Opinion statement
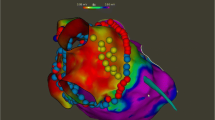
Special attention must be paid to detect, diagnose, and optimize management of reversible or treatable causes of long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation (LSPAF) such as obesity, obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), hypertension, hypo or hyperthyroidism, inflammatory and infectious diseases, and stress. Though, we strongly believe that the role of the pulmonary veins (PVs) is more pronounced in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) than in persistent AF, performing an adequate pulmonary vein isolation is still key in LSPAF. Patients with LSPAF will frequently require a more aggressive mapping and ablative approach. We do not encourage the use of empiric lines or complex fractionated atrial electrograms. Ablation of sites associated with non-PV triggers such as the entire posterior wall, the roof, the anterior part of the left atrium septum, left atrial appendage (LAA), the CS and SVC has been shown to improve the freedom from AF at follow-up when combined with PVs isolation. During the isoproterenol challenge, non-PV triggers are detected in most patients with AF. Mapping non-PV triggers is guided by multiple catheters positioned along both the right and left atriums: a 10-pole circular mapping catheter in the left superior PV recording the far-field LAA activity, the ablation catheter in the right superior PV that records the far-field interatrial septum and a 20-pole catheter with electrodes spanning from the SVC to the CS. With this simple catheter setup, when focal ectopic atrial activity is observed (a single ectopic beat is enough) their activation sequence is compared to that of sinus rhythm, allowing to quickly identify their area of origin. For significant non-PV triggers (repetitive isolated beats, focal atrial tachycardias or beats triggering AF/atrial flutter, a more detailed activation mapping is performed in the area of origin. They are subsequently targeted with focal ablation, exception being the triggers originating from the SVC, LAA or CS, in which cases complete isolation of these structures is the ablation strategy of choice. We truly believe the LAA deserves special consideration when managing patients with persistent AF and LSPAF.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AF:
-
Atrial fibrillation
- CA:
-
Catheter ablation
- CFAE:
-
Complex fractionated atrial electrograms
- CF:
-
Contact force
- CS:
-
Coronary sinus
- SVC:
-
Superior vena cava
- FIRM:
-
Focal impulse rotor modulation
- GP:
-
Ganglionated plexus
- LA:
-
Left atrium
- LAA:
-
Left atrial appendage
- OSA:
-
Obstructive sleep apnea
- PVI:
-
Pulmonary vein isolation
- RA:
-
Right atrium
References and Recommended Reading
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: •• Of major importance
Go AS, Hylek EM, Phillips KA, Chang Y, Henault LE, Selby JV, Singer DE. Prevalence of diagnosed atrial fibrillation in adults: national implications for rhythm management and stroke prevention: the AnTicoagulation and risk factors in atrial fibrillation (ATRIA) study. JAMA. 2001;285:2370–5.
Miyasaka Y, Barnes ME, Gersh BJ, Cha SS, Bailey KR, Abhayaratna WP, Seward JB, Tsang TS. Secular trends in incidence of atrial fibrillation in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1980 to 2000, and implications on the projections for future prevalence. Circulation. 2006;114:119–25.
Moe GK. Evidence for reentry as a mechanism of cardiac arrhythmias. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1975;72:55–81.
Lee S, Sahadevan J, Khrestian CM, Durand DM, Waldo AL. High density mapping of atrial fibrillation during vagal nerve stimulation in the canine heart: restudying the Moe hypothesis. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2013;24:328–35.
Allessie MA, de Groot NM, Houben RP, Schotten U, Boersma E, Smeets JL, Crijns HJ. Electropathological substrate of long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation in patients with structural heart disease: longitudinal dissociation. Circulation Arrhythmia and electrophysiology. 2010;3:606–15.
de Groot N, van der Does L, Yaksh A, Lanters E, Teuwen C, Knops P, van de Woestijne P, Bekkers J, Kik C, Bogers A and Allessie M. Direct proof of endo-epicardial asynchrony of the atrial wall during atrial fibrillation in humans. Circulation Arrhythmia and electrophysiology. 2016;9.
Mohanty S, Mohanty P, Di Biase L, Bai R, Trivedi C, Santangeli P, Santoro F, Hongo R, Hao S, Beheiry S, Burkhardt D, Gallinghouse JG, Horton R, Sanchez JE, Bailey S, Hranitzky PM, Zagrodzky J, Natale A. Long-term outcome of catheter ablation in atrial fibrillation patients with coexistent metabolic syndrome and obstructive sleep apnea: impact of repeat procedures versus lifestyle changes. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2014;25:930–8.
Haissaguerre M, Jais P, Shah DC, Takahashi A, Hocini M, Quiniou G, Garrigue S, Le Mouroux A, Le Metayer P, Clementy J. Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:659–66.
Santangeli P, Zado ES, Hutchinson MD, Riley MP, Lin D, Frankel DS, Supple GE, Garcia FC, Dixit S, Callans DJ, Marchlinski FE. Prevalence and distribution of focal triggers in persistent and long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation. Heart rhythm: the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society. 2016;13:374–82.
Ouyang F, Antz M, Ernst S, Hachiya H, Mavrakis H, Deger FT, Schaumann A, Chun J, Falk P, Hennig D, Liu X, Bansch D, Kuck KH. Recovered pulmonary vein conduction as a dominant factor for recurrent atrial tachyarrhythmias after complete circular isolation of the pulmonary veins: lessons from double lasso technique. Circulation. 2005;111:127–35.
Proietti R, Santangeli P, Di Biase L, Joza J, Bernier ML, Wang Y, Sagone A, Viecca M, Essebag V, Natale A. Comparative effectiveness of wide antral versus ostial pulmonary vein isolation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Circulation Arrhythmia and electrophysiology. 2014;7:39–45.
Natale A, Reddy VY, Monir G, Wilber DJ, Lindsay BD, McElderry HT, Kantipudi C, Mansour MC, Melby DP, Packer DL, Nakagawa H, Zhang B, Stagg RB, Boo LM, Marchlinski FE. Paroxysmal AF catheter ablation with a contact force sensing catheter: results of the prospective, multicenter SMART-AF trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64:647–56.
Nakagawa H, Kautzner J, Natale A, Peichl P, Cihak R, Wichterle D, Ikeda A, Santangeli P, Di Biase L, Jackman WM. Locations of high contact force during left atrial mapping in atrial fibrillation patients: electrogram amplitude and impedance are poor predictors of electrode-tissue contact force for ablation of atrial fibrillation. Circulation Arrhythmia and electrophysiology. 2013;6:746–53.
Perna F, Heist EK, Danik SB, Barrett CD, Ruskin JN, Mansour M. Assessment of catheter tip contact force resulting in cardiac perforation in swine atria using force sensing technology. Circulation Arrhythmia and electrophysiology. 2011;4:218–24.
Reddy VY, Dukkipati SR, Neuzil P, Natale A, Albenque JP, Kautzner J, Shah D, Michaud G, Wharton M, Harari D, Mahapatra S, Lambert H, Mansour M. Randomized, controlled trial of the safety and effectiveness of a contact force-sensing irrigated catheter for ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: results of the TactiCath contact force ablation catheter study for atrial fibrillation (TOCCASTAR) study. Circulation. 2015;132:907–15.
Steven D, Sultan A, Reddy V, Luker J, Altenburg M, Hoffmann B, Rostock T, Servatius H, Stevenson WG, Willems S, Michaud GF. Benefit of pulmonary vein isolation guided by loss of pace capture on the ablation line: results from a prospective 2-center randomized trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:44–50.
Kapa S, Desjardins B, Callans DJ, Marchlinski FE and Dixit S. Contact electroanatomic mapping derived voltage criteria for characterizing left atrial scar in patients undergoing ablation for atrial fibrillation. Journal of cardiovascular electrophysiology. 2014.
Reichlin T, Knecht S, Lane C, Kuhne M, Nof E, Chopra N, Tadros TM, Reddy VY, Schaer B, John RM, Osswald S, Stevenson WG, Sticherling C, Michaud GF. Initial impedance decrease as an indicator of good catheter contact: insights from radiofrequency ablation with force sensing catheters. Heart rhythm: the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society. 2014;11:194–201.
Reichlin T, Lane C, Nagashima K, Nof E, Chopra N, Ng J, Barbhaiya C, Tadros T, John RM, Stevenson WG, Michaud GF. Feasibility, efficacy, and safety of radiofrequency ablation of atrial fibrillation guided by monitoring of the initial impedance decrease as a surrogate of catheter contact. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2015;26:390–6.
Cheung JW, Ip JE, Chung JH, Markowitz SM, Liu CF, Thomas G, Lee JM, Lessner SJ, Lerman BB. Differential effects of adenosine on pulmonary vein ectopy after pulmonary vein isolation: implications for arrhythmogenesis. Circulation Arrhythmia and electrophysiology. 2012a;5:659–66.
Cheung JW, Chung JH, Ip JE, Markowitz SM, Liu CF, Thomas G, Lerman BB. Time course of adenosine-induced pulmonary vein reconnection after isolation: implications for mechanism of dormant conduction. Pacing and clinical electrophysiology: PACE. 2012b;35:556–63.
Macle L, Khairy P, Weerasooriya R, Novak P, Verma A, Willems S, Arentz T, Deisenhofer I, Veenhuyzen G, Scavee C, Jais P, Puererfellner H, Levesque S, Andrade JG, Rivard L, Guerra PG, Dubuc M, Thibault B, Talajic M, Roy D, Nattel S, investigators At. Adenosine-guided pulmonary vein isolation for the treatment of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: an international, multicentre, randomised superiority trial. Lancet. 2015;386:672–9.
Kobori A, Shizuta S, Inoue K, Kaitani K, Morimoto T, Nakazawa Y, Ozawa T, Kurotobi T, Morishima I, Miura F, Watanabe T, Masuda M, Naito M, Fujimoto H, Nishida T, Furukawa Y, Shirayama T, Tanaka M, Okajima K, Yao T, Egami Y, Satomi K, Noda T, Miyamoto K, Haruna T, Kawaji T, Yoshizawa T, Toyota T, Yahata M, Nakai K, Sugiyama H, Higashi Y, Ito M, Horie M, Kusano KF, Shimizu W, Kamakura S, Kimura T, Investigators U-AT. Adenosine triphosphate-guided pulmonary vein isolation for atrial fibrillation: the UNmasking dormant electrical Reconduction by adenosine TriPhosphate (UNDER-ATP) trial. Eur Heart J. 2015;36:3276–87.
Schmidt M, Nolker G, Marschang H, Gutleben KJ, Schibgilla V, Rittger H, Sinha AM, Ritscher G, Mayer D, Brachmann J, Marrouche NF. Incidence of oesophageal wall injury post-pulmonary vein antrum isolation for treatment of patients with atrial fibrillation. Europace: European pacing, arrhythmias, and cardiac electrophysiology: journal of the working groups on cardiac pacing, arrhythmias, and cardiac cellular electrophysiology of the European Society of Cardiology. 2008;10:205–9.
Di Biase L, Saenz LC, Burkhardt DJ, Vacca M, Elayi CS, Barrett CD, Horton R, Bai R, Siu A, Fahmy TS, Patel D, Armaganijan L, Wu CT, Kai S, Ching CK, Phillips K, Schweikert RA, Cummings JE, Arruda M, Saliba WI, Dodig M, Natale A. Esophageal capsule endoscopy after radiofrequency catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation: documented higher risk of luminal esophageal damage with general anesthesia as compared with conscious sedation. Circulation Arrhythmia and electrophysiology. 2009;2:108–12.
Pappone C, Oral H, Santinelli V, Vicedomini G, Lang CC, Manguso F, Torracca L, Benussi S, Alfieri O, Hong R, Lau W, Hirata K, Shikuma N, Hall B, Morady F. Atrio-esophageal fistula as a complication of percutaneous transcatheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2004;109:2724–6.
Zellerhoff S, Ullerich H, Lenze F, Meister T, Wasmer K, Monnig G, Kobe J, Milberg P, Bittner A, Domschke W, Breithardt G, Eckardt L. Damage to the esophagus after atrial fibrillation ablation: just the tip of the iceberg? High prevalence of mediastinal changes diagnosed by endosonography. Circulation Arrhythmia and electrophysiology. 2010;3:155–9.
Shah D, Dumonceau JM, Burri H, Sunthorn H, Schroft A, Gentil-Baron P, Yokoyama Y, Takahashi A. Acute pyloric spasm and gastric hypomotility: an extracardiac adverse effect of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;46:327–30.
Buch E, Vaseghi M, Cesario DA, Shivkumar K. A novel method for preventing phrenic nerve injury during catheter ablation. Heart rhythm: the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society. 2007;4:95–8.
Nakahara S, Ramirez RJ, Buch E, Michowitz Y, Vaseghi M, de Diego C, Boyle NG, Mahajan A, Shivkumar K. Intrapericardial balloon placement for prevention of collateral injury during catheter ablation of the left atrium in a porcine model. Heart rhythm: the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society. 2010;7:81–7.
Buch E, Nakahara S, Shivkumar K. Intra-pericardial balloon retraction of the left atrium: a novel method to prevent esophageal injury during catheter ablation. Heart rhythm: the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society. 2008;5:1473–5.
Cheema A, Dong J, Dalal D, Marine JE, Henrikson CA, Spragg D, Cheng A, Nazarian S, Bilchick KC, Almasry I, Sinha S, Scherr D, Halperin H, Berger R, Calkins H. Circumferential ablation with pulmonary vein isolation in permanent atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 2007;99:1425–8.
Burkhardt JD, Di Biase L, Natale A. Long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation: the metastatic cancer of electrophysiology. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60:1930–2.
Tilz RR, Rillig A, Thum AM, Arya A, Wohlmuth P, Metzner A, Mathew S, Yoshiga Y, Wissner E, Kuck KH, Ouyang F. Catheter ablation of long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation: 5-year outcomes of the Hamburg sequential ablation strategy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60:1921–9.
Seitz J, Horvilleur J, Curel L, Lacotte J, Maluski A, Ferracci A, Bremondy M, Rosier A, Monchi M, Penaranda G, Faure J, Beurtheret S, Pisapia A. Active or passive pulmonary vein in atrial fibrillation: is pulmonary vein isolation always essential? Heart rhythm: the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society. 2014;11:579–86.
Pascale P, Shah AJ, Roten L, Scherr D, Komatsu Y, Ramoul K, Daly M, Denis A, Derval N, Sacher F, Hocini M, Jais P, Haissaguerre M. Pulmonary veins to left atrium cycle length gradient predicts procedural and clinical outcomes of persistent atrial fibrillation ablation. Circulation Arrhythmia and electrophysiology. 2014;7:473–82.
O'Neill MD, Wright M, Knecht S, Jais P, Hocini M, Takahashi Y, Jonsson A, Sacher F, Matsuo S, Lim KT, Arantes L, Derval N, Lellouche N, Nault I, Bordachar P, Clementy J, Haissaguerre M. Long-term follow-up of persistent atrial fibrillation ablation using termination as a procedural endpoint. Eur Heart J. 2009;30:1105–12.
Elayi CS, Di Biase L, Barrett C, Ching CK, al Aly M, Lucciola M, Bai R, Horton R, Fahmy TS, Verma A, Khaykin Y, Shah J, Morales G, Hongo R, Hao S, Beheiry S, Arruda M, Schweikert RA, Cummings J, Burkhardt JD, Wang P, Al-Ahmad A, Cauchemez B, Gaita F, Natale A. Atrial fibrillation termination as a procedural endpoint during ablation in long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation. Heart rhythm: the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society. 2010;7:1216–23.
Brooks AG, Stiles MK, Laborderie J, Lau DH, Kuklik P, Shipp NJ, Hsu LF, Sanders P. Outcomes of long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation ablation: a systematic review. Heart rhythm: the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society. 2010;7:835–46.
Hocini M, Jais P, Sanders P, Takahashi Y, Rotter M, Rostock T, Hsu LF, Sacher F, Reuter S, Clementy J, Haissaguerre M. Techniques, evaluation, and consequences of linear block at the left atrial roof in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: a prospective randomized study. Circulation. 2005;112:3688–96.
Sanders P, Jais P, Hocini M, Hsu LF, Scavee C, Sacher F, Rotter M, Takahashi Y, Pasquie JL, Shah DC, Garrigue S, Clementy J, Haissaguerre M. Electrophysiologic and clinical consequences of linear catheter ablation to transect the anterior left atrium in patients with atrial fibrillation. Heart rhythm: the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society. 2004;1:176–84.
Jais P, Hocini M, Hsu LF, Sanders P, Scavee C, Weerasooriya R, Macle L, Raybaud F, Garrigue S, Shah DC, Le Metayer P, Clementy J, Haissaguerre M. Technique and results of linear ablation at the mitral isthmus. Circulation. 2004;110:2996–3002.
Jais P, Shah DC, Takahashi A, Hocini M, Haissaguerre M, Clementy J. Long-term follow-up after right atrial radiofrequency catheter treatment of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Pacing and clinical electrophysiology: PACE. 1998;21:2533–8.
Garg A, Finneran W, Mollerus M, Birgersdotter-Green U, Fujimura O, Tone L, Feld GK. Right atrial compartmentalization using radiofrequency catheter ablation for management of patients with refractory atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 1999;10:763–71.
Konings KT, Kirchhof CJ, Smeets JR, Wellens HJ, Penn OC, Allessie MA. High-density mapping of electrically induced atrial fibrillation in humans. Circulation. 1994;89:1665–80.
Konings KT, Smeets JL, Penn OC, Wellens HJ, Allessie MA. Configuration of unipolar atrial electrograms during electrically induced atrial fibrillation in humans. Circulation. 1997;95:1231–41.
Gerstenfeld EP, Sahakian AV, Swiryn S. Evidence for transient linking of atrial excitation during atrial fibrillation in humans. Circulation. 1992;86:375–82.
Nademanee K, McKenzie J, Kosar E, Schwab M, Sunsaneewitayakul B, Vasavakul T, Khunnawat C, Ngarmukos T. A new approach for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: mapping of the electrophysiologic substrate. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43:2044–53.
Nademanee K, Schwab MC, Kosar EM, Karwecki M, Moran MD, Visessook N, Michael AD, Ngarmukos T. Clinical outcomes of catheter substrate ablation for high-risk patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;51:843–9.
Oral H, Chugh A, Good E, Crawford T, Sarrazin JF, Kuhne M, Chalfoun N, Wells D, Boonyapisit W, Gadeela N, Sankaran S, Kfahagi A, Jongnarangsin K, Pelosi Jr F, Bogun F, Morady F. Randomized evaluation of right atrial ablation after left atrial ablation of complex fractionated atrial electrograms for long-lasting persistent atrial fibrillation. Circulation Arrhythmia and electrophysiology. 2008;1:6–13.
Elayi CS, Verma A, Di Biase L, Ching CK, Patel D, Barrett C, Martin D, Rong B, Fahmy TS, Khaykin Y, Hongo R, Hao S, Pelargonio G, Dello Russo A, Casella M, Santarelli P, Potenza D, Fanelli R, Massaro R, Arruda M, Schweikert RA, Natale A. Ablation for longstanding permanent atrial fibrillation: results from a randomized study comparing three different strategies. Heart rhythm: the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society. 2008;5:1658–64.
Oral H, Chugh A, Yoshida K, Sarrazin JF, Kuhne M, Crawford T, Chalfoun N, Wells D, Boonyapisit W, Veerareddy S, Billakanty S, Wong WS, Good E, Jongnarangsin K, Pelosi Jr F, Bogun F, Morady F. A randomized assessment of the incremental role of ablation of complex fractionated atrial electrograms after antral pulmonary vein isolation for long-lasting persistent atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53:782–9.
Hayward RM, Upadhyay GA, Mela T, Ellinor PT, Barrett CD, Heist EK, Verma A, Choudhry NK, Singh JP. Pulmonary vein isolation with complex fractionated atrial electrogram ablation for paroxysmal and nonparoxysmal atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis. Heart rhythm: the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society. 2011;8:994–1000.
Kong MH, Piccini JP, Bahnson TD. Efficacy of adjunctive ablation of complex fractionated atrial electrograms and pulmonary vein isolation for the treatment of atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Europace: European pacing, arrhythmias, and cardiac electrophysiology: journal of the working groups on cardiac pacing, arrhythmias, and cardiac cellular electrophysiology of the European Society of Cardiology. 2011;13:193–204.
Verma A, Mantovan R, Macle L, De Martino G, Chen J, Morillo CA, Novak P, Calzolari V, Guerra PG, Nair G, Torrecilla EG, Khaykin Y. Substrate and trigger ablation for reduction of atrial fibrillation (STAR AF): a randomized, multicentre, international trial. Eur Heart J. 2010;31:1344–56.
Verma A, Jiang CY, Betts TR, Chen J, Deisenhofer I, Mantovan R, Macle L, Morillo CA, Haverkamp W, Weerasooriya R, Albenque JP, Nardi S, Menardi E, Novak P, Sanders P, Investigators SAI. Approaches to catheter ablation for persistent atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:1812–22.
Jadidi AS, Cochet H, Shah AJ, Kim SJ, Duncan E, Miyazaki S, Sermesant M, Lehrmann H, Lederlin M, Linton N, Forclaz A, Nault I, Rivard L, Wright M, Liu X, Scherr D, Wilton SB, Roten L, Pascale P, Derval N, Sacher F, Knecht S, Keyl C, Hocini M, Montaudon M, Laurent F, Haissaguerre M, Jais P. Inverse relationship between fractionated electrograms and atrial fibrosis in persistent atrial fibrillation: combined magnetic resonance imaging and high-density mapping. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:802–12.
•• Di Biase L, Mohanty P, Mohanty S, Santangeli P, Trivedi C, Lakkireddy D, Reddy M, Jais P, Themistoclakis S, Dello Russo A, Casella M, Pelargonio G, Narducci ML, Schweikert R, Neuzil P, Sanchez J, Horton R, Beheiry S, Hongo R, Hao S, Rossillo A, Forleo G, Tondo C, Burkhardt JD, Haissaguerre M, Natale A. Ablation versus amiodarone for treatment of persistent atrial fibrillation in patients with congestive heart failure and an implanted device: results from the AATAC multicenter randomized trial. Circulation. 2016a;133:1637–44. Multicenter randomized trial which proved that patients with persistent AF and left ventricular ejection fraction <40% had a better prognosis if treated with catheter ablation when compared with amiodarone. More importantly, higher success was reported in patients undergoing PVI and posterior wall isolation in comparison with PVI alone. There was no significant difference between PVI alone and amiodarone.
Di Biase L, Santangeli P, Natale A. How to ablate long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation? Curr Opin Cardiol. 2013;28:26–35.
Gerstenfeld EP, Callans DJ, Dixit S, Zado E, Marchlinski FE. Incidence and location of focal atrial fibrillation triggers in patients undergoing repeat pulmonary vein isolation: implications for ablation strategies. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2003;14:685–90.
Calkins H, Kuck KH, Cappato R, Brugada J, Camm AJ, Chen SA, Crijns HJ, Damiano Jr RJ, Davies DW, DiMarco J, Edgerton J, Ellenbogen K, Ezekowitz MD, Haines DE, Haissaguerre M, Hindricks G, Iesaka Y, Jackman W, Jalife J, Jais P, Kalman J, Keane D, Kim YH, Kirchhof P, Klein G, Kottkamp H, Kumagai K, Lindsay BD, Mansour M, Marchlinski FE, McCarthy PM, Mont JL, Morady F, Nademanee K, Nakagawa H, Natale A, Nattel S, Packer DL, Pappone C, Prystowsky E, Raviele A, Reddy V, Ruskin JN, Shemin RJ, Tsao HM, Wilber D. Heart Rhythm Society task force on C and surgical ablation of atrial F. 2012 HRS/EHRA/ECAS expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation: recommendations for patient selection, procedural techniques, patient management and follow-up, definitions, endpoints, and research trial design: a report of the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) task force on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. Developed in partnership with the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA), a registered branch of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Cardiac Arrhythmia Society (ECAS); and in collaboration with the American College of Cardiology (ACC), American Heart Association (AHA), the Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS), and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS). Endorsed by the governing bodies of the American College of Cardiology Foundation, the American Heart Association, the European Cardiac Arrhythmia Society, the European Heart Rhythm Association, the Society of Thoracic Surgeons, the Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society, and the Heart Rhythm Society. Heart rhythm: the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society. 2012;9:632–96. e21
Raviele A, Natale A, Calkins H, Camm JA, Cappato R, Ann Chen S, Connolly SJ, Damiano Jr R, DEP R, Edgerton JR, Haissaguerre M, Hindricks G, Ho SY, Jalife J, Kirchhof P, Kottkamp H, Kuck KH, Marchlinski FE, Packer DL, Pappone C, Prystowsky E, Reddy VK, Themistoclakis S, Verma A, Wilber DJ, Willems S, Venice C. Venice chart international consensus document on atrial fibrillation ablation: 2011 update. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2012;23:890–923.
Lin WS, Tai CT, Hsieh MH, Tsai CF, Lin YK, Tsao HM, Huang JL, Yu WC, Yang SP, Ding YA, Chang MS, Chen SA. Catheter ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation initiated by non-pulmonary vein ectopy. Circulation. 2003;107:3176–83.
Goya M, Ouyang F, Ernst S, Volkmer M, Antz M, Kuck KH. Electroanatomic mapping and catheter ablation of breakthroughs from the right atrium to the SVC in patients with atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2002;106:1317–20.
Tsai CF, Tai CT, Hsieh MH, Lin WS, Yu WC, Ueng KC, Ding YA, Chang MS, Chen SA. Initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating from the SVC: electrophysiological characteristics and results of radiofrequency ablation. Circulation. 2000;102:67–74.
Arruda M, Mlcochova H, Prasad SK, Kilicaslan F, Saliba W, Patel D, Fahmy T, Morales LS, Schweikert R, Martin D, Burkhardt D, Cummings J, Bhargava M, Dresing T, Wazni O, Kanj M, Natale A. Electrical isolation of the SVC: an adjunctive strategy to pulmonary vein antrum isolation improving the outcome of AF ablation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2007;18:1261–6.
Oral H, Ozaydin M, Chugh A, Scharf C, Tada H, Hall B, Cheung P, Pelosi F, Knight BP, Morady F. Role of the CS in maintenance of atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2003;14:1329–36.
Kim DT, Lai AC, Hwang C, Fan LT, Karagueuzian HS, Chen PS, Fishbein MC. The ligament of Marshall: a structural analysis in human hearts with implications for atrial arrhythmias. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;36:1324–7.
Veinot JP, Harrity PJ, Gentile F, Khandheria BK, Bailey KR, Eickholt JT, Seward JB, Tajik AJ, Edwards WD. Anatomy of the normal left atrial appendage: a quantitative study of age-related changes in 500 autopsy hearts: implications for echocardiographic examination. Circulation. 1997;96:3112–5.
Horak D, Svec F, Kalal J, Adamyan A, Titova M, Trostenyuk N, Skuba N, Dan V, Voronkova O, Gumargalieva K. Biologically active thrombin-containing hydrogels based on poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) for endovascular occlusion. Polim Med. 1991;21:31–41.
Di Biase L, Burkhardt JD, Mohanty P, Sanchez J, Mohanty S, Horton R, Gallinghouse GJ, Bailey SM, Zagrodzky JD, Santangeli P, Hao S, Hongo R, Beheiry S, Themistoclakis S, Bonso A, Rossillo A, Corrado A, Raviele A, Al-Ahmad A, Wang P, Cummings JE, Schweikert RA, Pelargonio G, Dello Russo A, Casella M, Santarelli P, Lewis WR, Natale A. Left atrial appendage: an underrecognized trigger site of atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2010;122:109–18.
Starck CT, Steffel J, Emmert MY, Plass A, Mahapatra S, Falk V, Salzberg SP. Epicardial left atrial appendage clip occlusion also provides the electrical isolation of the left atrial appendage. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2012;15:416–8.
Han FT, Bartus K, Lakkireddy D, Rojas F, Bednarek J, Kapelak B, Bartus M, Sadowski J, Badhwar N, Earnest M, Valderrabano M, Lee RJ. The effects of LAA ligation on LAA electrical activity. Heart rhythm: the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society. 2014;11:864–70.
Dhanunjaya R, Lakkireddy MR, Sridhar ARM, Pillarisetti J, Maybrook R, Kanmanthareddy A, Matthew Earnest VS, Atkins D, Bommana S, Nath J, Ferrell R, Dawn B. Left atrial appendage ligation and ablation for persistent atrial fibrillation (LAALA-AF registry). JACC. 2014;63:A390.
Panikker S, Jarman JW, Virmani R, Kutys R, Haldar S, Lim E, Butcher C, Khan H, Mantziari L, Nicol E, Foran JP, Markides V and Wong T. Left atrial appendage electrical isolation and concomitant device occlusion to treat persistent atrial fibrillation: a first-in-human safety, feasibility, and efficacy study. Circulation Arrhythmia and electrophysiology. 2016;9.
•• Di Biase L, David Burkhardt J, Mohanty P, Mohanty S, Sanchez JE, Trivedi C, Günes M, Glan YG, Gianni C, Horton RP, Themistoclakis S, Joseph Gallinghouse G, Bailey S, Zagrodzky JD, Hongo RH, Beheiry S, Santangeli P, Casella M, Dello Russo A, Al-Ahmad A, Hranitzky P, Lakkireddy D, Tondo C, Natale A. Left atrial appendage isolation in patients with longstanding persistent AF undergoing catheter ablation. BELIEF trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016b;68:1929–40. This randomized clinical trial demonstrated the benefit of empirical LAA isolation in patients with LSPAF.
Pandit SV, Jalife J. Rotors and the dynamics of cardiac fibrillation. Circ Res. 2013;112:849–62.
Narayan SM, Krummen DE, Rappel WJ. Clinical mapping approach to diagnose electrical rotors and focal impulse sources for human atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2012a;23:447–54.
Narayan SM, Krummen DE, Shivkumar K, Clopton P, Rappel WJ, Miller JM. Treatment of atrial fibrillation by the ablation of localized sources: CONFIRM (conventional ablation for atrial fibrillation with or without focal impulse and rotor modulation) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012b;60:628–36.
Shivkumar K, Ellenbogen KA, Hummel JD, Miller JM, Steinberg JS. Acute termination of human atrial fibrillation by identification and catheter ablation of localized rotors and sources: first multicenter experience of focal impulse and rotor modulation (FIRM) ablation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2012;23:1277–85.
Narayan SM, Krummen DE, Clopton P, Shivkumar K, Miller JM. Direct or coincidental elimination of stable rotors or focal sources may explain successful atrial fibrillation ablation: on-treatment analysis of the CONFIRM trial (conventional ablation for AF with or without focal impulse and rotor modulation). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:138–47.
Narayan SM, Baykaner T, Clopton P, Schricker A, Lalani GG, Krummen DE, Shivkumar K, Miller JM. Ablation of rotor and focal sources reduces late recurrence of atrial fibrillation compared with trigger ablation alone: extended follow-up of the CONFIRM trial (conventional ablation for atrial fibrillation with or without focal impulse and rotor modulation). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63:1761–8.
Chou CC, Chang PC, Wen MS, Lee HL, Chen TC, Yeh SJ, Wu D. Epicardial ablation of rotors suppresses inducibility of acetylcholine-induced atrial fibrillation in left pulmonary vein-left atrium preparations in a beagle heart failure model. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58:158–66.
Miller JM, Kowal RC, Swarup V, Daubert JP, Daoud EG, Day JD, Ellenbogen KA, Hummel JD, Baykaner T, Krummen DE, Narayan SM, Reddy VY, Shivkumar K, Steinberg JS, Wheelan KR. Initial independent outcomes from focal impulse and rotor modulation ablation for atrial fibrillation: multicenter FIRM registry. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2014;25:921–9.
Benharash P, Buch E, Frank P, Share M, Tung R, Shivkumar K, Mandapati R. Quantitative analysis of localized sources identified by focal impulse and rotor modulation mapping in atrial fibrillation. Circulation Arrhythmia and electrophysiology. 2015;8:554–61.
Buch E, Share M, Tung R, Benharash P, Sharma P, Koneru J, Mandapati R, Ellenbogen KA, Shivkumar K. Long-term clinical outcomes of focal impulse and rotor modulation for treatment of atrial fibrillation: a multicenter experience. Heart rhythm: the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society. 2016;13:636–41.
Lemery R, Birnie D, Tang AS, Green M, Gollob M. Feasibility study of endocardial mapping of ganglionated plexuses during catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart rhythm: the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society. 2006;3:387–96.
Mikhaylov E, Kanidieva A, Sviridova N, Abramov M, Gureev S, Szili-Torok T, Lebedev D. Outcome of anatomic ganglionated plexi ablation to treat paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: a 3-year follow-up study. Europace: European pacing, arrhythmias, and cardiac electrophysiology: journal of the working groups on cardiac pacing, arrhythmias, and cardiac cellular electrophysiology of the European Society of Cardiology. 2011;13:362–70.
Verma A, Saliba WI, Lakkireddy D, Burkhardt JD, Cummings JE, Wazni OM, Belden WA, Thal S, Schweikert RA, Martin DO, Tchou PJ, Natale A. Vagal responses induced by endocardial left atrial autonomic ganglion stimulation before and after pulmonary vein antrum isolation for atrial fibrillation. Heart rhythm: the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society. 2007;4:1177–82.
Malcolme-Lawes LC, Lim PB, Wright I, Kojodjojo P, Koa-Wing M, Jamil-Copley S, Dehbi HM, Francis DP, Davies DW, Peters NS, Kanagaratnam P. Characterization of the left atrial neural network and its impact on autonomic modification procedures. Circulation Arrhythmia and electrophysiology. 2013;6:632–40.
Katritsis DG, Pokushalov E, Romanov A, Giazitzoglou E, Siontis GC, Po SS, Camm AJ, Ioannidis JP. Autonomic denervation added to pulmonary vein isolation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: a randomized clinical trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:2318–25.
Lo LW, Scherlag BJ, Chang HY, Lin YJ, Chen SA, Po SS. Paradoxical long-term proarrhythmic effects after ablating the "head station" ganglionated plexi of the vagal innervation to the heart. Heart rhythm: the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society. 2013;10:751–7.
Mao J, Yin X, Zhang Y, Yan Q, Dong J, Ma C, Liu X. Ablation of epicardial ganglionated plexi increases atrial vulnerability to arrhythmias in dogs. Circulation Arrhythmia and electrophysiology. 2014;7:711–7.
Verheule S, Eckstein J, Linz D, Maesen B, Bidar E, Gharaviri A and Schotten U. Role of endo-epicardial dissociation of electrical activity and transmural conduction in the development of persistent atrial fibrillation. Progress in biophysics and molecular biology. 2014.
Michowitz Y, Nakahara S, Bourke T, Buch E, Vaseghi M, De Diego C, Wiener I, Mahajan A, Shivkumar K. Electrophysiological differences between the epicardium and the endocardium of the left atrium. Pacing and clinical electrophysiology: PACE. 2011;34:37–46.
Lee G, Kumar S, Teh A, Madry A, Spence S, Larobina M, Goldblatt J, Brown R, Atkinson V, Moten S, Morton JB, Sanders P, Kistler PM, Kalman JM. Epicardial wave mapping in human long-lasting persistent atrial fibrillation: transient rotational circuits, complex wavefronts, and disorganized activity. Eur Heart J. 2014;35:86–97.
Edgerton Z, Perini AP, Horton R, Trivedi C, Santangeli P, Bai R, Gianni C, Mohanty S, Burkhardt JD, Gallinghouse GJ, Sanchez JE, Bailey S, Lane M, DIB L, Santoro F, Price J, Natale A. Hybrid procedure (endo/epicardial) versus standard manual ablation in patients undergoing ablation of longstanding persistent atrial fibrillation: results from a single center. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2016;27:524–30.
Boersma LV, Castella M, van Boven W, Berruezo A, Yilmaz A, Nadal M, Sandoval E, Calvo N, Brugada J, Kelder J, Wijffels M, Mont L. Atrial fibrillation catheter ablation versus surgical ablation treatment (FAST): a 2-center randomized clinical trial. Circulation. 2012;125:23–30.
Takahashi Y, O'Neill MD, Hocini M, Dubois R, Matsuo S, Knecht S, Mahapatra S, Lim KT, Jais P, Jonsson A, Sacher F, Sanders P, Rostock T, Bordachar P, Clementy J, Klein GJ, Haissaguerre M. Characterization of electrograms associated with termination of chronic atrial fibrillation by catheter ablation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;51:1003–10.
Rostock T, Steven D, Hoffmann B, Servatius H, Drewitz I, Sydow K, Mullerleile K, Ventura R, Wegscheider K, Meinertz T, Willems S. Chronic atrial fibrillation is a biatrial arrhythmia: data from catheter ablation of chronic atrial fibrillation aiming arrhythmia termination using a sequential ablation approach. Circulation Arrhythmia and electrophysiology. 2008;1:344–53.
Sacher F, Corcuff JB, Schraub P, Le Bouffos V, Georges A, Jones SO, Lafitte S, Bordachar P, Hocini M, Clementy J, Haissaguerre M, Bordenave L, Roudaut R, Jais P. Chronic atrial fibrillation ablation impact on endocrine and mechanical cardiac functions. Eur Heart J. 2008;29:1290–5.
Haissaguerre M, Hocini M, Sanders P, Sacher F, Rotter M, Takahashi Y, Rostock T, Hsu LF, Bordachar P, Reuter S, Roudaut R, Clementy J, Jais P. Catheter ablation of long-lasting persistent atrial fibrillation: clinical outcome and mechanisms of subsequent arrhythmias. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2005;16:1138–47.
Kanj M, Wazni O, Natale A. Pulmonary vein antrum isolation. Heart rhythm: the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society. 2007;4:S73–9.
He X, Zhou Y, Chen Y, Wu L, Huang Y, He J. Left atrial posterior wall isolation reduces the recurrence of atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2016;46:267–74.
Mohanty S, Di Biase L, Mohanty P, Trivedi C, Santangeli P, Bai R, Burkhardt JD, Gallinghouse JG, Horton R, Sanchez JE, Hranitzky PM, Zagrodzky J, Al-Ahmad A, Pelargonio G, Lakkireddy D, Reddy M, Forleo G, Rossillo A, Themistoclakis S, Hongo R, Beheiry S, Casella M, Dello Russo A, Tondo C, Natale A. Effect of periprocedural amiodarone on procedure outcome in patients with longstanding persistent atrial fibrillation undergoing extended pulmonary vein antrum isolation: results from a randomized study (SPECULATE). Heart rhythm: the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society. 2015;12:477–83.
Elayi CS, Di Biase L, Bai R, Burkhardt JD, Mohanty P, Santangeli P, Sanchez J, Hongo R, Gallinghouse GJ, Horton R, Bailey S, Beheiry S, Natale A. Administration of isoproterenol and adenosine to guide supplemental ablation after pulmonary vein antrum isolation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2013;24:1199–206.
Gladstone DJ, Spring M, Dorian P, Panzov V, Thorpe KE, Hall J, Vaid H, O' Donnell M, Laupacis A, Cote R, Sharma M, Blakely JA, Shuaib A, Hachinski V, Coutts SB, Sahlas DJ, Teal P, Yip S, Spence JD, Buck B, Verreault S, Casaubon LK, Penn A, Selchen D, Jin A, Howse D, Mehdiratta M, Boyle K, Aviv R, Kapral MK, Mamdani M, Investigators E and Coordinators. Atrial fibrillation in patients with cryptogenic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2467–77.
Sanna T, Diener HC, Passman RS, Di Lazzaro V, Bernstein RA, Morillo CA, Rymer MM, Thijs V, Rogers T, Beckers F, Lindborg K, Brachmann J, Investigators CA. Cryptogenic stroke and underlying atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2478–86.
Marrouche NF, Wilber D, Hindricks G, Jais P, Akoum N, Marchlinski F, Kholmovski E, Burgon N, Hu N, Mont L, Deneke T, Duytschaever M, Neumann T, Mansour M, Mahnkopf C, Herweg B, Daoud E, Wissner E, Bansmann P, Brachmann J. Association of atrial tissue fibrosis identified by delayed enhancement MRI and atrial fibrillation catheter ablation: the DECAAF study. JAMA. 2014;311:498–506.
Anselmino M, Matta M, D'Ascenzo F, Bunch TJ, Schilling RJ, Hunter RJ, Pappone C, Neumann T, Noelker G, Fiala M, Bertaglia E, Frontera A, Duncan E, Nalliah C, Jais P, Weerasooriya R, Kalman JM and Gaita F. Catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation in patients with left ventricular systolic dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Circulation Arrhythmia and electrophysiology. 2014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Jorge Romero and Carola Gianni each declare no potential conflicts of interest. Andrea Natale received speaker honorariums from Boston Scientific, Biosense Webster, Medtronic, and St. Jude. Luigi Di Biase is a consultant for Biosense Webster, Boston Scientific, and St Jude Medical. Dr. Di Biase has received speaker honoraria/travel from Medtronic, Atricure, EPiEP, and Biotronik.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Arrhythmia
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Romero, J., Gianni, C., Natale, A. et al. What Is the Appropriate Lesion Set for Ablation in Patients with Persistent Atrial Fibrillation?. Curr Treat Options Cardio Med 19, 35 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11936-017-0534-6
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11936-017-0534-6