Abstract
To provide a critical contemporary review of daily PDE5-inhibitor (PDE5-I) use in urological and nonurological conditions. PDE5-Is can be taken up to once a day. However, at present only tadalafil is approved for use in both erectile dysfunction (ED) and benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH) with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS). Evolving research in penile rehabilitation, Peyronie’s disease, male infertility, pulmonary arterial hypertension, muscular dystrophy and Raynaud’s phenomenon shows these therapeutic areas may also benefit from PDE5i therapy. This review examines the role of chronic PDE5 inhibition in ED, BPH-LUTS and other therapeutic targets which may shape our clinical practice in the years to come.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: •• Of major importance
FDA approves oral therapy for erectile dysfunction. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 1998;55(10):981–4.
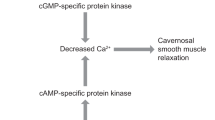
Corbin JD, Francis SH, Webb DJ. Phosphodiesterase type 5 as a pharmacologic target in erectile dysfunction. Urology. 2002;60(2 Suppl 2):4–11.
Corona G, Mondaini N, Ungar A, et al. Phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors in erectile dysfunction: the proper drug for the proper patient. J Sex Med. 2011;8(12):3418–32.
Christ GJ, Lue T. Physiology and biochemistry of erections. Endocrine. 2004;23(2-3):93–100.
Porst H, Hell-Momeni K, Buttner H. Chronic PDE-5 inhibition in patients with erectile dysfunction – a treatment approach using tadalafil once-daily. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2012;13(10):1481–94.
Wrishko R, Sorsaburu S, Wong D, et al. Safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetic overview of low-dose daily administration of tadalafil. J Sex Med. 2009;6(7):2039–48.
McMahon CN, Smith CJ, Shabsigh R. Treating erectile dysfunction when PDE5 inhibitors fail. BMJ. 2006;332:589–92.
Son H, Park K, Kim SW, et al. Reasons for discontinuation of sildenafil citrate after successful restoration of erectile function. Asian J Androl. 2004;6:117–20.
Martin-Morales A, Haro JM, Beardsworth A, et al. Therapeutic effectiveness and patient satisfaction after 6 months of treatment with tadalafil, sildenafil, and vardenafil: results from the erectile dysfunction observational study (EDOS). Eur Urol. 2007;51:541–50.
McMahon CG. Comparison, efficacy, and tolerability of on-demand tadalafil and daily dosed tadalafil for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med. 2005;2(3):415–25.
Paduch DA, Bolyakov A, Polzer PK, Watts SD. Effects of 12 weeks of tadalafil treatment on ejaculatory and orgasmic dysfunction and sexual satisfaction in patients with mild to severe erectile dysfunction: integrated analysis of 17 placebo-controlled studies. BJU Int. 2013;111(2):334–43.
McMahon CG. Efficacy and safety of daily tadalafil in men with erectile dysfunction previously unresponsive to on-demand tadalafil. J Sex Med. 2004;1(3):292–300.
Vernet D, Magee T, Qian A, Nolazco G, et al. Phosphodiesterase type 5 is not upregulated by tadalafil in cultures of human penile cells. J Sex Med. 2006;3(1):84–94. discussion 94–5.
Aversa A, Vitale C, Volterrani M, et al. Chronic administration of Sildenafil improves markers of endothelial function in men with Type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2008;25:37–44.
De Young LX, Domes T, Lim K, et al. Endothelial rehabilitation: the impact of chronic PDE5 inhibitors on erectile function and protein alterations in cavernous tissue of diabetic rats. Eur Urol. 2008;54(1):213–20.
Porst H, Glina S, Ralph D, et al. Durability of response following cessation of tadalafil taken once daily as treatment for erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med. 2010;7:3487–94.
Kim JW, Oh MM, Park MG, et al. Combination therapy of testosterone enanthate and tadalafil on PDE5 inhibitor non-reponders with severe and intermediate testosterone deficiency. Int J Impot Res. 2013;25(1):29–33.
Broderick GA, Brock GB, Roehrborn CG, et al. Effects of Tadalafil on Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Secondary to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Men With or Without Erectile Dysfunction. Urology. 2010;75:1452–9.
Roehrborn CG, Kaminetsky JC, Auerbach SM, et al. Changes in peak urinary flow and voiding efficiency in men with signs and symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia during once daily tadalafil treatment. BJU Int. 2009;105:502–7.
Oelke M, Giuliano F, Mirone V, et al. Monotherapy with tadalafil or tamsulosin similarly improved lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia in an international, randomised, parallel, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Eur Urol. 2012;61(5):917–25.
Donatucci CF, Brock GB, Goldfischer ER, et al. Tadalafil administered once daily for lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia: a 1-year, open-label extension study. BJU Int. 2011;107:1110–6.
Egerdie RB, Auerbach S, Roehrborn CG, et al. Tadalafil 2.5 or 5 mg administered once daily for 12 weeks in men with both erectile dysfunction and signs and symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia: results of a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. J Sex Med. 2012;9(1):271–81.
Giuliano F, Oelke M, Jungwirth A, et al. Tadalafil once daily improves ejaculatory function, erectile function, and sexual satisfaction in men with lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia and erectile dysfunction: results from a randomized, placebo- and tamsulosin-controlled, 12-week double-blind study. J Sex Med. 2013;10(3):857–65.
•• Porst H, Kim ED, Casabé AR, et al. Efficacy and safety of tadalafil once daily in the treatment of men with lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia: results of an international randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eur Urol. 2011;60(5):1105–13. This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial was well-conducted and showed convincing evidence that daily tadalafil can provide clinically significant relief of bothersome LUTS.
Heidenreich A, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, et al. EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Part 1: Screening, diagnosis, and treatment of clinically localised disease. Eur Urol. 2011;59:61–71.
Chung E, Brock G. Sexual rehabilitation and cancer survivorship: A state of art review of current literature and management strategies in male sexual dysfunction among prostate cancer survivors. J Sex Med. 2013;10 suppl 1:102–11.
Tal R, Alphs HH, Krebs P, et al. Erectile function recovery rate after radical prostatectomy: A metaanalysis. J Sex Med. 2009;6:2538–46.
Montorsi F, Guazzoni G, Strambi LF, et al. Recovery of spontaneous erectile function after nerve-sparing radical retropubic prostatectomy with and without early intracavernous injections of alprostadil: Results of a prospective, randomised trial. J Urol. 1997;158:1408–10.
Raina R, Agarwal A, Ausmundson S, et al. Early use of vacuum constriction device following radical prostatectomy facilitates early sexual activity and potentially earlier return of erectile function. Int J Impot Res. 2006;18:77–81.
Montorsi F, Brock G, Lee J, et al. Effect of nightly versus on-demand vardenafil on recovery of erectile function in men following bilateral nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2008;54:924–31.
Padma-Nathan H, McCullough AR, Levine LA, et al. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of postoperative nightly sildenafil citrate for the prevention of erectile dysfunction after bilateral nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy. Int J Impot Res. 2008;20:479–86.
Bannowsky A, Schulze H, van der Horst C, et al. Recovery of erectile function after nerve sparing radical prostatectomy: Improvement with nightly low dose sildenafil. BJU Int. 2008;101:1279–83.
•• Briganti A, Di Trapani E, Abdollah F, et al. Choosing the best candidates for penile rehabilitation after bilateral nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy. J Sex Med. 2012;9:608–17. Although retrospective in nature, this study provided us with a clearer role of daily PDE5-Is in the penile rehabilitation of men with intermediate risk of developing ED after a bilateral nerve-sparing prostatectomy.
Bannowsky A, van Ahlen H, Loch T. Increasing the dose of vardenafil on a daily basis does not improve erectile function after unilateral nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy. J Sex Med. 2012;9(5):1448–53.
Vasconcelos JS, Figueiredo RT, Nascimento FL, et al. The natural history of penile length after radical prostatectomy: a long-term prospective study. Urology. 2012;80(6):1293–6.
Ferrini MG, Davila HH, Kovanecz I, et al. Vardenafil prevents fibrosis and loss of corporal smooth muscle that occurs after bilateral cavernosal nerve resection in the rat. Urology. 2006;68(2):429–35.
Kovanecz I, Rambhatla A, Ferrini MG, et al. Chronic daily tadalafil prevents the corporal fibrosis and veno-occlusive dysfunction that occurs after cavernosal nerve resection. BJU Int. 2008;101(2):203–10.
Sirad F, Hlaing S, Kovanecz I, et al. Sildenafil promotes smooth muscle preservation and ameliorates fibrosis through modulation of extracellular matrix and tissue growth factor gene expression after bilateral cavernosal nerve resection in the rat. J Sex Med. 2011;8(4):1048–60.
Hatzimouratidis K, Eardley I, Giuliano F, et al. EAU guidelines on penile curvature. Eur Urol. 2012;62(3):543–52.
Levine LA, Latchamsetty KC. Treatment of erectile dysfunction in patients with Peyronie's disease using sildenafil citrate. Int J Impot Res. 2002;14(6):478–82.
Al-Shaiji TF, Brock GB. Peyronie's disease: evolving surgical management and the role of phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors. Sci World J. 2009;9:822–45.
Gonzalez-Cadavid NF, Rajfer J. Treatment of Peyronie's disease with PDE5 inhibitors: an antifibrotic strategy. Nat Rev Urol. 2010;7(4):215–21.
Ferrini MG, Kovanecz I, Nolazco G, et al. Effects of long-term vardenafil treatment on the development of fibrotic plaques in a rat model of Peyronie’s disease. BJU. 2006;97:625–33.
•• Chung E, Deyoung L, Brock GB. The role of PDE5 inhibitors in penile septal scar remodeling: assessment of clinical and radiological outcomes. J Sex Med. 2011;8(5):1472–7. This study showed the penile scar modelling effect of daily tadalafil, which has not been demonstrated in human subjects before.
Dimitriadis F, Giannakis D, Pardalidis N, et al. Effects of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors on sperm parameters and fertilizing capacity. Asian J Androl. 2008;10(1):115–33.
Rago R, Salacone P, Caponecchia L, et al. Effect of vardenafil on semen parameters in infertile men: a pilot study evaluating short-term treatment. J Endocrinol Invest. 2012;35(10):897–900.
Hellstrom WJ, Overstreet JW, Yu A, et al. Tadalafil has no effect on spermatogenesis or reproductive hormones. J Urol. 2003;170(3):887–91.
•• Dimitriadis F, Tsambalas S, Tsounapi P, et al. Effects of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors on Leydig cell secretory function in oligoasthenospermic infertile men: a randomized trial. BJU Int. 2010;106(8):1181–5. Although PDE-Is have been shown to improve sperm parameters in certain subpopulations of infertile men, the mechanism is not well understood. The findings of this study showed that Leydig cell secretory function could be the link where future research can be directed.
Galiè N, Brundage BH, Ghofrani HA, et al. Tadalafil therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation. 2009;119(22):2894–903.
Oudiz RJ, Brundage BH, Galiè N, et al. Tadalafil for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension: a double-blind 52-week uncontrolled extension study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60(8):768–74.
Shlobin OA, Brown AW, Weir N, et al. Transition of PH patients from sildenafil to tadalafil: feasibility and practical considerations. Lung. 2012;190(5):573–8.
Bowling JC, Dowd PM. Raynaud’s disease. Lancet. 2003;361:2078–80.
Herrick A. Diagnosis and management of scleroderma peripheral vascular disease. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2008;34:89–114.
Schiopu E, Hsu VM, Impens AJ, et al. Randomized placebo-controlled crossover trial of tadalafil in Raynaud's phenomenon secondary to systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol. 2009;36(10):2264–8.
Shenoy PD, Kumar S, Jha LK, et al. Efficacy of tadalafil in secondary Raynaud's phenomenon resistant to vasodilator therapy: a double-blind randomized cross-over trial. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010;49(12):2420–8.
Asai A, Sahani N, Kaneki M, et al. Primary role of functional ischemia, quantitative evidence for the two-hit mechanism, and phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor therapy in mouse muscular dystrophy. PLoS One. 2007;2(8):e806.
Adamo CM, Dai DF, Percival JM, et al. Sildenafil reverses cardiac dysfunction in the mdx mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107(44):19079–83.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
Conflict of Interest
Dr. King Chien Joe Lee reported no potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
Dr. Gerald Brock reported board membership, receiving consultancies, receiving honoraria, receiving payment for the development of educational presentations including service on speakers’ bureaus, and travel/accommodations expenses covered or reimbursed from Pfizer, Lilly, J&J, Astellas, GSK, Abbott, and Bayer. Dr. Brock reported holding stock/stock options in Pfizer, Lilly, J&J, GSK, and Abbott. Dr. Brock reported receiving payment for expert testimony from Pfizer and J&J.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, K.C.J., Brock, G.B. Daily Dosing of PDE5 Inhibitors: Where Does it Fit in?. Curr Urol Rep 14, 269–278 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11934-013-0342-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11934-013-0342-9