nucleus (STN) improves restless leg syndrome (RLS) in patients with Parkinson disease (PD). Mov Disord. 2017;91:e1013–21.
Kedia S, Moro E, Tagliati M, Lang AE, Kumar R. Emergence of restless legs syndrome during subthalamic stimulation for Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2004;63:2410–2.
Marques A, Fantini ML, Morand D, Pereira B, Derost P, Ulla M, et al. Emergence of restless legs syndrome after subthalamic stimulation in Parkinson’s disease: a dopaminergic overstimulation? Sleep Med. 2015;16:583–8 Interesting discussion on the mechanism of RLS and its improvement by DBS.
Rye D, DeLong M. Amelioration of sensory limb discomfort of restless legs syndrome by pallidotomy. Ann Neurol. 1999;46:800–1.
Zhao H, Zhu W, Pan T, Xie W, Zhang A, Ondo WG, et al. Spinal cord dopamine receptor expression and function in mice with 6-OHDA lesion of the A11 nucleus and dietary iron deprivation. J Neurosci Res. 2007;85:1065–76.
Okun MS, Fernandez HH, Foote KD. Deep brain stimulation of the GPi treats restless legs syndrome associated with dystonia. Mov Disord. 2005;20:500–1.
de la Fuente-Fernandez R, Stoessl AJ. The placebo effect in Parkinson’s disease. Trends Neurosci. 2002;25:302–6.
Fulda S, Wetter TC. Where dopamine meets opioids: a meta-analysis of the placebo effect in restless legs syndrome treatment studies. Brain. 2008;13:902–17.
De la Fuente-Fernández R, Ruth TJ, Sossi V, Schulzer M, Calne DB, Stoessl AJ. Expectation and dopamine release: mechanism of the placebo effect in Parkinson’s disease. Science. 2001;293:1164–6.
Lettieri CJ, Eliasson AH. Pneumatic compression devices are an effective therapy for restless legs syndrome: a prospective, randomized, double-blinded, sham-controlled trial. Chest. 2009;135:74–80. The only randomized study on a non-drug therapy of idiopathic RLS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The author declares that she has no competing interests.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Sleep Disorders
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cochen De Cock, V. Therapies for Restless Legs in Parkinson’s Disease. Curr Treat Options Neurol 21, 56 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-019-0596-8
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-019-0596-8