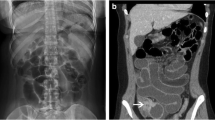
Opinion statement
The definition of chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction (CIIP) is somewhat vague because it was based on clinical observations that preceded modern advances in the measurement of gut motility and neuromuscular integrity. Appropriate management of patients with CIIP requires an initial consideration, supported by pertinent diagnostic tests, of the tissue affected (muscle, nerves, both), extent and magnitude of gut propulsive failure, and extraintestinal disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Dudley HAF, Sinclair ISR, McLaren IF, et al.: Intestinal pseudo-obstruction. J R Coll Surg Edinb 1958, 3:206–217.
Christensen J, Dent J, Malagelada JR, et al.: Pseudoobstruction. Gastroenterol Int 1990, 3:107–119.
Camilleri M, Brown ML, Malagelada JR: Impaired transit of chyme in chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction: correction with cisapride. Gastroenterology 1986, 91:619–626.
Murr MM, Sarr MG, Camilleri M: The surgeon’s role in the treatment of chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction. Am J Gastroenterol 1995, 90:2147–2151.
Mansell PI, Tattersall RB, Balsitis M: Megaduodenum due to hollow visceral myopathy successfully managed by duodenoplasty and feeding jejunostomy. Gut 1991, 32:334–337.
Stanghellini V, Camilleri M, Malagelada JR: Chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction: clinical and intestinal manometric findings. Gut 1987, 28:5–12.
Scolapio JS, Ukleja A, Bouras EP, Romano M: Nutritional management of chronic intestinal pseudoobstruction. J Clin Gastroenterol 1999, 28:306–312. A comprehensive review of nutritional manangement of pseudo-obstruction.
Vandenplas Y: Clinical use of cisapride and its risk-benefit in paediatric patients. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1998, 10:871–881. Good review of cisapride usage in children.
Verne GN, Eaker EY, Hardy E, Sninsky CA: Effect of octreotide and erythromycin on idiopathic and scleroderma-associated intestinal pseudo-obstruction. Dig Dis Sci 1995, 40:1892–1901.
Mann SD, Debinski HS, Kamm MA: Clinical characteristics of chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction in adults. Gut 1997, 41:75–81.
Noel RF Jr, Schuffler MD, Helton WS: Small bowel resection for relief of chronic intestinal pseudoobstruction. Am J Gastroenterol 1995, 90:1142–1145.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malagelada, J.R. Chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction. Curr Treat Options Gastro 3, 335–340 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11938-000-0047-2
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11938-000-0047-2