Abstract
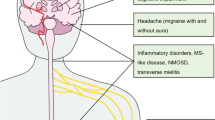
The antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is a systemic autoimmune disorder characterized by autoantibody production and thrombosis or pregnancy morbidity. The most prevalent neurologic manifestation of APS is cerebrovascular ischemic events due to arterial thromboses. Antiphospholipid antibodies can also cause neurologic impairments unrelated to thrombosis, through antibody-cellular interactions, possibly because of a disrupted blood-brain barrier. Antiplatelet or anticoagulant therapies are currently indicated for APS-related ischemic strokes, but they remain controversial for non-thrombotic neurologic manifestations. Scant literature exists on neurologic manifestations and treatment regimens in childhood APS. Modifiable cardiac risk factors and valvular heart disease may worsen APS cerebrovascular outcomes. Adjunctive therapies (eg, statins, antimalarials, and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors) warrant clinical trials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Bertolaccini ML, Khamashta MA, Hughes GR: Diagnosis of antiphospholipid syndrome. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol 2005, 1:40–46.
Levine JS, Branch DW, Rauch J: The antiphospholipid syndrome. N Engl J Med 2002, 346:752–763.
Miyakis S, Lockshin MD, Atsumi T, et al.: International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome. J Thromb Haemost 2006, 4:295–306.
Pierangelli SS, Chen PP, González EB: Antiphospholipid antibodies and the antiphospholipid syndrome: an update on treatment and pathogenic mechanisms. Curr Opin Hematol 2006, 13:366–375.
Hanly JG: Antiphospholipid syndrome: an overview. CMAJ 2003, 168:1675–1682.
Lim W, Crowther MA, Eikelboom JW: Management of the antiphospholipid antibody syndrome: a systemic review. JAMA 2006, 295:1050–1057.
Kamat AV, D’Cruz DP, Hunt BJ, et al.: Managing antiphospholipid antibodies and antiphospholipid syndrome in children. Haematologica 2006, 91:1674–1680.
Lockshin MD, Erkan D: Treatment of the antiphospholipid syndrome. N Engl J Med 2003, 349:1177–1179.
Cervera R, Khamashta MA, Font J, et al.: Morbidity and mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus during a 10-year period: A comparison of early and late manifestations in a cohort of 1,000 patients. Medicine 2003, 82:299–308.
Merrill JT, Asherson RA: Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol 2006, 2:81–89.
Brandt JT, Triplett DA, Alving B, Scharrer I: Criteria for the diagnosis of lupus anticoagulants: an update. On behalf of the subcommittee on lupus anticoagulant/ antiphospholipid antibody of the scientific and standardization committee of the ISTH. Thromb Haemost 1995, 74:1185–1190.
Galli M, Luciani D, Bertolini G, Barbui T: Lupus anticoagulants are stronger risk factors for thrombosis than anticardiolipin antibodies in the antiphospholipid syndrome: a systematic review of the literature. Blood 2005, 101:1827–1832.
Pierangelli SS, Vega-Ostertag ME, Harris EN: Intracellular signaling triggered by antiphospholipid antibodies in platelets and endothelial cells a pathway to targeted therapies. Thromb Res 2004, 114:467–476.
Salmon JE, Girardi G, Holers VM: Complement activation as a mediator of antiphospholipid antibody induced pregnancy loss and thrombosis. Ann Rheum Dis 2002, 61:46–50.
Dignat-George F, Camoin-Jau L, Sabatier F, et al.: Endothelial microparticles: a potential contribution to the thrombotic complications of the antiphospholipid syndrome. Thromb Haemost 2004, 91:667–673.
Pierangeli SS, Vega-Ostertag ME, Raschi E, et al.: Toll-like receptor and antiphospholipid-mediated thrombosis: in vivo studies. Ann Rheum Dis 2007, 66:1327–1333.
Hulstein JJ, Lenting PJ, de Laat B, et al.: Beta2-Glycoprotein I inhibits von Willebrand factor dependent platelet adhesion and aggregation. Blood 2007, 110:1483–1491.
Meroni PL, Tincani A, Sepp N, et al.: Endothelium and the brain in CNS lupus. Lupus 2003, 12:919–928.
Abbott NJ, Mendonca LL, Dolman DE: The blood-brain barrier in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2003, 12:908–915.
Connor P, Hunt BJ: Cerebral haemostasis and antiphospholipid antibodies. Lupus 2003, 12:929–934.
Trysberg E, Nylen K, Rosengren LE. et al.: Neuronal and astrocytic damage in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with central nervous system involvement. Arthritis Rheum 2003, 48:2881–2887.
Caronti B, Calderaro C, Alessandri C, et al.: Serum anti-beta2-glycoprotein I antibodies from patients with antiphospholipid antibody syndrome bind central nervous system cells. J Autoimmun 1998, 11:425–429.
Chapman J, Cohen-Armon M, Shoenfeld Y, et al.: Antiphospholipid antibodies permeabilize and depolarize brain synaptoneurosomes. Lupus 1999, 8:127–133.
Riccio A, Andreassi C, Eboli M: Antiphospholipid antibodies bind to rat cerebellar granule cells: the role of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Neurosci Lett 1998, 257:116–118.
Ziporen L, Shoenfeld Y, Levy Y, et al.: Neurological dysfunction and hyperactive behavior associated with antiphospholipid antibodies: a mouse model. J Clin Invest 1997, 100:613–619.
Sanna G, Bertolaccini ML, Cuadrado MJ, et al.: Central nervous system involvement in the antiphospholipid (Hughes) syndrome. Rheumatology 2003, 42:200–213.
Brey RL: Management of the neurological manifestations of APS-what do the trials tell us? Thromb Res 2004, 114:489–499.
Janhardan V, Wolf PA, Kase CS, et al.: Anticardiolipin antibodies and risk of ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attacks: the Framingham cohort and offspring study. Stroke 2004, 35:736–741.
Menon S, Jameson-Shortall E, Newman SP, et al.: A longitudinal study of anticardiolipin antibody levels and cognitive functioning in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 1999, 42:735–741.
McLaurin E, Holliday SL, Williams P, Brey RL: Predictors of cognitive dysfunction in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Neurology 2005, 64:297–303.
Jacobson MW, Rapport LJ, Keenan PA, et al.: Neuropsychological deficits associated with antiphospholipid antibodies. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 1999, 21:251–264.
Buller HR, Agnelli G, Hull RD, et al.: Antithrombotic therapy for venous thromboem bolic disease: the seventh ACCP conference on antithrombotic and thrombolytic therapy. Chest 2004, 126(3 Suppl):401S–428S.
Rosove MH, Brewer PM: Antiphospholipid thrombosis: clinical course after the first thrombotic event in 70 patients. Ann Intern Med 1992, 117:303–308.
Khamashta MA, Cudardo MJ, Mujic F, et al.: The management of thrombosis in the antiphospholipid syndrome. N Engl J Med 1995, 332:993–997.
Crowther MA, Ginsberg JS, Julian J, et al.: A comparison of two intensities of warfarin for the prevention of recurrent thrombosis in patients with the antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. N Engl J Med 2003, 349:1133–1138.
Finazzi G, Marchioli R, Brancaccio V, et al.: A randomized clinical trial of high-intensity warfarin vs. conventional antithrombotic therapy for the prevention of recurrent thrombosis in patients with the antiphospholipid syndrome (WAPS). J Thromb Haemost 2005, 3:848–853.
The APASS Writing Committee: Antiphospholipid antibodies and subsequent thrombo-occlusive events in patients with ischemic stroke. JAMA 2004, 291:576–584.
Toloza SM, Uribe AG, McGwin G, et al.: Systemic lupus erythematosus in a multiethnic US cohort (LUMINA): XXIII. Baseline predictors of vascular events. Arthritis Rheum 2004, 50:3947–3957.
Akimoto T: Risk factors for recurrent thrombosis: Prospective study of a cohort of Japanese systemic lupus erythematosus. Angiology 2005, 56:601–609.
Roldan CA, Gelgand EA, Qualls CR, et al.: Valvular heart disease as a cause of cerebrovascular disease in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Cardiol 2005, 95:1441–1447.
Krause I, Lev S, Fraser A, et al.: Close association between valvular heart disease and central nervous system manifestations in the antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 2005, 64:1490–1493.
Alarcon-Segovia D, Boffa MC, Branch W, et al.: Prophylaxis of the antiphospholipid syndrome: a consensus report. Lupus 2003, 12:499–503.
Erkan D, Harrison MJ, Levy R, et al.: Aspirin for primary thrombosis prevention in the antiphospholipid syndrome: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in asymptomatic antiphospholipid antibody-positive individuals. Arthritis Rheum 2007, 56:2382–2391.
Chapman J, Rand JH, Brey RL, et al.: Non-stroke neurological syndromes associated with antiphospholipid antibodies: evaluation of clinical and experimental studies. Lupus 2003, 12:514–517.
Angelini L, Ravelli A, Caporali R, et al.: High prevalence of antiphospholipid antibodies in children with idiopathic cerebral ischemia. Pediatrics 1994, 94:500–503.
Lanthier S, Kirkham FJ, Mitchell LG, et al.: Increased anticardiolipin antibody IgG titers do not predict recurrent stroke or TIA in children. Neurology 2004, 62:194–200.
Berkun Y, Padeh S, Barash J, et al.: Antiphospholipid syndrome and recurrent thrombosis in children. Arthritis Rheum 2006, 55:850–855.
Roubey RA: New approaches to prevention of thrombosis in the antiphospholipid syndrome: Hopes, trials and tribulations. Arthritis Rheum 2003, 48:3004–3008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muscal, E., Brey, R.L. Neurologic manifestations of the antiphospholipid syndrome: Integrating molecular and clinical lessons. Curr Rheumatol Rep 10, 67–73 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-008-0012-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-008-0012-y