Opinion statement
-
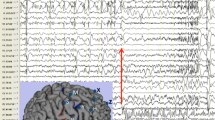
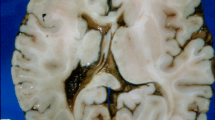
•Focal cortical dysplasias (FCD) and diffuse cortical dysplasias (DCD) are a heterogeneous group of disorders defined by abnormal cerebral cortical cytoarchitecture that are associated with epilepsy. Patients with either DCD or FCD may suffer from a variety of epilepsy subtypes and these are often refractory to most anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) despite polytherapy. The etiologies of cortical dysplasias (CD) are diverse, and include inherited genetic syndromes such as Miller-Dieker or X-linked lissencephaly, subcortical band heterotopia, and the tuberous sclerosis complex, as well as nongenetic exogenous insults such as hypoxic-ischemic injury, viral or other type of central nervous system infection, or traumatic injury. A large number of FCD cases are idiopathic and very small regions of FCD (microdysgenesis) are now being identified in resected epilepsy specimens. Recent data suggests that nearly 30% of epilepsy specimens evaluated histologically will contain regions of overt or microscopic CD.
-
•The mainstay of appropriate therapy for CD remains the standard AEDs or epilepsy surgery. In too few disorders, specific AEDs provide therapeutic advantage in the setting of individual forms of CD. The ketogenic diet may provide seizure control in a subpopulation of patients. In both DCD and FCD, surgical resection can be curative in the appropriately selected patients. Surgical approaches include focal neocortical resections, temporal lobectomy, or larger hemispheric resection procedures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crino PB, Eberwine JH: Molecular and cellular pathophysiology of cerebral dysgenesis. J Neurosci Res 1997, 50:907–916.
Rorke LB: A perspective: the role of disordered genetic control of neurogenesis in the pathogenesis migration disorders. J Neuropath Exp Neurol 1994, 53:105–117. Eexcellent review of the pathogenesis and developmental relevance of cortical dysplasias.
Palmini A, Andermann F, Olivier A, et al.: Focal neuronal migration disorders and intractable partial epilepsy: results of surgical treatment. Ann Neurol 1991, 30:750–757.
Kuzneicky R, Garcia JH, Faught E, Morawetz RB: Cortical dysplasia in temporal lobe epilepsy: magnetic resonance imaging correlations. Ann Neurol 1991, 29:293–298.
Whiting S, Duchowny M: Clinical spectrum of cortical dysplasia in childhood: diagnosis and treatment issues. J Child Neurol 1999, 14:759–771.
Aicardi J, Mumford JP, Dumas C, Wood S: Vigabatrin as initial therapy for infantile spasms: a European retrospective survey. Sabril IS Investigator and Peer Review Groups. Epilepsia 1996, 37:638–642.
Reiner O, Carrozzo R, Shen Y, et al.: Isolation of a Miller-Dieker lissencephaly gene containing G protein beta-subunit-like repeats. Nature 1993, 364(6439):717–721.
Dobyns WB, Andermann E, Andermann F, et al.: X-linked malformations of neuronal migration. Neurology 1996, 47:331–339.
Fox JW, Lamperti ED, Eksioglu YZ, et al.: Mutations in filamin 1 prevent migration of cerebral cortical neurons in human periventricular heterotopia. Neuron 1998, 21:1315–1325.
Gleeson JG, Luo RF, Grant PE, et al.: Genetic and neuroradiological heterogeneity of double cortex syndrome. Ann Neurol 2000, 47:265–269.
Arai Y, Edwards V, Becker LE: A comparison of cell phenotypes in hemimegalencephaly and tuberous sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 1999, 98:407–413.
Yasha TC, Santosh V, Das S, Shankar SK: Hemimegalencephaly: morphological and immunocytochemical study. Clin Neuropathol 1997, 16(1):17–22.
Packard AM, Miller VS, Delgado MR: Schizencephaly: correlations of clinical and radiologic features. Neurology 1997, 48(5):1427–1434.
Faiella A, Brunelli S, Granata T, et al.: A number of schizencephaly patients including 2 brothers heterozygous for germline mutations in the homeobox gene EMX2. Eur J Hum Genet 1997, 5(4):186–190.
Crino PB, Henske EP: New developments in the neurobiology of the tuberous sclerosis complex. Neurology 1999, 53:1384–1391. This review outlines the diagnostic criteria and molecular genetics of tuberous sclerosis complex as well as the neurobiology of the tuberous sclerosis complex genes.
Wolf H, Wiestler O: Surgical pathology of chronic epileptic seizure disorders. Brain Path 1993, 3:371–380.
Mischel PS, Nguyen LP, Vinters HV: Cerebral cortical dysplasia associated with pediatric epilepsy. Review of neuropathologic features and proposal for a grading system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 1995, 54:137–153.
Crino PB, Trojanowski J, Eberwine J: Internexin and nestin in focal cortical dysplasia and hemimegalencephaly as developmental markers. Acta Neuropathologica (Berl) 1997, 93:619–627.
Preul MC, Leblanc R, Cendes F, et al.: Function and organization in dysgenic cortex: case report. J Neurosurg 1991, 87:113–121.
Mattia D, Olivier A, Avoli M: Seizure-like discharges recorded in human dysplastic neocortex maintained in vitro. Neurology 1995, 45(7):1391–1395.
Palmini A, Gambardella A, Andermann F, et al.: Intrinsic epileptogenicity of human dysplastic cortex as suggested by corticography and surgical results. Ann Neurol 1995, 37(4):476–487.
Lequin MH, Barkovich AJ: Current concepts of cerebral malformation syndromes. Curr Opin Pediatr 1999, 11(6):492–496.
Barkovich AJ, Kuzniecky RI: Neuroimaging of focal malformations of cortical development. J Clin Neurophysiol 1996, 13(6):481–494.
Chugani DC, Chugani HT, Muzik O, et al.: Imaging epileptogenic tubers in children with tuberous sclerosis complex using alpha-[11C]methyl-Ltryptophan positron emission tomography. Ann Neurol 1998, 44(6):858–866.
Vigevano F, Bertini E, Boldrini R, et al.: Hemimegalencephaly and intractable epilepsy: benefits of hemispherectomy. Epilepsia 1989, 30:833–843.
Katyal NG, Koehler AN, McGhee B, et al.: The ketogenic diet in refractory epilepsy: the experience of Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh. Clin Pediatr 2000, 39(3):153–159.
Stafstrom CE, Spencer S: The ketogenic diet: a therapy in search of an explanation. Neurology 2000, 54(2):282–283.
Sirven J, Whedon B, Caplan D, et al.: The ketogenic diet for intractable epilepsy in adults: preliminary results. Epilepsia 1999, 40:1721–1726.
Zentner J, Hufnagel A, Ostertun B, et al.: Surgical treatment of extratemporal epilepsy: clinical, radiologic, and histopathologic findings in 60 patients. Epilepsia 1996, 37:1072–1080.
Hirabayashi S, Minnie CD, Janota I, Polkey CE: Surgical treatment of epilepsy due to cortical dysplasia: clinical and EEG findings. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1993, 56:765–770.
Sugimoto T, Otsubo H, Hwang PA, et al.: Outcome of epilepsy surgery in the first three years of life. Epilepsia 1999, 40:560–565.
Wyllie E, Comair YG, Kotagal P, et al.: Seizure outcome after epilepsy surgery in children and adolescents. Ann Neurol 1998, 44:740–748.
Engel JJ: Surgery for seizures. N Engl J Med 1996, 334:647–652. This is an excellent review of the indications for epilepsy surgery.
Cascino GD, Kelly PJ, Hirschorn KA, et al.: Stereotactic resection of intra-axial cerebral lesions in partial epilepsy. Mayo Clin Proc 1990, 65:1053–1060.
Kuzniecky R, Mountz JM, Wheatley G, Morawetz R: Ictal single-photon emission computed tomography demonstrates localized epileptogenesis in cortical dysplasia. Ann Neurol 1993, 34(4):627–631.
Hardiman O, Burke T, Phillips J: Mircrodysgenesis in resected temporal neocortex: incidence and significance in focal epilepsy. Neurology 1988, 38:1041–1047.
Ho SS, Kuzniecky RI, Gilliam F, et al.: Temporal lobe developmental malformations and epilepsy: dual pathology and bilateral hippocampal abnormalities. Neurology 1998, 50:748–754.
Wyllie E, Comair YG, Kotagal P, et al.: Epilepsy surgery in infants. Epilepsia 1996, 37:625–637.
Morrell F, Whisler WW, Bleck TP: Multiple subpial transection: a new approach to the surgical treatment of focal epilepsy. J Neurosurg 1989, 70:231–239.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crino, P.B., Chou, K. Epilepsy and cortical dysplasias. Curr Treat Options Neurol 2, 543–551 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-000-0032-z
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-000-0032-z