Abstract
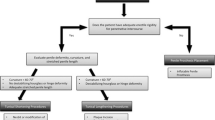
Surgical treatment options for Peyronie’s disease include tunica shortening (Nesbit and plication) and grafting procedures. Tunica shortening procedures are associated with penile shortening. However, the amount of penile shortening is rarely significant for the patient. Although grafting procedures aim to prevent penile shortening, this may still be an issue due to the pathologic extent of Peyronie’s disease. Long-term postoperative erectile dysfunction is the major drawback. Many types of grafting material have been used, but only saphenous vein has gained certain acceptance. Grafting procedures must be restricted to patients with normal preoperative erectile status and excessive curvature. Nesbit or plication procedures may be associated with significant penile shortening. Grafting procedures are also indicated in cases of hourglass deformities, because they cannot be corrected by the Nesbit procedure. Nesbit wedge resection is still the gold standard for treating Peyronie’s disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Gelbard MK, Dorey F, James K: The natural history of Peyronie’s disease. J Urol 1990, 144:1376–1379.
Devine CJ, Jr., Somers KD, Jordan SG, et al.: Proposal: trauma as the cause of the Peyronie’s lesion. J Urol 1997, 157:285–290.
El-Sakka AI, Hassoba HM, Pillarisetty RJ, et al.: Peyronie’s disease is associated with an increase in transforming growth factor-beta protein expression. J Urol 1997, 158:1391–1394.
Pryor J, Akkus E, Alter G, et al.: Peyronie’s Disease. J Sex Med 2004, 1:110–115.
Rehman J, Benet A, Minsky LS, et al.: Results of surgical treatment for abnormal penile curvature: Peyronie’s disease and congenital deviation by Modified Nesbit plication (tunical shaving and plication). J Urol 1997, 157:1288–1291.
Bailey MJ, Yande S, Walmsley B, et al.: Surgery for Peyronie’s disease. A review of 200 patients. Br J Urol 1985, 57:746–749.
Metz P, Ebbehoj J, Uhrenholdt A, et al.: Peyronie’s disease and erectile failure. J Urol 1983, 130:1103–1104.
Poulsen J, Kirkeby HJ: Treatment of penile curvature: a retrospective study of 175 patients operated with plication of the tunica albuginea or with the Nesbit procedure. Br J Urol 1995, 75:370–374.
Pryor JP, Fitzpatrick JM: A new approach to the correction of the penile deformity in Peyronie’s disease. J Urol 1979, 122:622–623.
Ralph DJ, al-Akraa M, Pryor JP: The Nesbit operation for Peyronie’s disease: 16-year experience. J Urol 1995, 154:1362–1363.
Ebbehoj J, Metz P: Congenital penile angulation. Br J Urol 1987, 60:264–266.
Savoca G, Trombetta C, Ciampalini S, et al.: Long-term results with Nesbit’s procedure as treatment of Peyronie’s disease. Int J Impot Res 2000, 12:289–293.
Yachia D: Modified corporoplasty for the treatment of penile curvature. J Urol 1990, 143:80–82.
Donatucci CF, Lue TF: Correction of penile deformity assisted by intracavernous injection of papaverine. J Urol 1992, 147:1108–1110.
Sulaiman MN, Gingell JC: Nesbit’s procedure for penile curvature. J Androl 1994, 15(Suppl):S54-S56.
Syed AH, Abbasi Z, Hargreave TB: Nesbit procedure for disabling Peyronie’s curvature: a median follow-up of 84 months. Urology 2003, 61:999–1003.
Savoca G, Scieri F, Pietropaolo F, et al.: Straightening corporoplasty for Peyronie’s disease: a review of 218 patients with median follow-up of 89 months. Eur Urol 2004, 46:610–614.
Nooter RI, Bosch JL, Schroder FH: Peyronie’s disease and congenital penile curvature: long-term results of operative treatment with the plication procedure. Br J Urol 1994, 74:497–500.
Klevmark B, Andersen M, Schultz A, et al.: Congenital and acquired curvature of the penis treated surgically by plication of the tunica albuginea. Br J Urol 1994, 74:501–506.
Kummerling S, Schubert J: Peyronie’s disease. Investigation of staging, erectile failure and operative management. Int Urol Nephrol 1995, 27:629–637.
Thiounn N, Missirliu A, Zerbib M, et al.: Corporeal plication for surgical correction of penile curvature. Experience with 60 patients. Eur Urol 1998, 33:401–404.
Schultheiss D, Meschi MR, Hagemann J, et al.: Congenital and acquired penile deviation treated with the essed plication method. Eur Urol 2000, 38:167–171.
Chahal R, Gogoi NK, Sundaram SK, et al.: Corporal plication for penile curvature caused by Peyronie’s disease: the patients’ perspective. BJU Int 2001, 87:352–356.
Cormio L, Zizzi V, Bettocchi C, et al.: Tunica albuginea plication for the correction of penile curvature. Scand J Urol Nephrol 2002, 36:307–310.
van der Drift DG, Vroege JA, Groenendijk PM, et al.: The plication procedure for penile curvature: surgical outcome and postoperative sexual functioning. Urol Int 2002, 69:120–124.
Gholami SS, Lue TF: Correction of penile curvature using the 16-dot plication technique: a review of 132 patients. J Urol 2002, 167:2066–2069.
Van Der Horst C, Martinez Portillo FJ, Seif C, et al.: Treatment of penile curvature with Essed-Schroder tunical plication: aspects of quality of life from the patients’ perspective. BJU Int 2004, 93:105–108.
Gholami SS, Lue TF: Peyronie’s disease. Urol Clin North Am 2001, 28:377–390.
Devine CJ, Jr., Horton CE: Surgical treatment of Peyronie’s disease with a dermal graff. J Urol 1974, 111:44–49.
Brannigan RE, Kim ED, Oyasu R, et al.: Comparison of tunica albuginea substitutes for the treatment of Peyronie’s disease. J Urol 1998, 159:1064–1068.
Fournier GR, Jr., Lue TF, Tanagho EA: Peyronie’s plaque: surgical treatment with the carbon dioxide laser and a deep dorsal vein patch graft. J Urol 1993, 149:1321–1325.
Brock G, Nunes L, von Heyden B, et al.: Can a venous patch graft be a substitute for the tunica albuginea of the penis? J Urol 1993, 150:1306–1309.
Schiffman ZJ, Gursel EO, Laor E: Use of Dacron patch graft in Peyronie disease. Urology 1985, 25:38–40.
Faerber GJ, Konnak JW: Results of combined Nesbit penile plication with plaque incision and placement of Dacron patch in patients with severe Peyronie’s disease. J Urol 1993, 149:1319–1320.
Ganabathi K, Dmochowski R, Zimmern PE, et al.: Peyronie’s disease: surgical treatment based on penile rigidity. J Urol 1995, 153:662–666.
Krishnamurti S: Penile dermal flap for defect reconstruction in Peyronie’s disease: operative technique and four years’ experience in 17 patients. Int J Impot Res 1995, 7:195–208.
Gelbard MK, Hayden B: Expanding contractures of the tunica albuginea due to Peyronie’s disease with temporalis fascia free grafts. J Urol 1991, 145:772–776.
Das S: Peyronie’s disease: excision and autografting with tunica vaginalis. J Urol 1980, 124:818–819.
Fallon B: Cadaveric dura mater graft for correction of penile curvature in Peyronie disease. Urology 1990, 35:127–129.
Hellstrom WJ, Reddy S: Application of pericardial graft in the surgical management of Peyronie’s disease. J Urol 2000, 163:1445–1447.
Chun JL, McGregor A, Krishnan R, et al.: A comparison of dermal and cadaveric pericardial grafts in the Modified Horton-Devine procedure for Peyronie’s disease. J Urol 2001, 166:185–188.
Levine LA, Estrada CR: Human cadaveric pericardial graft for the surgical correction of Peyronie’s disease. J Urol 2003, 170:2359–2362.
Bruschini H, Mitre AI: Peyronie disease: surgical treatment with muscular aponeurosis. Urology 1979, 13:505–506.
Knoll LD: Use of porcine small intestinal submucosal graft in the surgical management of Peyronie’s disease. Urology 2001, 57:753–757.
Shioshvili TJ, Kakonashvili AP: The surgical treatment of Peyronie’s disease: replacement of plaque by free autograft of buccal mucosa. Eur Urol 2005, 48:129–133.
El-Sakka AI, Rashwan HM, Lue TF: Venous patch graft for Peyronie’s disease. Part II: outcome analysis. J Urol 1998, 160:2050–2053.
Kadioglu A, Tefekli A, Usta M, et al.: Surgical treatment of Peyronie’s disease with incision and venous patch technique. Int J Impot Res 1999, 11:75–81.
Montorsi F, Salonia A, Maga T, et al.: Evidence based assessment of long-term results of plaque incision and vein grafting for Peyronie’s disease. J Urol 2000, 163:1704–1708.
Akkus E, Ozkara H, Alici B, et al.: Incision and venous patch graft in the surgical treatment of penile curvature in Peyronie’s disease. Eur Urol 2001, 40:531–536.
Adeniyi AA, Goorney SR, Pryor JP, et al.: The Lue procedure: an analysis of the outcome in Peyronie’s disease. BJU Int 2002, 89:404–408.
Chang JA, Gholami SS, Lue TF: Surgical management: saphenous vein grafts. Int J Impot Res 2002, 14:375–378.
Teloken C, Grazziotin T, Rhoden E, et al.: Penile straightening with crural graft of the corpus cavernosum. J Urol 2000, 164:107–108.
Hatzichristou DG, Hatzimouratidis K, Apostolidis A, et al.: Corporoplasty using tunica albuginea free grafts for penile curvature: surgical technique and long-term results. J Urol 2002, 167:1367–1370.
Schwarzer JU, Muhlen B, Schukai O: Penile corporoplasty using tunica albuginea free graft from proximal corpus cavernosum: a new technique for treatment of penile curvature in Peyronie’s disease. Eur Urol 2003, 44:720–723.
Hellstrom WJ, Usta MF: Surgical approaches for advanced Peyronie’s disease patients. Int J Impot Res 2003, 15(Supp l5):S121-S124.
Dalkin BL, Carter MF: Venogenic impotence following dermal graft repair for Peyronie’s disease. J Urol 1991, 146:849–851.
Carson CC, Chun JL: Peyronie’s disease: surgical management: autologous materials. Int J Impot Res 2002, 14:329–335.
Collins JP: Experience with lyophilized human dura for treatment of Peyronie disease. Urology 1988, 31:379–381.
Schultheiss D, Lorenz RR, Meister R, et al.: Functional tissue engineering of autologous tunica albuginea: a possible graft for Peyronie’s disease surgery. Eur Urol 2004, 45:781–786.
Lue TF, El-Sakka AI: Venous patch graft for Peyronie’s disease. Part I: technique. J Urol 1998, 160:2047–2049.
Montorsi F, Briganti A, Da Posso L, et al.: Five years followup of plaque incision and vein grafting for peyronie’s disease. Int J Impot Res 2003, 15:S14 (MP13–18).
Jordan GH, Angermeier KW: Preoperative evaluation of erectile function with dynamic infusion cavernosometry/ cavernosography in patients undergoing surgery for Peyronie’s disease: correlation with postoperative results. J Urol 1993, 150:1138–1142.
Levine L, Greenfield J, Estrada CR: Erectile dysfunction following surgical correction of Peyronie’s disease and a pilot study of the use of sildenafil citrate rehabilitation for postoperative erectile dysfunction. J Sexual Medicine 2005, 2:241–247.
Licht MR, Lewis RW: Modified Nesbit procedure for the treatment of Peyronie’s disease: a comparative outcome analysis. J Urol 1997, 158:460–463.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hatzimouratidis, K., Hatzichristou, D.G. Plaque incision and grafting represents the best surgical approach to the Peyronie’s disease patient: Con. Current Sexual Health Reports 3, 56–60 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11930-996-0003-9
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11930-996-0003-9