Abstract
Purpose of Review
The exact pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) remains unclear. Accumulating finds have indicated the roles of the non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) acting as novel epigenetic regulatory elements in the dysfunction of the immune system in SLE. This review will introduce recent studies on how ncRNAs are involved in the development of SLE.
Recent Findings
Recent advances in ncRNAs biology have greatly expanded our understanding of epigenetic regulation of immune responses and inflammation, and increasing evidence suggests ncRNAs are important players in SLE development. Identifications of abnormal expression patterns of ncRNAs and relevant biological impacts in lupus patients have revealed their potential as novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets for SLE.
Summary
The dysregulation of ncRNAs contributes to the immunopathogenesis of SLE. Clarifying the functions and mechanisms of SLE-associated ncRNAs provides new opportunities for disease biomarkers and targeted therapies.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Kiriakidou M, Ching CL. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172(11):ITC81–96. https://doi.org/10.7326/AITC202006020.
Tsokos GC, Lo MS, Costa Reis P, Sullivan KE. New insights into the immunopathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(12):716–30. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2016.186.
Esteller M. Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12(12):861–74. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3074.
Bartel DP. Metazoan MicroRNAs. Cell. 2018;173(1):20–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.03.006.
Statello L, Guo C-J, Chen L-L, Huarte M. Gene regulation by long noncoding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22(2). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-020-00315-9.
Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW, Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB, Kjems J. The biogenesis, biology, and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2019;20(11):675–91. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-019-0158-7.
Atianand MK, Caffrey DR, Fitzgerald KA. Immunobiology of long noncoding RNAs. Annu Rev Immunol. 2017;35:177–98. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-immunol-041015-055459.
Singh RP, Massachi I, Manickavel S, Singh S, Rao NP, Hasan S, et al. The role of miRNA in inflammation and autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev. 2013;12(12):1160–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2013.07.003.
Mowel WK, Kotzin JJ, McCright SJ, Neal VD, Henao-Mejia J. Control of immune cell homeostasis and function by lncRNAs. Trends Immunol. 2018;39(1):55–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2017.08.009.
Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang K-J, Baltimore D. NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(33):12481–6.
Du F, Yu F, Wang Y, Hui Y, Carnevale K, Fu M, et al. MicroRNA-155 deficiency results in decreased macrophage inflammation and attenuated atherogenesis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014;34(4):759–67. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.302701.
Yu D, Rao S, Tsai LM, Lee SK, He Y, Sutcliffe EL, et al. The transcriptional repressor Bcl-6 directs T follicular helper cell lineage commitment. Immunity. 2009;31(3):457–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2009.07.002.
Li Z, Chao T-C, Chang K-Y, Lin N, Patil VS, Shimizu C, et al. The long noncoding RNA THRIL regulates TNFα expression through its interaction with hnRNPL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(3):1002–7. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1313768111.
Jiang R, Tang J, Chen Y, Deng L, Ji J, Xie Y, et al. The long noncoding RNA lnc-EGFR stimulates T-regulatory cells differentiation thus promoting hepatocellular carcinoma immune evasion. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15129. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15129.
Wang J, Zhao X, Wang Y, Ren F, Sun D, Yan Y, et al. circRNA-002178 act as a ceRNA to promote PDL1/PD1 expression in lung adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(1):32. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2230-9.
Navarro-Quiroz E, Pacheco-Lugo L, Lorenzi H, Díaz-Olmos Y, Almendrales L, Rico E, et al. High-throughput sequencing reveals circulating miRNAs as potential biomarkers of kidney damage in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS One. 2016;11(11):e0166202. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0166202.
Tang Y, Luo X, Cui H, Ni X, Yuan M, Guo Y, et al. MicroRNA-146A contributes to abnormal activation of the type I interferon pathway in human lupus by targeting the key signaling proteins. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(4):1065–75. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.24436.
Wang J, Peng H, Tian J, Ma J, Tang X, Rui K, et al. Upregulation of long noncoding RNA TMEVPG1 enhances T helper type 1 cell response in patients with Sjögren syndrome. Immunol Res. 2016;64(2):489–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-015-8715-4.
Tang X, Wang J, Xia X, Tian J, Rui K, Xu H, et al. Elevated expression of ciRS-7 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Diagn Pathol. 2019;14(1):11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13000-019-0783-7.
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75(5):843–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(93)90529-y.
Zanoaga O, Braicu C, Chiroi P, Andreea N, Hajjar NA, Mărgărit S, et al. The role of miR-155 in nutrition: Modulating cancer-associated inflammation. Nutrients. 2021;13(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072245.
O'Connell RM, Chaudhuri AA, Rao DS, Baltimore D. Inositol phosphatase SHIP1 is a primary target of miR-155. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(17):7113–8. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0902636106.
Wang W, Bian H, Li F, Li X, Zhang D, Sun S, et al. HBeAg induces the expression of macrophage miR-155 to accelerate liver injury via promoting production of inflammatory cytokines. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018;75(14):2627–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-018-2753-8.
Zhang Y, Mei H, Chang X, Chen F, Zhu Y, Han X. Adipocyte-derived microvesicles from obese mice induce M1 macrophage phenotype through secreted miR-155. J Mol Cell Biol. 2016;8(6):505–17.
Karrich JJ, Jachimowski LCM, Libouban M, Iyer A, Brandwijk K, Taanman-Kueter EW, et al. MicroRNA-146a regulates survival and maturation of human plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Blood. 2013;122(17):3001–9. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-12-475087.
Xiao C, Calado DP, Galler G, Thai TH, Patterson HC, Wang J, et al. MiR-150 controls B cell differentiation by targeting the transcription factor c-Myb. Cell. 2007;131(1):146–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.07.021.
Mehta A, Mann M, Zhao JL, Marinov GK, Majumdar D, Garcia-Flores Y, et al. The microRNA-212/132 cluster regulates B cell development by targeting Sox4. J Exp Med. 2015;212(10):1679–92. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20150489.
Rao DS, O'Connell RM, Chaudhuri AA, Garcia-Flores Y, Geiger TL, Baltimore D. MicroRNA-34a perturbs B lymphocyte development by repressing the forkhead box transcription factor Foxp1. Immunity. 2010;33(1):48–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2010.06.013.
Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ. MicroRNA therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16(3):203–22. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2016.246.
Carlsen AL, Schetter AJ, Nielsen CT, Lood C, Knudsen S, Voss A, et al. Circulating microRNA expression profiles associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(5):1324–34. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.37890.
Pan W, Zhu S, Yuan M, Cui H, Wang L, Luo X, et al. MicroRNA-21 and microRNA-148a contribute to DNA hypomethylation in lupus CD4+ T cells by directly and indirectly targeting DNA methyltransferase 1. J Immunol. 2010;184(12):6773–81. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0904060.
Liu Z, Velpula KK, Devireddy L. 3-Hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase-2 and ferritin-H synergistically regulate intracellular iron. FEBS J. 2014;281(10):2410–21. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.12794.
Zhao M, Li M-Y, Gao X-F, Jia S-J, Gao K-Q, Zhou Y, et al. Downregulation of BDH2 modulates iron homeostasis and promotes DNA demethylation in CD4 T cells of systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol. 2018;187:113–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2017.11.002.
Qu B, Cao J, Zhang F, Cui H, Teng J, Li J, et al. Type I interferon inhibition of MicroRNA-146a maturation through up-regulation of monocyte chemotactic protein-induced protein 1 in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol (Hoboken, NJ). 2015;67(12):3209–18. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.39398.
Hou J, Wang P, Lin L, Liu X, Ma F, An H, et al. MicroRNA-146a feedback inhibits RIG-I-dependent Type I IFN production in macrophages by targeting TRAF6, IRAK1, and IRAK2. J Immunol. 2009;183(3):2150–8. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0900707.
Dominguez-Gutierrez PR, Ceribelli A, Satoh M, Sobel ES, Reeves WH, Chan EKL. Positive correlation of STAT1 and miR-146a with anemia in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Immunol. 2014;34(2):171–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-013-9973-3.
• Perez-Hernandez J, Martinez-Arroyo O, Ortega A, Galera M, Solis-Salguero MA, Chaves FJ, et al. Urinary exosomal miR-146a as a marker of albuminuria, activity changes and disease flares in lupus nephritis. J Nephrol. 2021;34(4):1157–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-020-00832-yThis study revealed urinary miR-146a as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker of LN.
Zhu Y, Xue Z, Di L. Regulation of MiR-146a and TRAF6 in the diagnose of lupus nephritis. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:2550–7. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.900667.
Stagakis E, Bertsias G, Verginis P, Nakou M, Hatziapostolou M, Kritikos H, et al. Identification of novel microRNA signatures linked to human lupus disease activity and pathogenesis: miR-21 regulates aberrant T cell responses through regulation of PDCD4 expression. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(8):1496–506. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2010.139857.
Zhao X, Tang Y, Qu B, Cui H, Wang S, Wang L, et al. MicroRNA-125a contributes to elevated inflammatory chemokine RANTES levels via targeting KLF13 in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(11):3425–35. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.27632.
Pan W, Zhu S, Dai D, Liu Z, Li D, Li B, et al. MiR-125a targets effector programs to stabilize Treg-mediated immune homeostasis. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7096. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8096.
Zhu S, Pan W, Song X, Liu Y, Shao X, Tang Y, et al. The microRNA miR-23b suppresses IL-17-associated autoimmune inflammation by targeting TAB2, TAB3 and IKK-α. Nat Med. 2012;18(7):1077–86. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2815.
Zhou H, Hasni SA, Perez P, Tandon M, Jang S-I, Zheng C, et al. miR-150 promotes renal fibrosis in lupus nephritis by downregulating SOCS1. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013;24(7):1073–87. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2012080849.
• Luan J, Fu J, Chen C, Jiao C, Kong W, Zhang Y, et al. LNA-anti-miR-150 ameliorated kidney injury of lupus nephritis by inhibiting renal fibrosis and macrophage infiltration. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):276. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-019-2044-2This study revealed the critical function of miR-150 in lupus nephritis and macrophage infiltration.
Solé C, Cortés-Hernández J, Felip ML, Vidal M, Ordi-Ros J. miR-29c in urinary exosomes as predictor of early renal fibrosis in lupus nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2015;30(9):1488–96. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfv128.
Zhou S, Wang Y, Meng Y, Xiao C, Liu Z, Brohawn P, et al. In vivo therapeutic success of microRNA-155 antagomir in a mouse model of lupus alveolar hemorrhage. Arthritis Rheumatol (Hoboken, NJ). 2016;68(4):953–64. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.39485.
• Tu Y, Guo R, Li J, Wang S, Leng L, Deng J, et al. MiRNA regulation of MIF in SLE and attenuation of murine lupus nephritis with miR-654. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2229. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02229This study showed that in vivo miR-654 treatment ameliorated murine lupus nephritis.
Duan W, Zhang W, Jia J, Lu Q, Eric GM. Exosomal microRNA in autoimmunity. Cell Mol Immunol. 2019;16(12):932–4. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-019-0319-9.
Long H, Wang X, Chen Y, Wang L, Zhao M, Lu Q. Dysregulation of microRNAs in autoimmune diseases: Pathogenesis, biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets. Cancer Lett. 2018;428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.04.016.
Schell SL, Rahman ZSM. miRNA-mediated control of B cell responses in immunity and SLE. Front Immunol. 2021;12:683710. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.683710.
Ponting CP, Oliver PL, Reik W. Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 2009;136(4):629–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.02.006.
Brockdorff N, Bowness JS, Wei G. Progress toward understanding chromosome silencing by Xist RNA. Genes Dev. 2020;34(11-12):733–44. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.337196.120.
Patil DP, Chen C-K, Pickering BF, Chow A, Jackson C, Guttman M, et al. m(6)A RNA methylation promotes XIST-mediated transcriptional repression. Nature. 2016;537(7620):369–73. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature19342.
Di Ruscio A, Ebralidze AK, Benoukraf T, Amabile G, Goff LA, Terragni J, et al. DNMT1-interacting RNAs block gene-specific DNA methylation. Nature. 2013;503(7476):371–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12598.
Somarowthu S, Legiewicz M, Chillón I, Marcia M, Liu F, Pyle AM. HOTAIR forms an intricate and modular secondary structure. Mol Cell. 2015;58(2):353–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2015.03.006.
Dong A, Preusch CB, So W-K, Lin K, Luan S, Yi R, et al. A long noncoding RNA, modulates chromatin accessibility to regulate muscle stem cell myogenic lineage progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(51):32464–75. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2005868117.
El Bassit G, Patel RS, Carter G, Shibu V, Patel AA, Song S, et al. MALAT1 in human adipose stem cells modulates survival and alternative splicing of PKCδII in HT22 cells. Endocrinology. 2017;158(1):183–95. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2016-1819.
Krawczyk M, Emerson BM. p50-associated COX-2 extragenic RNA (PACER) activates COX-2 gene expression by occluding repressive NF-κB complexes. Elife. 2014;3:e01776. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.01776.
Atianand MK, Hu W, Satpathy AT, Shen Y, Ricci EP, Alvarez-Dominguez JR, et al. A long noncoding RNA lincRNA-EPS acts as a transcriptional brake to restrain inflammation. Cell. 2016;165(7):1672–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.075.
Castellanos-Rubio A, Fernandez-Jimenez N, Kratchmarov R, Luo X, Bhagat G, Green PHR, et al. A long noncoding RNA associated with susceptibility to celiac disease. Science. 2016;352(6281):91–5. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad0467.
Qian C, Cao X. Dendritic cells in the regulation of immunity and inflammation. Semin Immunol. 2018;35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smim.2017.12.002.
Wang P, Xue Y, Han Y, Lin L, Wu C, Xu S, et al. The STAT3-binding long noncoding RNA lnc-DC controls human dendritic cell differentiation. Science. 2014;344(6181):310–3. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1251456.
Collier SP, Collins PL, Williams CL, Boothby MR, Aune TM. Cutting edge: Influence of Tmevpg1, a long intergenic noncoding RNA, on the expression of Ifng by Th1 cells. J Immunol. 2012;189(5):2084–8. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1200774.
Huang W, Thomas B, Flynn RA, Gavzy SJ, Wu L, Kim SV, et al. DDX5 and its associated lncRNA Rmrp modulate TH17 cell effector functions. Nature. 2015;528(7583):517–22. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16193.
Huang W, Thomas B, Flynn RA, Gavzy SJ, Wu L, Kim SV, et al. Retraction Note: DDX5 and its associated lncRNA Rmrp modulate T17 cell effector functions. Nature. 2018;562(7725):150. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0311-z.
Xue Z, Cui C, Liao Z, Xia S, Zhang P, Qin J, et al. Identification of LncRNA Linc00513 containing lupus-associated genetic variants as a novel regulator of interferon signaling pathway. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2967. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.02967.
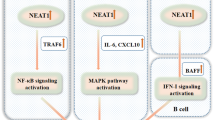
Zhang F, Wu L, Qian J, Qu B, Xia S, La T, et al. Identification of the long noncoding RNA NEAT1 as a novel inflammatory regulator acting through MAPK pathway in human lupus. J Autoimmun. 2016;75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2016.07.012.
Jiang CR, Li TH. Circulating UCA1 is highly expressed in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and promotes the progression through the AKT pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(8):2364–71. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201804_14828.
• Liao Z, Ye Z, Xue Z, Wu L, Ouyang Y, Yao C, et al. Identification of renal long non-coding RNA RP11-2B6.2 as a positive regulator of type I interferon signaling pathway in lupus nephritis. Front Immunol. 2019;10:975. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00975This study found that renal lncRNA RP11-2B6.2 promoted the over-activation of IFN-I signaling pathway in LN.
• Wang X, Zhang C, Wu Z, Chen Y, Shi W. CircIBTK inhibits DNA demethylation and activation of AKT signaling pathway via miR-29b in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1):118. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1618-8This study found that circIBTK regulated DNA demethylation and AKT signaling pathway and might function as a biomarker in SLE.
•• Liu C-X, Li X, Nan F, Jiang S, Gao X, Guo S-K et al. Structure and degradation of circular RNAs regulate PKR activation in innate immunity. Cell. 2019;177(4). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.03.046. This study offered a novel insight into the connection between circRNAs and SLE.
Wu G-C, Li J, Leng R-X, Li X-P, Li X-M, Wang D-G, et al. Identification of long noncoding RNAs GAS5, linc0597 and lnc-DC in plasma as novel biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematosus. Oncotarget. 2017;8(14):23650–63. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.15569.
Kino T, Hurt DE, Ichijo T, Nader N, Chrousos GP. Noncoding RNA gas5 is a growth arrest- and starvation-associated repressor of the glucocorticoid receptor. Sci Signal. 2010;3(107):ra8. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2000568.
• Liu C-H, Lu Y-L, Huang H-T, Wang C-F, Luo H-C, Wei G-J, et al. Association of LncRNA-GAS5 gene polymorphisms and PBMC LncRNA-GAS5 level with risk of systemic lupus erythematosus in Chinese population. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(7):3548–59. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.16438This study found certain polymorphisms of lncRNA GAS5 associated with SLE risk.
Li L-J, Zhu Z-W, Zhao W, Tao S-S, Li B-Z, Xu S-Z, et al. Circular RNA expression profile and potential function of hsa_circ_0045272 in systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology. 2018;155(1):137–49. https://doi.org/10.1111/imm.12940.
Zhang C, Wang X, Chen Y, Wu Z, Zhang C, Shi W. The down-regulation of hsa_circ_0012919, the sponge for, contributes to DNA methylation of CD11a and CD70 in CD4 T cells of systemic lupus erythematous. Clin Sci (Lond). 2018;132(21):2285–98. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20180403.
Kwon SJ, Crespo-Barreto J, Zhang W, Wang T, Kim DS, Krensky A, et al. KLF13 cooperates with c-Maf to regulate IL-4 expression in CD4+ T cells. J Immunol. 2014;192(12):5703–9. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1302830.
Wu Y, Zhang F, Ma J, Zhang X, Wu L, Qu B, et al. Association of large intergenic noncoding RNA expression with disease activity and organ damage in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:131. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-015-0632-3.
• Wu G-C, Hu Y, Guan S-Y, Ye D-Q, Pan H-F. Differential plasma expression profiles of long noncoding RNAs reveal potential biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematosus. Biomolecules. 2019;9(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9060206. This cross-sectional study revealed a panel of lncRNAs that could distinguish SLE from RA and pSS.
Miao Q, Zhong Z, Jiang Z, Lin Y, Ni B, Yang W, et al. RNA-seq of circular RNAs identified circPTPN22 as a potential new activity indicator in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2019;28(4):520–8. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203319830493.
•• Luan J, Jiao C, Kong W, Fu J, Qu W, Chen Y, et al. circHLA-C plays an important role in lupus nephritis by sponging miR-150. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018;10:245–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2017.12.006This study found that circHLA-C could act as a promising biomarker in lupus nephritis with an underlying role in the LN pathogenesis.
Suarez-Gestal M, Calaza M, Endreffy E, Pullmann R, Ordi-Ros J, Sebastiani GD, et al. Replication of recently identified systemic lupus erythematosus genetic associations: A case-control study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(3):R69. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar2698.
Anders H-J, Saxena R, Zhao M-H, Parodis I, Salmon JE, Mohan C. Lupus nephritis. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2020;6(1):7. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-019-0141-9.
Chen L-L. The expanding regulatory mechanisms and cellular functions of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(8):475–90. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-020-0243-y.
Hsu MT, Coca-Prados M. Electron microscopic evidence for the circular form of RNA in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1979;280(5720):339–40. https://doi.org/10.1038/280339a0.
Szabo L, Salzman J. Detecting circular RNAs: Bioinformatic and experimental challenges. Nat Rev Genet. 2016;17(11):679–92. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg.2016.114.
Zhou Z, Sun B, Huang S, Zhao L. Roles of circular RNAs in immune regulation and autoimmune diseases. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(7):503. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1744-5.
Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Li X, Zhang M, Lv K. Microarray analysis of circular RNA expression patterns in polarized macrophages. Int J Mol Med. 2017;39(2):373–9. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2017.2852.
Xia P, Wang S, Ye B, Du Y, Li C, Xiong Z, et al. A Circular RNA protects dormant hematopoietic stem cells from DNA sensor cGAS-mediated exhaustion. Immunity. 2018;48(4). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2018.03.016.
Chen X, Ouyang Z, Shen Y, Liu B, Zhang Q, Wan L, et al. CircRNA_28313/miR-195a/CSF1 axis modulates osteoclast differentiation to affect OVX-induced bone absorption in mice. RNA Biol. 2019;16(9):1249–62. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2019.1624470.
Chen Q, Mang G, Wu J, Sun P, Li T, Zhang H, et al. Circular RNA circSnx5 controls immunogenicity of dendritic cells through the miR-544/SOCS1 axis and PU.1 Activity Regulation. Mol Ther. 2020;28(11):2503–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.07.001.
Ouyang Q, Wu J, Jiang Z, Zhao J, Wang R, Lou A, et al. Microarray expression profile of circular RNAs in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(2):651–9. https://doi.org/10.1159/000477883.
Su L-C, Xu W-D, Liu X-Y, Fu L, Huang A-F. Altered expression of circular RNA in primary Sjögren's syndrome. Clin Rheumatol. 2019;38(12):3425–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04728-6.
Iparraguirre L, Muñoz-Culla M, Prada-Luengo I, Castillo-Triviño T, Olascoaga J, Otaegui D. Circular RNA profiling reveals that circular RNAs from ANXA2 can be used as new biomarkers for multiple sclerosis. Hum Mol Genet. 2017;26(18):3564–72. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddx243.
Grolleau A, Kaplan MJ, Hanash SM, Beretta L, Richardson B. Impaired translational response and increased protein kinase PKR expression in T cells from lupus patients. J Clin Invest. 2000;106(12):1561–8. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI9352.
Li H, Li K, Lai W, Li X, Wang H, Yang J, et al. Comprehensive circular RNA profiles in plasma reveals that circular RNAs can be used as novel biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Chim Acta. 2018;480:17–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2018.01.026.
Ouyang Q, Huang Q, Jiang Z, Zhao J, Shi G-P, Yang M. Using plasma circRNA_002453 as a novel biomarker in the diagnosis of lupus nephritis. Mol Immunol. 2018;101:531–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2018.07.029.
Li S, Zhang J, Tan X, Deng J, Li Y, Piao Y, et al. Microarray expression profile of circular RNAs and mRNAs in children with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol. 2019;38(5):1339–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4392-8.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31630021, 31930037, and 81102266), National Human Genetic Resources Sharing Service Platform (2005DKA21300), Shanghai Municipal Key Medical Center Construction Project (2017ZZ01024-002), Shenzhen Science and Technology Project (JCYJ20180504170414637), Futian Healthcare Research Project (FTWS2021006), Sanming Project of Medicine in Shenzhen (SZSM201602087), and Shanghai Clinical Research Center for Rheumatism and Immune Diseases (20MC1920300).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
All the authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, Y., Qu, B. & Shen, N. Expanding Roles of Noncoding RNAs in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Curr Rheumatol Rep 24, 64–75 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-022-01058-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-022-01058-6