Abstract
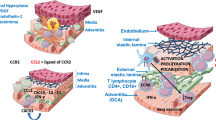
Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR)/temporal arteritis (TA) frequently causes significant morbidity in patients older than 50 years of age. This review highlights recent trends in clinical findings, epidemiology, pathogenesis, and laboratory and radiologic assessment of the disease. Although steroids are the mainstay of therapy because of their effectiveness and ease of administration, they have numerous side effects, particularly in an aging population. Furthermore, recent evidence suggests that steroids only suppress clinical symptoms, while a smoldering level of damaging vascular inflammation persists. As a result, alternative agents are actively being investigated. We compare their successes and shortcomings and offer insight into their potential role in the treatment of this disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Wilke WS, Hoffman GS: Treatment of corticosteroid resistant giant cell arteritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 1995, 21:59–71.
Bahlas S, Ramos-Remus C, Davis P: Clinical outcome of 149 patients with polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis. J Rheumatol 1998, 25:99–104.
Gabriel S, Sunku J, Salvarani C, et al.: Adverse outcomes of anti-inflammatory therapy among patients with polymyalgia rheumatica. Arthritis Rheum 1997, 40:1873–1878.
Nesher G, Sonnenblick M, Friedlander Y: Analysis of steroid related complications and mortality in temporal arteritis: a 15 year survey of 43 patients. J Rheumatol 1994, 21:1283–1286.
Weyand CM, Fulbright JW, Hunder GG, et al.: Treatment of giant cell arteritis: interleukin-6 as a biologic marker of disease activity. Arthritis Rheum 2000, 43:1041–1048.
Uddhammar AC: Von Willebrand factor in polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2000, 18:S32–33.
Mohan N, Kerr G: Spectrum of giant cell vasculitis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2000, 2:390–395.
Cimmino MA, Zaccaria A: Epidemiology of polymyalgia rheumatica. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2000, 18:S9–11.
Ghanchi FD, Dutton GN: Current concepts in giant cell (temporal) arteritis. Surv Ophthalmol 1997, 42:99–123.
Salvarani C, Gabriel SE, O’Fallon WM, Hunder GG: The incidence of giant cell arteritis in Olmsted County, Minnesota: apparent fluctuations in a cyclic pattern. Ann Intern Med 1995, 123:192–194.
Reinhold-Keller E, Zeidler A, Gutfleisch J, et al.: Giant cell arteritis is more prevalent in urban than in rural populations: results of an epidemiological study of primary systemic vasculitides in Germany. Rheumatology 2000, 39:1396–1402.
Weyand CM: The pathogenesis of giant cell arteritis. J Rheumatol 2000, 27:517–522.
Dal Canto AJ, Virgin HW: Animal models of infection-mediated vasculitis: implications for human disease. Int J Cardiol 2000, 75:S37-S45.
Dangler CA, Baker SE, Njenga MK, et al.: Murine cytomegalovirusassociated arteritis. Vet Pathol 1995, 32:127–133.
Presti RM, Pollock JL, Dal Canto AJ, et al.: Interferon-gamma regulates acute and latent murine cytomegalovirus infection and chronic disease of the great vessels. J Exp Med 1998, 188:577–588.
Weck KE, Dal Canto AJ, Gould JD, et al.: Murine gamma-herpesvirus 68 causes large vessel arteritis in mice lacking interferon-gamma responsiveness: a new model for virus induced vascular disease. Nat Med 1997, 3:1346–1353.
Elling H, Olsson AT, Elling P: Human Parvovirus and giant cell arteritis: a selective arteritic impact? Clin Exp Rheumatol 2000, 18:S12-S14.
Rimenti G, Blasi F, Cosentini R, et al.: Temporal arteritis associated with Chlamydia pneumoniae DNA detected in an artery specimen. J Rheumatol 2000, 27:2718–2720.
Uddhammar A, Boman J, Juto P, et al.: Antibodies against Chlamydia pneumoniae, cytomegalovirus, enteroviruses and respiratory syncytial virus in patients with polymyalgia rheumatica. Clin Exp Rheumatol 1997, 15:299–302.
Duhaut P, Bosshar S, Calvet A, et al.: Giant cell arteritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, and viral hypotheses: a multicenter, prospective case-control study. J Rheumatol 1999, 26:361–369.
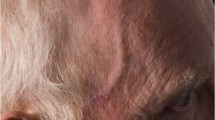
Hunder GG: Clinical features of GCA/PMR. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2000, 18:S6-S8.
Hunder GG, Bloch DA, Michel BA, et al.: The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheum 1990, 33:122–128.
Cantini F, Salvarani C, Olivieri I, et al.: Erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein in the evaluation of disease activity and severity in polymyalgia rheumatica: a prospective follow-up study. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2000, 30:17–24. Discusses the frequency and clinical features of PMR patients with normal ESRs and compares the ESR and CRP during disease relapses.
Martinez-Taboada VM, Blanco R, Rodriguez-Valverde V: Polymyalgia rheumatica with normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate: clinical aspects. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2000, 18:S34–37.
Gonzalez-Gay MA, Garcia-Porrua C, Llorca J, et al.: Biopsy-negative giant cell arteritis: clinical spectrum and predictive factors for positive temporal artery biopsy. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2001, 30:249–256. Discusses the frequency and clinical features of biopsy-negative giant cell arteritis.
Pavlica P, Barozzi L, Salvarani C, et al.: Magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of PMR. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2000, 18:S38–39.
Salvarani C, Cantini F, Olivieri I, et al.: Proximal bursitis in active polymyalgia rheumatica. Ann Intern Med 1997, 127:27–31.
Schmidt WA: Doppler ultrasonography in the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2000, 18:S40–42.
Schmidt WA, Kraft HE, Vorpahl K, et al.: Color duplex ultrasonography in the diagnosis of temporal arteritis. New Engl J Med 1997, 24:1570–1574.
Salvarini C, Silingardi M, Ghirarduzzi A, et al.: Is duplux ultrasonography useful for the diagnosis of temporal arteritis? Arthritis Rheum 2000, 43:S366.
Blockmans D, Stroobants S, Maes A, Mortelmans L: Positron emission tomography in giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica: evidence for inflammation of the aortic arch. Am J Med 2000, 108:246–269. Discusses the high specificity of PET scanning with radiolabeled fluoro-18-deoxyglucose in the diagnosis of PMR/GCA. Supports the arguments that PMR is a form of vasculitis, and that the large arteries and temporal arteries may be affected in these diseases.
Gran JT: Current therapy of polymyalgia rheumatica. Scand J Rheumatol 1999, 28:269–272.
Myles AB, Perera T, Ridley MG: Prevention of blindness in giant cell arteritis by corticosteroid treatment. Br J Rheumatol 1992, 31:103–105.
Hunder GG: Giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica. Med Clin North Am 1997, 81:195–219.
Hunder GG, Sheps SG, Allen GL, Joyce JW: Daily and alternateday corticosteroid regimens in treatment of giant cell arteritis: comparison in a prospective study. Ann Intern Med 1975, 82:613–618.
Dasgupta B, Dolan AL, Panayi GS, Fernandes L: An initially double blind controlled 96 week trial of depot methylprednisolone against oral prednisolone in the treatment of polymyalgia rheumatica. Br J Rheumatol 1998, 37:189–195.
Salvarani C, Cantini F, Olivieri I, et al.: Corticosteroid injections in polymyalgia rheumatica: a double blind, prospective, randomized, placebo controlled study. J Rheumatol 2000, 27:1470–1476.
Li C, Dasgupta B: Corticosteroids in polymyalgia rheumatica —a review of different treatment schedules. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2000, 18:S56–57.
Cacoub P, Chemlal K, Khalifa P, et al.: Deflazacort versus prednisone in patients with giant cell arteritis: a randomized, double blind comparative trial studying the effects on bone mass loss. Arthritis Rheum 2000, 43:S163.
Krogsgaard MR, Thamsborg G, Lund B: Changes in bone mass during low dose corticosteroid treatment in patients with polymyalgia rheumatica: a double blind, prospective comparison between prednisolone and deflazacort. Ann Rheum Dis 1996, 55:143–146.
Ferraccioli GF, Salaffi F, De Vita S, et al.: Methotrexate in polymyalgia rheumatica: preliminary results of an open, randomized study. J Rheumatol 1996, 23:624–628.
Feinberg HL, Sherman JD, Schrepferman CG, et al.: The use of methotrexate in polymyalgia rheumatica. J Rheumatol 1996, 23:1550–1552.
Van der Veen MJ, Dinant HJ, van Booma-Frankfort C, et al.: Can methotrexate be used as a steroid sparing agent in the treatment of polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis? Ann Rheum Dis 1996, 55:218–223.
Hoffman G, Cid M, Hellmann D, et al.: A multicenter placebo controlled study of methotrexate in giant cell arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2000, 43:S115. Large multicenter, randomized, prospective, placebo-controlled trial comparing prednisone alone with prednisone plus methotrexate in the treatment of newly diagnosed GCA.
Jover JA, Hernandez-Garcia C, Morado IC, et al.: Combined treatment of giant-cell arteritis with methotrexate and prednisone. Ann Intern Med 2001, 134:106–114. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial comparing prednisone and prednisone plus methotrexate in newly diagnosed GCA.
De Silva M, Hazleman BL: Azathioprine in giant cell arteritis/ polymyalgia rheumatica: a double blind study. Ann Rheum Dis 1986, 45:136–138.
Doury P, Pattin S, Eulry F, Thabaut A: The use of dapsone in the treatment of giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica [letter]. Arthritis Rheum 1983, 30:689–690.
Boesen P, Dideriksen K, Stentoft J, Jensen MK: Dapsone in temporal arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica [letter]. J Rheumatol 1988, 15:879–880.
Reinitz E, Aversa A: Long-term treatment of temporal arteritis with dapsone [letter]. Am J Med 1988, 85:456–457.
Liozon F, Vidal E, Barrier J: Dose dapsone have a role in the treatment of temporal arteritis with regard to efficacy and toxicity? Clin Exp Rheumatol 1993, 11:694–695.
Schaufelberger C, Andersson R, Nordborg E: No additive effect of cyclosporin A compared with glucocorticoid treatment alone in giant cell arteritis: results of an open, controlled, randomized study. Br J Rheumatol 1998, 37:464–465.
Le Guennec P, Dromer C, Sixou L, et al.: Treatment of Horton disease. Value of synthetic antimalarials. Apropos of a retrospective study of 36 patients. Revue du rheumatisme. Edition Francaise 1994, 61:485–490.
De Vita S, Tavoni A, Jeracitano G, et al.: Treatment of giant cell arteritis with cyclophosphamide pulses [letter]. J Intern Med 1992, 232:373–375.
Galezowski N, Nguyen TB, Blanche P: Sulfamethoxazole/ trimethoprim therapy for polymyalgia rheumatica. Report of 5 cases [letter]. J Rheumatol 1997, 24:1451–1452.
Pearce G, Ryan PFJ, Delmas PD, et al.: The deleterious effects of low-dose corticosteroids on bone density in patients with polymyalgia rheumatica. Br J Rheumatol 1998, 37:292–299.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barilla-LaBarca, ML., Lenschow, D.J. & Brasington, R.D. Polymyalgia rheumatica/temporal arteritis: Recent advances. Curr Rheumatol Rep 4, 39–46 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-002-0022-0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-002-0022-0