Abstract
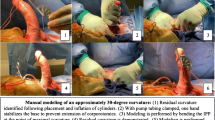
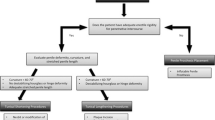
Peyronie’s disease (PD) is a wound healing disorder of the tunica albuginea of the penis. PD is generally categorized into two phases: the early acute inflammatory and late chronic fibrotic. Surgical reconstruction is only recommended during the latter established phase. There are a variety of options when erections are functional. However, when erectile dysfunction is present, the gold standard treatment is the placement of an inflatable penile prosthesis with or without additional straightening procedures. General recommendations include that after implanting and inflating the cylinders, if a clinically significant curvature is present, manual modeling is performed. If a residual curve >30° remains after modeling, then various techniques, including plaque releasing incision, is the next step. Grafting can be considered if tunical defects are >2.0 cm. Causes of corporal fibrosis include complications from an infected implant such as explantation, priapism, penile trauma, and prolonged use of an intracavernosal injection agent. Implant placement in the setting of corporal fibrosis can be technically challenging. Available strategies include incision or excision of the scar, corporotomies with or without grafting, the use of cavernotomes, or other specialized dilators, implant downsizing, and transcorporeal resection.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance
Ralph D, Gonzalez-Cadavid N, Mirone V, et al. The management of Peyronie’s disease: evidence-based 2010 guidelines. J Sex Med. 2010;7(7):2359–74.
Mulhall JP, Schiff J, Guhring P. An analysis of the natural history of Peyronie’s disease. J Urol. 2006;175:2115–8.
Nelson CJ, Mulhall JP. Psychological impact of Peyronie’s disease: a review. J Sex Med. 2013;10:653–60.
Hatzimouratidis K, Eardley I, Giuliano F, et al. EAU guidelines on penile curvature. Eur Urol. 2012;62(3):543–52.
Levine LA, Dimitrou RJ. A surgical algorithm for penile prosthesis placement in men with erectile failure and Peyronie’s disease. Int J Impot Res. 2000;12(3):147–51.
Taylor FL, Abern MR, Levine LA. Predicting erectile dysfunction following surgical correction of Peyronie’s disease without inflatable penile prosthesis placement: vascular assessment and preoperative risk factors. J Sex Med. 2012;9(1):296–301.
Levine LA, Lenting E. A surgical algorithm for the treatment of Peyronie’s disease. J Urol. 1997;158:2149–52.
Mulhall JP, Anderson M, Parker M. A surgical algorithm for men with combined Peyronie’s disease and erectile dysfunction: functional and satisfaction outcomes. J Sex Med. 2005;2:132–8.
Levine LA, Benson J, Hoover C. Inflatable penile prosthesis placement in men with Peyronie’s disease and drug-resistant erectile dysfunction: a single-center study. J Sex Med. 2010;7:3775–83.
Levine LA, Burnett AL. Standard operating procedures for Peyronie’s disease. J Sex Med. 2013;10(1):230–44. Excellent review of the current literature on the surgical options for Peyronie’s disease.
Mulhall J, Ahmed A, Anderson M. Penile prosthetic surgery for Peyronie’s disease: defining the need for intraoperative adjuvant maneuvers. J Sex Med. 2004;1:318–21.
Zaid UB, Alwaal A, Zhang X, Lue TF. Surgical management of Peyronie’s disease. Curr Urol Rep. 2014;15(10):446. Thorough review of the current literature on the surgical options for Peyronie’s disease.
Montorsi F, Guazzoni G, Bergamaschi F, Rigatti P. Patient-partner satisfaction with semirigid penile prostheses for Peyronie’s disease: a 5-year follow-up study. J Urol. 1993;150(6):1819–21.
Ghanem HM, Fahmy I, el-Meliegy A. Malleable penile implants without plaque surgery in the treatment of Peyronie’s disease. Int J Impot Res. 1998;10:171–3.
Wilson SK, Delk 2nd JR. A new treatment for Peyronie’s disease: modeling the penis over an inflatable penile prosthesis. J Urol. 1994;152:1121–3.
Chung E, Solomon M, Deyoung L, Brock GB. Comparison between AMS 700TM CX and ColoplastTM Titan inflatable penile prosthesis for Peyronie’s disease treatment and remodeling: clinical outcomes and patient satisfaction. J Sex Med. 2012;10(11):2855–60. Head-to-head study showing similar positive outcomes with two different inflatable penile prostheses.
Levine LA, Larsen SM. Surgery for Peyronie’s disease. Asian J Androl. 2013;15(1):27–34. Comprehensive review of the surgical literature for Peyronie’s disease.
Montague DK, Angermeier KW, Lakin MM, Ingleright BJ. AMS 3-piece inflatable penile prosthesis implantation in men with Peyronie’s disease: comparison of CX and Ultrex cylinders. J Urol. 1996;156:1633–5.
Wilson SK, Cleves MA, Delk JR. Long-term follow-up of treatment for Peyronie’s disease: modeling the penis over an inflatable penile prosthesis. J Urol. 2001;165(3):825–9.
Chung PH, Scott JF, Morey AF. High patient satisfaction of inflatable penile prosthesis insertion with synchronous penile plication for erectile dysfunction and Peyronie’s disease. J Sex Med. 2014;11:1593–8.
DiBlasio CJ, Kurta JM, Botta S, et al. Peyronie’s disease compromises the durability and component-malfunction rates in patients implanted with an inflatable penile prosthesis. BJU Int. 2010;106(5):691–4.
Carson CC, Levine LA. Outcomes of surgical treatment of Peyronie’s disease. BJU Int. 2014;113(5):704–13. State-of-the-art review of the surgical options for Peyronie’s disease.
Wang R, Howard GE, Hoang A, Yuan JH, Lin HC, Dai YT. Prospective and long-term evaluation of erect penile length obtained with inflatable penile prosthesis to that induced by intracavernosal injection. Asian J Androl. 2009;11(4):411–5.
Egydio PH, Sansalone S. Peyronie’s reconstruction for maximum length and girth gain: geometrical principles. Adv Urol. 2008;205739.
Egydio PH, Kuehhas FE, Sansalone S. Penile length and girth restoration in severe Peyronie’s disease using circular and longitudinal grafting. BJU Int. 2013;111:E213–9. New interesting technique to preserve penile length and girth using geometrical principles.
Rolle L, Ceruti C, Timpano M, et al. A new, innovative lengthening surgical procedure for Peyronie’s disease by penile prosthesis implantation with double dorsal-ventral patch graft: the ”sliding technique”. J Sex Med. 2012;9(9):2389–95.
Sansalone S, Garaffa G, Djinovic R, et al. Simultaneous penile lengthening and penile prosthesis implantation in patients with Peyronie’s disease, refractory erectile dysfunction, and severe penile shortening. J Sex Med. 2012;9:316–21.
Shaeer O. Supersizing the penis following penile prosthesis implantation. J Sex Med. 2010;7(7):2608–16.
Shaeer O. Trans-corporal incision of Peyronie’s plaques. J Sex Med. 2011;8(2):589–93. Innovative technique to incise a Peyronie’s plaque using endoscopic equipment.
Silvani M, Pecoraro S, Zucchi A. Corporoplasty for induratio penis plastica with soft axial tutors, single relaxing albugineal incision and safenous grafting. A 3-year follow up. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2012;84(2):84–8.
Austoni E, Colombo F, Romano AL, et al. Soft prosthesis implant and relaxing albugineal incision with saphenous grafting for surgical therapy of Peyronie’s disease: a 5-year experience and long-term follow-up on 145 operated patients. Eur Urol. 2005;47(2):223–9.
Grasso M, Lania C, Fortuna F, Blanco S, Piacentini I. Preservation of cavernosal erectile function after soft penile prosthesis implant in Peyronie’s disease: long-term follow-up. Adv Urol. 2008;646052.
Zucchi A, Silvani M, Pecoraro S. Corporoplasty with small soft axial prostheses (VIRILIS I®) and bovine pericardial graft (HYDRIX®) in Peyronie’s disease. Asian J Androl. 2013;15(2):275–9.
Levine LA, Greenfield JM, Estrada CR. Erectile dysfunction following surgical correction of Peyronie’s disease and a pilot study of the use of sildenafil citrate rehabilitation for postoperative erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med. 2005;2(2):241–7.
Segal RL, Burnett AL. Surgical management for Peyronie’s disease. World J Mens Health. 2013;31(1):1–11. Good review of the surgical knowledge on Peyronie’s disease.
Levine LA, Rybak J. Traction therapy for men with shortened penis prior to penile prosthesis implantation: a pilot study. J Sex Med. 2011;8(7):2112–7.
Martínez-Salamanca JI, Mueller A, Moncada I, Carballido J, Mulhall JP. Penile prosthesis surgery in patients with corporal fibrosis: a state of the art review. J Sex Med. 2011;8(7):1880–9. Best available review on the different techniques used for penile prosthesis surgery with corporal fibrosis.
Jordan GH, Angermeier KW. Preoperative evaluation of erectile function with dynamic infusion cavernosometry/cavernosography in patients undergoing surgery for Peyronie’s disease: correlation with postoperative results. J Urol. 1993;150(4):1138–42.
Rajpurkar AA, Li HH, Dhabuwala CCB. Penile implant success in patients with corporal fibrosis using multiple incisions and minimal scar tissue excision. Urology. 1999;54:145–7.
Montague DK, Angermeier KW. Corporeal excavation: new technique for penile prosthesis implantation in men with severe corporeal fibrosis. Urology. 2006;67:1072–5.
Shaeer OO, Shaeer AA. Corporoscopic excavation of the fibrosed corpora cavernosal for penile prosthesis implantation: optical corporotomy and trans-corporeal resection, Shaeer’s technique. J Sex Med. 2007;4:218–25.
Shaeer O. Penile prosthesis implantation in cases of fibrosis: ultrasound-guided cavernotomy and sheathed trochar excavation. J Sex Med. 2007;4:809–14.
Sansalone S et al. Simultaneous total corporal reconstruction and implantation of a penile prosthesis in patients with erectile dysfunction and severe fibrosis of the corpora cavernosa. J Sex Med. 2012;9(7):1937–44.
Summerton DJ, Terry TR, Delk JR, Wilson SK. Reimplantation of inflatable penile prostheses (IPP) into scarred corporeal bodies facilitated by the new AMS 700 CXR cylinders. BJU Int. 2005;95:102.
Knoll LD, Furlow WL, Benson Jr RC, Bilhartz DL. Management of nondilatable cavernous fibrosis with the use of a downsized inflatable penile prosthesis. J Urol. 1995;153(2):366–7.
Egydio PH, Kuehhas FE. Distal penile shaft reconstruction and reinforcement: the “double-windsocks” technique. J Sex Med. 2013;10(10):2571–8. Innovative technique using grafts to create neocorpora.
Szostak MJ, DelPizzo JJ, Sklar GN. The plug and patch: a new technique for repair of corporal perforation during placement of penile prostheses. J Urol. 2000;163(4):1203–5.
Mulcahy JJ. Crural perforation during penile prosthetic surgery. J Sex Med. 2006;3(1):177–80.
Kohler TS, Modder JK, Dupree JM, Bush NC, McVary KT. Malleable implant substitution for the management of penile prosthesis pump erosion: a pilot study. J Sex Med. 2009;6:1474–8.
Knoll LD, Fisher J, Benson Jr RC, Bilhartz DL, Minich PJ, Furlow WL. Treatment of penile fibrosis with prosthetic implantation and flap advancement with tissue debulking. J Urol. 1996;156:394–7.
Borges F, Hakim L, Kline C. Surgical technique to maintain penile length after insertion of an inflatable penile prosthesis via infrapubic approach. J Sex Med. 2006;3:550–3.
Wilson SK, Delk JR, Mulcahy JJ, Cleves M, Salem EA. Upsizing of inflatable penile implant cylinders in patients with corporal fibrosis. J Sex Med. 2006;3:736–42.
Swords K, Martinez DR, Lockhart JL, Carrion R. A preliminary report on the usage of an intracorporal antibiotic cast with synthetic high purity CaSO4 for the treatment of infected penile implant. J Sex Med. 2013;10:1162–9.
Trost LW, Baum N, Hellstrom WJ. Managing the difficult penile prosthesis patient. J Sex Med. 2013;10(4):893–906. Excellent review of factors that cause patient satisfaction or dissatisfaction following penile prosthesis placement.
Eid JF, Wilson SK, Cleves M, Salem EA. Coated implants and "no touch" surgical technique decreases risk of infection in inflatable penile prosthesis implantation to 0.46%. Urology. 2012;79(6):1310–5.
Lynch MJ, Scott GM, Inglis JA, Pryor JP. Reducing the loss of implants following penile prosthetic surgery. Br J Urol. 1994;73:423–7.
Mulcahy JJ, Carson 3rd CC. Long-term infection rates in diabetic patients implanted with antibiotic-impregnated versus nonimpregnated inflatable penile prostheses: 7-year outcomes. Eur Urol. 2011;60:167–72.
Radomski SB, Herschorn S. Risk factors associated with penile prosthesis infection. J Urol. 1992;147:383–5.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
Conflict of Interest
Dr. Faysal A Yafi, Dr. Premsant Sangkum, and Dr. Ian Ross McCaslin each declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Dr. Wayne J. G. Hellstrom reports personal fees from Coloplast; personal fees from American Medical Systems; personal fees from Antares; grants from Auxilium; personal fees from Endo; personal fees from Lilly, USA; personal fees from New England Research Institutes, Inc; personal fees from Promescent, other from NIH, and other from Theralogix.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Men’s Health
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yafi, F.A., Sangkum, P., McCaslin, I.R. et al. Strategies for Penile Prosthesis Placement in Peyronie’s Disease and Corporal Fibrosis. Curr Urol Rep 16, 21 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11934-015-0491-0
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11934-015-0491-0