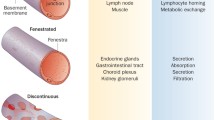
Abstract
Pseudovasculitis, vasculitis-like syndromes, or mimics of vasculitis represent a heterogeneous collection of disorders that are capable of simulating a vasculitic disorder. Some conditions such as cardiac myxomas, cholesterol embolization, and fibromuscular dysplasia are more apt to cause confusion, but numerous other conditions can do so also. Inappropriate diagnosis leads to delay or absence of proper management and exposure to potentially deleterious treatment modalities such as corticosteroids and cytotoxic agents. The diagnosis of a pseudovasculitic disorder requires a high index of suspicion and should always be part of the differential diagnosis of vasculitis. The endothelium is thought to be pivotal in vascular injury; much has been learned using in vitro human umbilical vein endothelial cell cultures. Application of this knowledge to human disease and to vasculitic disorders and their imitators is still premature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Lie JT: The classification and diagnosis of vasculitis in large and medium-sized blood vessels. Pathol Annu 1987, 22:125–162.
Hunder GG, Arend WP, Bloch DA, et al.: The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of vasculitis. Introduction. Arthritis Rheum 1990, 33:1065–1067.
Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Andrassy K, et al.: Nomenclature of systemic vasculitides. Proposal of an international consensus conference. Arthritis Rheum 1994, 37:1871–1892.
Rao JK, Allen NB, Pincus T: Limitations of the 1990 American College of Rheumatology classification criteria in the diagnosis of vasculitis. Ann Intern Med 1998, 129:345–352.
Sacks KE: Mimickers of vasculitis. In Arthritis and Allied Conditions, edn 13. Edited by William J Koopman. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins; 1997:1525–1546. A thorough review of this topic with an extensive bibliography. The only such review in a standard textbook of rheumatology.
Lie JT: Vasculitis simulators and vasculitis look-alikes. Curr Opin Rheumatol 1992, 4:47–55. Limited but insightful review of the topic from an extremely knowledgeable author.
Witort-Serraglini E, Del Rosso M, Lotti T, Mattucci-Cerinic M: Endothelial injury in vasculitides. Clin Derm 1999, 17:587–590.
Allaire E, Clowes AW: Endothelial cell injury in cardiovascular surgery: the intimal hyperplastic response. Ann Thorac Surg 1997, 63:582–591.
Pober JS: Activation and injury of endothelial cells by cytokines. Path Biol 1998, 46:159–163.
Bratt J, Palmblad J: Cytokine-induced neutrophil-mediated injury of human endothelial cells. J Immunol 1997, 159:912–918.
Gross WL, Trabandt A, Reinhold-Keller E: Diagnosis and evaluation of vasculitis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2000, 39:245–252.
Pepin M, Schwarze V, Superti-Furga A, Byers PH: Clinical and genetic features of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV, the vascular type. N Engl J Med 2000, 342:673–680.
Daniels SR, Loggie JM, McEnery PT, Toubin RB: Clinical spectrum of intrinsic renovascular hypertension in children. Pediatrics 1987, 80:698–704.
Burns LJ, Pooley JC, Walsh DJ, et al.: Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression in endothelial cells is activated by cytomegalovirus immediate early proteins. Transplantation 1999, 67:137–144.
Eremeeva ME, Silverman DJ: Rickettsia ricketsii infection of the EA.hy 926 endothelial cell line: morphological response to infection and evidence of oxidative injury. Microbiology 1998, 144:2037–2048.
O’Connor MM, Mayberg MR: Effects of radiation on cerebral vasculature: a review. Neurosurgery 2000, 46:138–149.
Pittilo M: Cigarette smoking, endothelial injury and cardiovascular disease. Int J Exp Pathol 2000, 81:219–230.
Jacob JR, Weisman MH, Rosenblatt SI, Bookstein JJ: Chronic pernio. A historical perspective of cold-induced vascular disease. Arch Intern Med 1986, 146:1589–1592.
Sonden A, Svensson B, Roman N, et al.: Laser-induce shock wave endothelial cell injury, Lasers Surg Med 2000, 26:364–375.
Reynen K: Medical progress: cardiac myxomas. N Engl J Med 1995, 333:1610–1617.
Wold LE, Lie JT: Cardiac myxomas: a clinicopathologic profile. Am J Pathol 1980, 101:219–229.
Seino Y, Ikeda U, Shimada K: Increased expression of interleukin-6 in cardiac myxomas. Br Heart J 1993, 69:565–567.
Greeson DM, Wright JE, Zanolli MD: Cutaneous findings associated with cardiac myxomas. Cutis 1998, 62:275–280.
Navarro PH, Bravo FP, Beltran GG: Atrial myxoma with livedoid macules as its sole cutaneous manifestation. J Am Acad Dermatol 1995, 32:881–883.
Boussen K, Moalla M, Blondeau P, et al.: Embolization of cardiac myxoma masquerading as polyarteritis nodosa. J Rheumatol 1991, 18:283–285.
Begelman SM, Olin JW: Fibromuscular dysplasia. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2000, 12:41–47. ellent review of the topic with fine radiologic examples
Harrison E Jr, McCormack L: Pathologic classification of renal arterial disease in renovascular hypertension. Mayo Clin Proc 1971, 6:161–167.
Jones HJ, Staud R, Williams RC: Rupture of a hepatic artery aneurysm and renal infarction: 2 complications of fibromuscular dysplasia that mimic vasculitis. J Rheumatol 1998, 25:2015–2018.
Siegert CEH, Macfarlane JD, Hollander AMJ, van Kemenade F: Systemic fibromuscular dysplasia masquerading as polyarteritis nodosa. Nephrol Dial Transplant 1996, 11:1356–1358.
Chan RJ, Goodman TA, Aretz TH, Lie JT: Segmental mediolytic arteriopathy of the splenic and hepatic arteries mimicking systemic necrotizing vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum 1997, 41:955–938.
Lie JT: Cholesterol atheromatous embolism. The great masquerader revisited. Pathol Annu 1992, 27:17–50.
Cappiello RA, Espinoza LR, Adelman H, et al.: Cholesterol embolism: a pseudovasculitic syndrome. Semin Arthritis Rheum 1989, 18:240–246.
Ballesteros AL, Bromsoms J, Valles M, et al.: Vasculitis lookalikes: variants of renal atheroembolic disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 1999, 14:430–433.
Sprabery AT, Newman K, Lohr KM: Aortic mural thrombus presenting as pseudovasculitis. Chest 1994, 106:282–283.
Spittell PC, Seward JB, Hallett JWJr: Mobile thrombi in the abdominal aorta in cases of lower extremity embolic arterial occlusion: value of extended transthoracic echocardiography. Am Heart J 2000, 139:241–244.
Peat DS, Mathieson PW: Cholesterol emboli may mimic systemic vasculitis. BMJ 1996, 313:546–547.
Sabatine MS, Oelberg DA, Mark EJ, Kanarek D: Pulmonary cholesterol crystal embolization. Chest 1997, 112:1687–1692.
Kusaba A, Imayama S, Furue M: Delayed appearance of livedo reticularis in 3 cases with a cholesterol embolism. Arch Dermatol 1999, 135:725–726.
Salvarani C, Gabriel SE, Gertz MA, et al.: Primary systemic amyloidosis presenting as giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica. Arthritis Rheum 1994, 37:1621–1626.
Rao JK, Allen NB: Primary systemic amyloidosis masquerading as giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheum 1993, 36:422–425.
Staud R, Williams RC Jr: Brain abscess mimicking giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheum 1995, 38:1710–1712.
Goupille P, Jeannou J, Brunais J, Valat JP: Sphenoid abscess mimicking giant cell arteritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 1996, 14:579–580.
Chittenden HB, Clearkin LG, Sidky K: Herpes zoster ophthalmicus masquerading as giant cell arteritis. Br J Hosp Med 1995, 54:49–50.
Rosenstein ED, Kramer Neil: Occult subacute thyroiditis mimicking classic giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheum 1994, 37:1618–1620.
Lortholary O, Genereau T, Dray JM, et al.: Bacteremia can mimic temporal arteritis relapse in older patients. J Am Geriatrics Soc 1998, 46:1056–1057.
Winterkorn MS, Odel JG, Behrens MM: Ergotamine headaches mistaken for temporal arteritis. Ann Neurol 1990, 28:396.
Lie JT: Malignant angioendotheliomatosis (intravascular lymphomatosis) clinically simulating primary angiitis of the central nervous system. Arthritis Rheum 1992, 35:831–834.
Kao NL, Broy S, Tillawi I: Malignant angioendotheliomatosis mimicking systemic necrotizing vasculitis. J Rheumatol 1992, 19:1133–1135.
Seinknecht CW, Whetsell WO, Pollock P: Intravascular malignant lymphoma (malignant angioendotheliomatosis) mimicking primary angiitis of the central nervous system. J Rheumatol 1995, 22:1769–1770.
Thomas R, Vuitch F, Lakhanpal S: Angiotropic T cell lymphoma masquerading as cutaneous vasculitis. J Rheumatol 1994, 21:760–762.
Adelman HM, Wallach PM, Gutierrez F, et al.: Scurvy resembling cutaneous vasculitis. Cutis 1994, 54:111–114.
Mehta CL, Cripps D, Bridges AJ: Systemic pseudovasculitis from scurvy in anorexia nervosa. Arthritis Rheum 1996, 39:532–533.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grau, R. Pseudovasculitis: Mechanisms of vascular injury and clinical spectrum. Curr Rheumatol Rep 4, 83–89 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-002-0028-7
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-002-0028-7