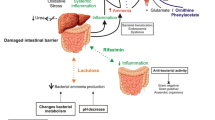
Opinion statement
Liver disease, both in its acute and chronic forms, can be associated with a wide spectrum of neurologic manifestations, both central and peripheral, ranging in severity from subclinical changes to neurocritical conditions. Neurologists are frequently consulted to participate in their management. In this review, we present an overview of management strategies for patients with hepatic disease whose clinical course is complicated by neurologic manifestations. Type A hepatic encephalopathy (HE), which occurs in acute liver failure, is a neurologic emergency, and multiple measures should be taken to prevent and treat cerebral edema. In Type C HE, which occurs in chronic liver disease, management should be aimed at correcting precipitant factors and hyperammonemia. There is an increasing spectrum of drug treatments available to minimize ammonia toxicity. Acquired hepatocerebral degeneration is a rare complication of the chronic form of HE, with typical clinical and brain MRI findings, whose most effective treatment is liver transplantation. Epilepsy is frequent and of multifactorial cause in patients with hepatic disease, and careful considerations should be made regarding choice of the appropriate anti-epileptic drugs. Several mechanisms increase the risk of stroke in hepatic disease, but many of the drugs used to treat and prevent stroke are contraindicated in severe hepatic failure. Hepatitis C infection increases the risk of ischemic stroke. Hemorrhagic stroke is more frequent in patients with liver disease of alcoholic etiology. Viral hepatitis is associated with a wide range of immune-mediated complications, mostly in the peripheral nervous system, which respond to different types of immunomodulatory treatment. Several drugs used to treat hepatic disease, such as the classical and the new direct-acting antivirals, may have neurologic complications which in some cases preclude its continued use.


Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Blachier M, Leleu H, Peck-Radosavljevic M, Valla D-C, Roudot-Thoraval F. The burden of liver disease in Europe: a review of available epidemiological data. J Hepatol. 2013;58:593–608.
Ferro JM, Oliveira S. Neurologic manifestations of gastrointestinal and liver diseases. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2014;14:487.
Sturgeon JP, Shawcross DL. Recent insights into the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy and treatments. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;8:83–100.
Palomero-Gallagher N, Zilles K. Neurotransmitter receptor alterations in hepatic encephalopathy: a review. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2013;536:109–21.
Vilstrup H, Amodio P, Bajaj J, Cordoba J, Ferenci P, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology. 2014;60:715–35. The most recently published guidelines with substantial discussion and levels of evidence of different treatment options for hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease.
Bernal W, Wendon J. Acute liver failure. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:2525–34. Clear and concise review on the management of acute liver failure.
Polson J, Lee WM. AASLD position paper: the management of acute liver failure: update 2011. Hepatology. 2005;41:1179–97. Most recent practice recommendations for the management of acute liver failure, by the American Association for The Study of Liver Disease.
Datar S, Wijdicks EFM. Neurologic manifestations of acute liver failure. Handb Clin Neurol. 2014;120:645–59.
Sureka B, Bansal K, Patidar Y, Rajesh S, Mukund A, et al. Neurologic manifestations of chronic liver disease and liver cirrhosis. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2015;44:449–61. Comprehensive review of the neuroimaging abnormalities related to chronic liver disease patients.
Karvellas CJ, Fix OK, Battenhouse H, Durkalski V, Sanders C, et al. Outcomes and complications of intracranial pressure monitoring in acute liver failure: a retrospective cohort study. Crit Care Med. 2014;42:1157–67.
Vaquero J. Therapeutic hypothermia in the management of acute liver failure. Neurochem Int. 2012;60:723–35.
Bhatia V, Batra Y, Acharya SK. Prophylactic phenytoin does not improve cerebral edema or survival in acute liver failure—a controlled clinical trial. J Hepatol. 2004;41:89–96.
Cadranel JF, Lebiez E, Di Martino V, Bernard B, El Koury S, et al. Focal neurological signs in hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients: an underestimated entity? Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96:515–8.
Yamamoto Y, Nishiyama Y, Katsura K-I, Yamazaki M, Katayama Y. Hepatic encephalopathy with reversible focal neurologic signs resembling acute stroke: case report. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2011;20:377–80.
Ben Amor S, Saied MZ, Harzallah MS, Benammou S. Hepatic myelopathy with spastic paraparesis: report of two cases and review of the literature. Eur Spine J. 2014;23 Suppl 2:167–71.
Kori P, Sahu R, Jaiswal A, Shukla R. Hepatic myelopathy: an unusual neurological complication of chronic liver disease presenting as quadriparesis. BMJ Case Rep. 2013. doi:10.1136/bcr-2013-009078
Premkumar M, Bagchi A, Kapoor N, Gupta A, Maurya G, et al. Hepatic myelopathy in a patient with decompensated alcoholic cirrhosis and portal colopathy. Case Reports Hepatol. 2012;2012:735906.
Cui M, Zhang X, Mu F. Hepatic myelopathy associated with advanced liver cirrhosis. Saudi Med J. 2012;33:1352–4.
Baccarani U, Zola E, Adani GL, Cavalletti M, Schiff S, et al. Reversal of hepatic myelopathy after liver transplantation: fifteen plus one. Liver Transpl. 2010;16:1336–7.
Guerit JM, Amantini A, Fischer C, Kaplan PW, Mecarelli O, et al. Neurophysiological investigations of hepatic encephalopathy: ISHEN practice guidelines. Liver Int. 2009;29:789–96. Practice recommendations for the neurophysiological investigation of hepatic encephalopathy related to chronic liver disease.
Conn HO, Levy LL. The nonspecificity of electroencephalographic triphasic waves: the emperor defrocked. Hepatology. 1989;9:337–8.
Lauridsen MM, Jepsen P, Vilstrup H. Critical flicker frequency and continuous reaction times for the diagnosis of minimal hepatic encephalopathy: a comparative study of 154 patients with liver disease. Metab Brain Dis. 2011;26:135–9.
Randolph C, Hilsabeck R, Kato A, Kharbanda P, Li YY, et al. Neuropsychological assessment of hepatic encephalopathy: ISHEN practice guidelines. Liver Int. 2009;29:629–35. Practice guidelines with extensive overview of neuropsychological tests used in hepatic encephalopathy related to chronic liver disease.
Mina A, Moran S, Ortiz-Olvera N, Mera R, Uribe M. Prevalence of minimal hepatic encephalopathy and quality of life in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. Hepatol Res. 2014;44:E92–9.
Als-Nielsen B, Gluud LL, Gluud C. Non-absorbable disaccharides for hepatic encephalopathy: systematic review of randomised trials. BMJ. 2004;328:1046.
Cammà C, Fiorello F, Tinè F, Marchesini G, Fabbri A, et al. Lactitol in treatment of chronic hepatic encephalopathy. A meta-analysis. Dig Dis Sci. 1993;38:916–22.
Rahimi RS, Singal AG, Cuthbert JA, Rockey DC. Lactulose vs polyethylene glycol 3350—electrolyte solution for treatment of overt hepatic encephalopathy. JAMA Intern Med. 2014;174:1727.
Eltawil KM, Laryea M, Peltekian K, Molinari M. Rifaximin vs. conventional oral therapy for hepatic encephalopathy: a meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:767–77.
Kimer N, Krag A, Møller S, Bendtsen F, Gluud LL. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the effects of rifaximin in hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014;40:123–32.
Bass NM, Mullen KD, Sanyal A, Poordad F, Neff G, et al. Rifaximin treatment in hepatic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1071–81.
Zhu G-Q, Shi K-Q, Huang S, Wang L-R, Lin Y-Q, et al. Systematic review with network meta-analysis: the comparative effectiveness and safety of interventions in patients with overt hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;41:624–35.
Gluud L, Dam G, Borre M, Les I. Oral branched-chain amino acids have a beneficial effect on manifestations of hepatic encephalopathy in a systematic review with meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. J Nutr. 2013;143(8):1263–8.
Bai M, Yang Z, Qi X, Fan D, Han G. l-ornithine-l-aspartate for hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;28:783–92.
Abid S, Jafri W, Mumtaz K, Islam M, Abbas Z, et al. Efficacy of L-ornithine-L-aspartate as an adjuvant therapy in cirrhotic patients with hepatic encephalopathy. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2011;21:666–71.
Sharma K, Pant S, Misra S, Dwivedi M, Misra A, et al. Effect of rifaximin, probiotics, and l-ornithine l-aspartate on minimal hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized controlled trial. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:225–32.
Holte K, Krag A, Gluud LL. Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials on probiotics for hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatol Res. 2012;42:1008–15.
Jiang Q, Jiang G, Shi K, Cai H, Wang Y, et al. Oral acetyl-L-carnitine treatment in hepatic encephalopathy: view of evidence-based medicine. Ann Hepatol. 2013;12:803–9.
Malaguarnera M, Vacante M, Motta M, Giordano M, Malaguarnera G, et al. Acetyl-L-carnitine improves cognitive functions in severe hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized and controlled clinical trial. Metab Brain Dis. 2011;26:281–9.
Burkard T, Biedermann A, Herold C, Dietlein M, Rauch M, et al. Treatment with a potassium-iron-phosphate-citrate complex improves PSE scores and quality of life in patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy: a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;25:352–8.
Simon-Talero M, Garcia-Martinez R, Torrens M, Augustin S, Gomez S, et al. Effects of intravenous albumin in patients with cirrhosis and episodic hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized double-blind study. J Hepatol. 2013;59:1184–92.
Rockey DC, Vierling JM, Mantry P, Ghabril M, Brown RSJ, et al. Randomized, double-blind, controlled study of glycerol phenylbutyrate in hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology. 2014;59:1073–83.
Wright G, Vairappan B, Stadlbauer V, Mookerjee RP, Davies NA, et al. Reduction in hyperammonaemia by ornithine phenylacetate prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced brain edema and coma in cirrhotic rats. Liver Int. 2012;32:410–9.
Junker AE, Als-Nielsen B, Gluud C, Gluud LL. Dopamine agents for hepatic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;2:CD003047.
Ampuero J, Ranchal I, Nunez D, Diaz-Herrero M del M, Maraver M, et al. Metformin inhibits glutaminase activity and protects against hepatic encephalopathy. PLoS One. 2012;7:e49279.
Amodio P, Canesso F, Montagnese S. Dietary management of hepatic encephalopathy revisited. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2014;17:448–52.
Amodio P, Bemeur C, Butterworth R, Cordoba J, Kato A, et al. The nutritional management of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: International Society for Hepatic Encephalopathy and Nitrogen Metabolism Consensus. Hepatology. 2013;58:325–36. Guidelines for nutritional management of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis patients.
An J, Kim KW, Han S, Lee J, Lim Y-S. Improvement in survival associated with embolisation of spontaneous portosystemic shunt in patients with recurrent hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014;39:1418–26.
García-Martínez R, Rovira A, Alonso J, Jacas C, Simón-Talero M, et al. hepatic encephalopathy is associated with posttransplant cognitive function and brain volume. Liver Transplant. 2011;17:38–46.
Bajaj JS, Schubert CM, Heuman DM, Wade JB, Gibson DP, et al. Persistence of cognitive impairment after resolution of overt hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterology. 2010;138:2332–40.
Burkhard PR, Delavelle J, Du Pasquier R, Spahr L. Chronic parkinsonism associated with cirrhosis: a distinct subset of acquired hepatocerebral degeneration. Arch Neurol. 2003;60:521–8.
Tryc AB, Goldbecker A, Berding G, Rumke S, Afshar K, et al. Cirrhosis-related Parkinsonism: prevalence, mechanisms and response to treatments. J Hepatol. 2013;58:698–705.
Butterworth RF. Parkinsonism in cirrhosis: pathogenesis and current therapeutic options. Metab Brain Dis. 2013;28:261–7.
Meissner W, Tison F. Acquired hepatocerebral degeneration. Handb Clin Neurol. 2011;100:193–7. Review of the most frequent clinical findings and treatment options for acquired hepatocerebral degeneration.
Maffeo E, Montuschi A, Stura G, Giordana MT. Chronic acquired hepatocerebral degeneration, pallidal T1 MRI hyperintensity and manganese in a series of cirrhotic patients. Neurol Sci. 2014;35:523–30.
Miletić V, Ozretić D, Relja M. Parkinsonian syndrome and ataxia as a presenting finding of acquired hepatocerebral degeneration. Metab Brain Dis. 2014;29:207–9.
Criswell SR, Perlmutter JS, Crippin JS, Tom O, Racette BA. Reduced uptake of FDOPA PET in end-stage liver disease with elevated manganese levels. Arch Neurol. 2012;69:394–7.
Ishii K, Shioya A, Fukuda K, Mori K, Tamaoka A. Acquired hepatocerebral degeneration with middle cerebellar peduncles lesions: case report and review of the literature. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2012;114:1361–4.
Park HK, Kim SM, Choi CG, Lee MC, Chung SJ. Effect of trientine on manganese intoxication in a patient with acquired hepatocerebral degeneration. Mov Disord. 2008;23:768–70.
Ueki Y, Isozaki E, Miyazaki Y, Koide R, Shimizu T, et al. Clinical and neuroradiological improvement in chronic acquired hepatocerebral degeneration after branched-chain amino acid therapy. Acta Neurol Scand. 2002;106:113–6.
Lazeyras F, Spahr L, DuPasquier R, Delavelle J, Burkhard P, et al. Persistence of mild parkinsonism 4 months after liver transplantation in patients with preoperative minimal hepatic encephalopathy: a study on neuroradiological and blood manganese changes. Transpl Int. 2002;15:188–95.
Hess CW, Saunders-Pullman R. Movement disorders and alcohol misuse. Addict Biol. 2006;11(2):117–25.
Asconapé JJ. Use of antiepileptic drugs in hepatic and renal disease. Handb Clin Neurol. 2014;119:417–32. Review of pharmacokinetic aspects and safety issues for the use of antiepileptic drugs in patients with hepatic disease.
Adinolfi LE, Zampino R, Restivo L, Lonardo A, Guerrera B, et al. Chronic hepatitis C virus infection and atherosclerosis: clinical impact and mechanisms. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:3410–7.
Hsu C-S, Kao J-H, Chao Y-C, Lin HH, Fan Y-C, et al. Interferon-based therapy reduces risk of stroke in chronic hepatitis C patients: a population-based cohort study in Taiwan. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013;38:415–23.
Yan P, Zhu A, Liao F, Xiao Q, Kraft AW, et al. Minocycline reduces spontaneous hemorrhage in mouse models of cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Stroke. 2015;46:1633–40.
Mehndiratta M, Pandey S, Nayak R, Saran RK. Acute onset distal symmetrical vasculitic polyneuropathy associated with acute hepatitis B. J Clin Neurosci. 2013;20:331–2.
Monaco S, Ferrari S, Gajofatto A, Zanusso G, Mariotto S. HCV-related nervous system disorders. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012;2012:236148.
Cheung MCM, Maguire J, Carey I, Wendon J, Agarwal K. Review of the neurological manifestations of hepatitis E infection. Ann Hepatol. 2012;11:618–22.
El Moutawakil B, Bourezgui M, Rafai MA, Sibai M, Boulaajaj FZ, et al. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis associated with hepatitis A virus infection. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2008;164:852–4.
Sellner J, Steiner I. Neurologic complications of hepatic viruses. Handb Clin Neurol. 2014;123:647–61.
Mengel AM, Stenzel W, Meisel A, Büning C. Hepatitis E induced severe myositis. Muscle Nerve. Published Online First: 29 October 2015.
Perrin HB, Cintas P, Abravanel F, Gérolami R, d’Alteroche L, et al. Neurologic disorders in immunocompetent patients with autochthonous acute hepatitis E. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015;21(11):1928–34.
Bazerbachi F, Haffar S, Garg SK, Lake JR. Extra-hepatic manifestations associated with hepatitis E virus infection: a comprehensive review of the literature. 2015.
Yazaki Y, Sugawara K, Honda M, Ohnishi H, Nagashima S, et al. Characteristics of 20 patients with autochthonous acute hepatitis E in Hokkaido, Japan: first report of bilateral facial palsy following the infection with genotype 4 hepatitis E virus. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2015;236:263–71.
Deroux A, Brion JP, Hyerle L, Belbezier A, Vaillant M, et al. Association between hepatitis E and neurological disorders: two case studies and literature review. J Clin Virol. 2014;60:60–2.
Domingos JP, Garrido C, Moreira Silva H, Monteiro C, Silva ES, et al. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy associated with autoimmune hepatitis. Pediatr Neurol. 2014;51:e13–4.
Park KH, Sohn SY, Sung JJ, Lee KW, Hong YH. Subacute sensorimotor polyneuropathy associated with autoimmune hepatitis. J Clin Neurol. 2016;12(1):123–5.
Cacoub P, Comarmond C, Domont F, Savey L, Saadoun D. Cryoglobulinemia vasculitis. Am J Med. 2015;128:950–5.
Cacoub P, Terrier B, Saadoun D. Hepatitis C virus-induced vasculitis: therapeutic options. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73:24–30. Review of treatment options for hepatitis C virus-induced vasculitis.
Sneller MC, Hu Z, Langford CA. A randomized controlled trial of rituximab following failure of antiviral therapy for hepatitis C virus-associated cryoglobulinemic vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64:835–42.
De Vita S, Quartuccio L, Isola M, Mazzaro C, Scaini P, et al. A randomized controlled trial of rituximab for the treatment of severe cryoglobulinemic vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64:843–53.
Benstead TJ, Chalk CH, Parks NE. Treatment for cryoglobulinemic and non-cryoglobulinemic peripheral neuropathy associated with hepatitis C virus infection. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;12:CD010404.
Ahrens CL, Manno EM. Neurotoxicity of commonly used hepatic drugs. Handb Clin Neurol. 2014;120:675–82. Overview of neurologic complications related to commonly used hepatic drugs.
Kowdley KV, Gordon SC, Reddy KR, Rossaro L, Bernstein DE, et al. Ledipasvir and sofosbuvir for 8 or 12 weeks for chronic HCV without cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:1879–88.
Afdhal N, Reddy KR, Nelson DR, Lawitz E, Gordon SC, et al. Ledipasvir and sofosbuvir for previously treated HCV genotype 1 infection. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:1483–93.
Lawitz E, Mangia A, Wyles D, Rodriguez-Torres M, Hassanein T, et al. Sofosbuvir for previously untreated chronic hepatitis C infection. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:1878–87.
Zeuzem S, Dusheiko GM, Salupere R, Mangia A, Flisiak R, et al. Sofosbuvir and ribavirin in HCV genotypes 2 and 3. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:1993–2001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Pedro Viana and Patrícia Santos declare that they have no conflict of interest.
José M. Ferro has received personal fees from Boheringer Ingelheim and Daiichi Sankyo.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Neurologic Manifestations of Systemic Disease
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferro, J.M., Viana, P. & Santos, P. Management of Neurologic Manifestations in Patients with Liver Disease. Curr Treat Options Neurol 18, 37 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-016-0419-0
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-016-0419-0