Abstract
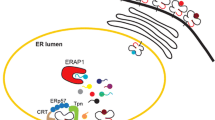
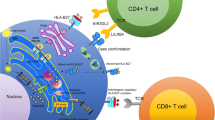
Endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 (ERAP1) and interleukin-23 receptor (IL-23R) gene polymorphisms were found to be associated with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) in a nonsynonymous single nucleotide polymorphism association study, and this has been replicated in several studies across different populations. ERAP1 variants could lead to significant changes in the repertoire of peptides presented by MHC-I. Reading this in conjunction with the known association of AS with HLA-B27, a functional interaction between ERAP1 and HLA-B27 is very likely. ERAP1 has additionally been shown to be involved in cytokine receptor shedding. The IL-23R is one of the two receptors that mediate the action of IL-23. AS is associated with the same polymorphisms of IL-23R as those linked to psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease. This suggests common genetic risks linking AS and extra-articular manifestations. This review focuses on the pathogenic potential of these two genes in AS.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Brown MA, Kennedy LG, MacGregor AJ, et al. Susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis in twins: the role of genes, HLA, and the environment. Arthritis Rheum. 1997;40:1823–8.
Jarvinen P. Occurrence of ankylosing spondylitis in a nationwide series of twins. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38:381–3.
Brewerton DA, Hart FD, Nicholls A, et al. Ankylosing spondylitis and HL-A 27. Lancet. 1973;1:904–7.
Brown MA, Laval SH, Brophy S, et al. Recurrence risk modelling of the genetic susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000;59:883–6.
Laval SH, Timms A, Edwards S, et al. Whole-genome screening in ankylosing spondylitis: evidence of non-MHC genetic-susceptibility loci. Am J Hum Genet. 2001;68:918–26.
Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium, Australo-Anglo-American Spondylitis Consortium (TASC), Burton PR, et al. Association scan of 14,500 nonsynonymous SNPs in four diseases identifies autoimmunity variants. Nat Genet. 2007;39:1329–37.
Serwold T, Gonzalez F, Kim J, et al. ERAAP customizes peptides for MHC class I molecules in the endoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 2002;419:480–3.
Saric T, Chang SC, Hattori A, et al. An IFN-gamma-induced aminopeptidase in the ER, ERAP1, trims precursors to MHC class I-presented peptides. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:1169–76.
Maksymowych WP, Inman RD, Gladman DD, et al. Association of a specific ERAP1/ARTS1 haplotype with disease susceptibility in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60:1317–23.
• Brown MA. Genetics of ankylosing spondylitis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010;22:126–32. A good review of the genetics of ankylosing spondylitis.
•• Tsui FW, Haroon N, Reveille JD, et al. Association of an ERAP1 ERAP2 haplotype with familial ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:733–6. This is the first publication to show a possible role of ERAP2 in ankylosing spondylitis.
Lee YH, Choi SJ, Ji JD, et al. Associations between ERAP1 polymorphisms and ankylosing spondylitis susceptibility: a meta-analysis. Inflamm Res. 2011;60:999–1003.
Evnouchidou I, Momburg F, Papakyriakou A, et al. The internal sequence of the peptide-substrate determines its N-terminus trimming by ERAP1. PLoS One. 2008;3:e3658.
•• Kochan G, Krojer T, Harvey D, et al. Crystal structures of the endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase-1 (ERAP1) reveal the molecular basis for N-terminal peptide trimming. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:7745–50. One of the two initial papers describing the crystal structure of ERAP1.
Nguyen TT, Chang SC, Evnouchidou I, et al. Structural basis for antigenic peptide precursor processing by the endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase ERAP1. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011;18:604–13. One of the two initial papers describing the crystal structure of ERAP1.
Cui X, Hawari F, Alsaaty S, et al. Identification of ARTS-1 as a novel TNFR1-binding protein that promotes TNFR1 ectodomain shedding. J Clin Invest. 2002;110:515–26.
Cui X, Rouhani FN, Hawari F, et al. Shedding of the type II IL-1 decoy receptor requires a multifunctional aminopeptidase, aminopeptidase regulator of TNF receptor type 1 shedding. J Immunol. 2003;171:6814–9.
Cui X, Rouhani FN, Hawari F, et al. An aminopeptidase, ARTS-1, is required for interleukin-6 receptor shedding. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:28677–85.
• Haroon N, Tsui FW, Chiu B, et al. Serum cytokine receptors in ankylosing spondylitis: relationship to inflammatory markers and endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase polymorphisms. J Rheumatol. 2010;37:1907–10. First functional study of ERAP1 in AS showing no role for receptor shedding function in ankylosing spondylitis.
Blanchard N, Shastri N. Coping with loss of perfection in the MHC class I peptide repertoire. Curr Opin Immunol. 2008;20:82–8.
Chang SC, Momburg F, Bhutani N, et al. The ER aminopeptidase, ERAP1, trims precursors to lengths of MHC class I peptides by a "molecular ruler" mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:17107–12.
York IA, Chang SC, Saric T, et al. The ER aminopeptidase ERAP1 enhances or limits antigen presentation by trimming epitopes to 8-9 residues. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:1177–84.
Hammer GE, Gonzalez F, James E, et al. In the absence of aminopeptidase ERAAP, MHC class I molecules present many unstable and highly immunogenic peptides. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:101–8.
••The Australo-Anglo-American Spondyloarthritis Consortium (TASC), the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2 (WTCCC2), Evans DM, et al. Interaction between ERAP1 and HLA-B27 in ankylosing spondylitis implicates peptide handling in the mechanism for HLA-B27 in disease susceptibility. Nat Genet. 2011;43:761–7. In this study, ERAP1 was associated with AS in only HLA-B27-positive patients and was in line with similar findings in psoriasis where a genetic interaction between ERAP1 and HLA-C was shown.
•• Genetic Analysis of Psoriasis Consortium & the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies new psoriasis susceptibility loci and an interaction between HLA-C and ERAP1. Nat Genet. 2010;42:985–90. The first study to establish a genetic link between ERAP1 and MHC-I. ERAP1 was associated with psoriasis only in HLA-C-positive individuals.
•• Haroon N, Tsui FW, Uchanska-Ziegler B, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 (ERAP1) exhibits functionally significant interaction with HLA-B27 and relates to subtype specificity in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71:589–95. This is the first study to establish a functional interaction between ERAP1 and HLA-B27 in AS patients. This study also showed a differential interaction between ERAP1 and HLA-B27 subtypes associated and not associated with AS.
Hattori A, Goto Y, Tsujimoto M. Exon 10 coding sequence is important for endoplasmic reticulum retention of endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35:601–5.
Kollnberger S, Chan A, Sun MY, et al. Interaction of HLA-B27 homodimers with KIR3DL1 and KIR3DL2, unlike HLA-B27 heterotrimers, is independent of the sequence of bound peptide. Eur J Immunol. 2007;37:1313–22.
•• Evnouchidou I, Kamal RP, Seregin SS, et al. Coding single nucleotide polymorphisms of endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 can affect antigenic peptide generation in vitro by influencing basic enzymatic properties of the enzyme. J Immunol. 2011;186:1909–13. This study showed that ERAP1 enzymatic action follows substrate inhibition kinetics and that activity of ERAP1 can be influenced by the type and amount of substrate in the reaction.
Haroon N, Inman RD. Endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidases: biology and pathogenic potential. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010;6:461–7.
Gaffen SL. Recent advances in the IL-17 cytokine family. Curr Opin Immunol. 2011;23:613–9.
Wilson NJ, Boniface K, Chan JR, et al. Development, cytokine profile and function of human interleukin 17-producing helper T cells. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:950–7.
Kimball AB, Gordon KB, Fakharzadeh S, et al. Long-term efficacy of ustekinumab in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis: results from the PHOENIX 1 trial through up to 3 years. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:861–72.
• Leonardi C, Matheson R, Zachariae C, et al. Anti-interleukin-17 monoclonal antibody ixekizumab in chronic plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:1190–9. One of two studies showing the efficacy of IL-17 blockage in psoriasis.
• Papp KA, Leonardi C, Menter A, et al. Brodalumab, an anti-interleukin-17-receptor antibody for psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:1181–9. One of two studies showing the efficacy of IL-17 blockage in psoriasis.
Cotterill L, Payne D, Levinson S, et al. Replication and meta-analysis of 13,000 cases defines the risk for interleukin-23 receptor and autophagy-related 16-like 1 variants in Crohn's disease. Can J Gastroenterol. 2010;24:297–302.
Nimmo ER, Prendergast JG, Aldhous MC, et al. Genome-wide methylation profiling in Crohn's disease identifies altered epigenetic regulation of key host defense mechanisms including the Th17 pathway. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2012;18:889–99.
•• Pidasheva S, Trifari S, Phillips A, et al. Functional studies on the IBD susceptibility gene IL23R implicate reduced receptor function in the protective genetic variant R381Q. PLoS One. 2011;6:e25038. Functional relevance of the IL23R association in with Crohn’s disease was shown in this study. The R381Q variant had decreased receptor function and was protective in Crohn’s disease.
Zwiers A, Kraal L, van de Pouw Kraan TC, et al. Cutting edge: a variant of the IL-23R gene associated with inflammatory bowel disease induces loss of microRNA regulation and enhanced protein production. J Immunol. 2012;188:1573–7.
Duan Z, Pan F, Zeng Z, et al. Interleukin-23 receptor genetic polymorphisms and ankylosing spondylitis susceptibility: a meta-analysis. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32:1209–14.
DeLay ML, Turner MJ, Klenk EI, et al. HLA-B27 misfolding and the unfolded protein response augment interleukin-23 production and are associated with Th17 activation in transgenic rats. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60:2633–43.
Zeng L, Lindstrom MJ, Smith JA. Ankylosing spondylitis macrophage production of higher levels of interleukin-23 in response to lipopolysaccharide without induction of a significant unfolded protein response. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:3807–17.
Shen H, Goodall JC, Hill Gaston JS. Frequency and phenotype of peripheral blood Th17 cells in ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60:1647–56.
Haroon N, Tsui FW, O'Shea FD, et al. From gene expression to serum proteins: biomarker discovery in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:297–300.
Appel H, Maier R, Wu P, et al. Analysis of IL-17(+) cells in facet joints of patients with spondyloarthritis suggests that the innate immune pathway might be of greater relevance than the Th17-mediated adaptive immune response. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13:R95.
Zvyagin IV, Mamedov IZ, Britanova OV, et al. Contribution of functional KIR3DL1 to ankylosing spondylitis. Cell Mol Immunol. 2010;7:471–6.
Lopez-Larrea C, Blanco-Gelaz MA, Torre-Alonso JC, et al. Contribution of KIR3DL1/3DS1 to ankylosing spondylitis in human leukocyte antigen-B27 Caucasian populations. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8:R101.
Chan AT, Kollnberger SD, Wedderburn LR, et al. Expansion and enhanced survival of natural killer cells expressing the killer immunoglobulin-like receptor KIR3DL2 in spondylarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:3586–95.
•• Bowness P, Ridley A, Shaw J, et al. Th17 cells expressing KIR3DL2+ and responsive to HLA-B27 homodimers are increased in ankylosing spondylitis. J Immunol. 2011;186:2672–80. This study showed that KIR3DL2 receptors are important in increasing the survival and IL-17 production by NK-T cells.
Kenna TJ, Davidson SI, Duan R, et al. Enrichment of circulating interleukin-17-secreting interleukin-23 receptor-positive gamma/delta T cells in patients with active ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64:1420–9.
Disclosure
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haroon, N. Endoplasmic Reticulum Aminopeptidase 1 and Interleukin-23 Receptor in Ankylosing Spondylitis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 14, 383–389 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-012-0268-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-012-0268-0