Abstract
Introduction
Around 10 % of renal cell carcinomas (RCC) are cystic, while some benign cysts have complex appearance in conventional diagnostic tests such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). These renal complex cystic masses (RCCMs) are a challenging entity in urological practice and sometimes have a difficult management, requiring surgical removal. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) is a very sensitive test detecting microvascularization in real time, and it has been used in the diagnostic workup of these kinds of lesions. The aim of our study was to assess the diagnostic power of CEUS in the evaluation of RCCM.
Material and Methods
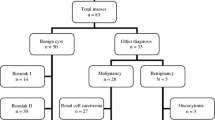
This is a prospective observational study between April 2011 and July 2014. A total of 66 patients with 67 RCCMs were enrolled (Bosniak 2–4). Twenty-four patients underwent surgical removal of the RCCM. All participants underwent CEUS (experimental) and CT (control). All CEUS procedures were performed by a single high-experienced observer (urologist). Benign lesions were defined as those Bosniak 2–2F, and malignant were Bosniak 3–4. Statistical analysis was made measuring consistency (kappa index and Landis-Koch scale) and validity (sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values) of the study.
Results
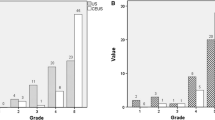
Median size of RCCM measured by CEUS and CT was 3.8 cm (interquartile range (AIQ) 3.2–4.6) and 3.9 cm (AIQ 3.2–4.5), respectively. Kappa index shows good agreement between both tests (0.71; 95 % CI 0.57–0.85), both overall and stratified by categories according to Bosniak classification. CEUS has a sensitivity 100 %, specificity 81.4 %, positive predictive value 70.4 %, and negative predictive value 100 %. A total of eight RCCMs were discordant, and seven of eight classified as malignant by CEUS and not by CT. Of those seven lesions classified as malignant by CEUS, six (six of seven, 85.7 %) were malignant in the pathological exam.
Conclusions
CEUS is a very useful tool for assessing RCCM, with good results in terms of consistency and validity. It has a good diagnostic power, with a sensitivity of 100 % and a negative predictive value of 100 %. Its main limitations are the experience required, a special software, and being observer-dependent.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Mitterberger M, Pelzer A, Colleselli D, Bartsch G, Strasser H, Pallwein L, et al. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound for diagnosis of prostate cancer and kidney lesions. Eur J Radiol. 2007;64:231–8.
Nilsson A. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound of the kidneys. Eur Radiol. 2004;148:104–9.
• Siracusano S, Quaia E, Bertolotto M, Ciciliato S, Tiberio A, Belgrano E. The application of ultrasound contrast agents in the characterization of renal tumors. World J Urol. 2004;22:316–22. Description about ultrasound contrast agents for the assessment of renal tumors.
Ophir J, Parker KJ. Contrast agents in diagnostic ultrasound. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1989;15:319–33.
Kalantarinia K, Okusa MD. Ultrasound contrast agents in the study of kidney function in health and disease. Drug Discov Today Dis Mech. 2007;4:153–8.
Filippone A, Muzi M, Basilico R, Di GV, Trapani AR, Bonomo L. Color doppler flow imaging of renal disease. Value of a new intravenous contrast agent: SH U 508 A (Levovist). Radiol Med. 1994;87:50.
Bosniak MA. The current radiological approach to renal cysts. Radiology. 1986;158:1–10.
Israel GM, Hindman N, Bosniak MA. Evaluation of cystic renal masses: comparison of CT and MRI by using the Bosniak classification system. Radiology. 2004;231:365–71.
• Park BK, Kim B, Kim SH, Ko K, Lee HM, Choi HY. Assessment of cystic renal masses based on Bosniak classification: comparison of CT and contrast-enhanced US. Eur J Radiol. 2007;61:310–4. Comparison between CT and CEUS and analyzing histology results.
• Ascenti G, Mazziotti S, Zimbaro G, Settineri N, Magno C, Melloni D, et al. Complex cystic renal masses: characterization with contrast-enhanced. Radiology. 2007;243:158–65. One of the first reports comparing CEUS and CT in the assessment of complex cystic renal masses.
Ko K, Kim B, Park B. The use of contrast enhanced ultrasonography in the evaluation of cystic renal masses: comparison with CT. In: Radiological Society of North America Scientific Assembly and Annual Meeting Program Oak Brook, III: Radiological Society of North America, 2004; 152.
Quaia E, Bertolotto M, Cioffi V, Rossi A, Baratella E, Pizzolato R, et al. Comparison of contrast-enhanced sonography with unenhanced sonography and contrast-enhanced CT in the diagnosis of malignancy in complex cystic renal masses. Am J Roentgenol. 2008;191:1239–49.
•• Xue LY, Lu Q, Huang BJ, Ma JJ, Yan LX, Wen JX, et al. Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for evaluation of cystic renal mass: in comparison to contrast-enhanced CT and conventional ultrasound. Abdom Imaging. 2014;39(6):1274–83. Largest study with 103 patients comparing CEUS and CT in the assessment of renal complex cystic masses.
•• Chen Y, Wu N, Xue T, Hao Y, Dai J. Comparison of contrast-enhanced sonography with MRI in the diagnosis of complex cystic renal masses. J Clin Ultrasound. 2014. doi:10.1002/jcu.22232. Study comparing CEUS and MRI, and correlating results with histology.
• Sanz Mayayo E, Hevia Palacios V, Arias Fúnez F, Alvarez Rodríguez S, Rodríguez-Patrón Rodríguez R, Mayayo Dehesa T, et al. Bibliographic review about the usefulness of ultrasound contrast media in the study of renal masses. Arch Esp Urol. 2012;65(5):556–66. Review about the usefulness of CEUS in the assessment of renal masses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Enrique Sanz, Vital Hevia, Victoria Gómez, Sara Álvarez, Jose-Javier Fabuel, Laura Martínez, Rafael Rodriguez-Patrón, Cristina González-Gordaliza, and Francisco-Javier Burgos each declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Kidney Diseases
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Contrast enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) in a Renal complex cystic mass Bosniak 4 located in lower pole of the left kidney. Left: contrast mode. Right: conventional ultrasound mode. After intravenous contrast administration, enhancement in solid components of the renal mass (circle) is observed in real-time (MP4 49391 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanz, E., Hevia, V., Gómez, V. et al. Renal Complex Cystic Masses: Usefulness of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS) in Their Assessment and Its Agreement with Computed Tomography. Curr Urol Rep 17, 89 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11934-016-0646-7
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11934-016-0646-7