Abstract
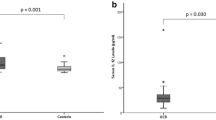
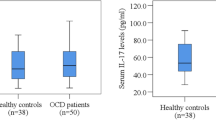
Several studies have examined levels of proinflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, and IL-6. This meta-analysis was conducted to examine the association between obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and plasma serum levels of proinflammatory cytokines. Twelve studies met inclusion criteria. The meta-analysis demonstrated a significant reduction in IL-1β levels in OCD. No significant difference in plasma levels of IL-6 or TNF-α was demonstrated. Stratified subgroup analysis revealed possible moderating effects of age and medication use on IL-6 levels. Studies including children on psychotropic medication had lower plasma IL-6 levels. Stratified subgroup analysis revealed a moderating effect of comorbid depression on TNF-α levels. Elevated TNF-α levels were reported in studies that included individuals with comorbid depression. Future studies examining immune function in OCD should adjust for potential confounding due to medication use and comorbid depression. Further studies assessing cerebrospinal fluid cytokine levels in OCD are also needed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance
Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, Jin R, Merikangas KR, Walters EE. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62:593–602.
Ruscio AM, Stein DJ, Chiu WT, Kessler RC. The epidemiology of obsessive-compulsive disorder in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Mol Psychiatry. 2010;15:53–63.
DuPont RL, Rice DP, Shiraki S, Rowland CR. Economic costs of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Med Interface. 1995;8:102–9.
First MB. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4th ed. Washington: American Psychiatric Association; 2000.
• de Oliveira S, Pelajo C. Pediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorders Associated with Streptococcal Infection (PANDAS): a controversial diagnosis. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2010;12:103–9. This review highlights important criticism of the PANDAS hypothesis..
da Rocha FF, Correa H, Teixeira AL. Obsessive-compulsive disorder and immunology: a review. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2008;32:1139–46.
Swedo SE, Grant PJ. Annotation: PANDAS: a model for human autoimmune disease. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2005;46:227–34.
Swedo SE, Leonard HL, Garvey M, et al. Pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcal infections: clinical description of the first 50 cases. Am J Psychiatry. 1998;155:264–71.
• Murphy TK, Kurlan R, Leckman J. The immunobiology of Tourette’s disorder, pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcus, and related disorders: a way forward. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2010;20:317–31. This review provides an overview of PANDAS, including diagnostic criteria and evidence supporting the PANDAS hypothesis..
Araki K, Turner AP, Shaffer VO, et al. mTOR regulates memory CD8 T-cell differentiation. Nature. 2009;460:108–12.
Shulman ST. Pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococci (PANDAS): update. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2009;21:127.
• Dowlati Y, Herrmann N, Swardfager W, et al. A meta-analysis of cytokines in major depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2010;67:446–57. This article demonstrates that cytokine levels are altered by mood disorders, which are highly comorbid in OCD..
Maes M, Bosmans E, De Jongh R, Kenis G, Vandoolaeghe E, Neels H. Increased serum IL-6 and IL-1 receptor antagonist concentrations in major depression and treatment resistant depression. Cytokine. 1997;9:853–8.
Penninx BWJH, Kritchevsky SB, Yaffe K, et al. Inflammatory markers and depressed mood in older persons: results from the health, aging and body composition study. Biol Psychiatry. 2003;54:566–72.
Empana JP, Sykes DH, Luc G, et al. Contributions of depressive mood and circulating inflammatory markers to coronary heart disease in healthy European men. Circulation. 2005;111:2299–305.
Kim YK, Suh IB, Kim H, et al. The plasma levels of interleukin-12 in schizophrenia, major depression, and bipolar mania: effects of psychotropic drugs. Mol Psychiatry. 2002;7:1107.
Jones AL, Mowry BJ, Pender MP, Greer JM. Immune dysregulation and self-reactivity in schizophrenia: do some cases of schizophrenia have an autoimmune basis? Immunol Cell Biol. 2005;83:9–17.
Strous RD, Shoenfeld Y. Schizophrenia, autoimmunity and immune system dysregulation: a comprehensive model updated and revisited. J Autoimmun. 2006;27:71–80.
Potvin S, Stip E, Sepehry AA, Gendron A, Bah R, Kouassi E. Inflammatory cytokine alterations in schizophrenia: a systematic quantitative review. Biol Psychiatry. 2008;63:801–8.
• Hannestad J, DellaGioia N, Bloch M. The effect of antidepressant medication treatment on serum levels of inflammatory cytokines: a meta-analysis. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011;36:2452–9. This article demonstrates that psychotropic medication alters inflammatory cytokine levels in major depressive disorder..
Murphy K, Travers P, Walport M. Janeway’s immunobiology. 7th ed. New York: Garland Science; 2008.
Steinke JW, Borish L. 3. Cytokines and chemokines. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117:S441–5.
Brough D, Tyrrell PJ, Allan SM. Regulation of interleukin-1 in acute brain injury. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2011;32:617–22.
Konuk N, Tek, #x131, et al. Plasma levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 in obsessive compulsive disorder. Mediat Inflamm. 2007;2007.
Pan W, Zadina JE, Harlan RE, Weber JT, Banks WA, Kastin AJ. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha: a neuromodulator in the CNS. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1997;21:603–13.
Schöbitz B, de Kloet ER, Sutanto W, Holsboer F. Cellular localization of interleukin 6 mRNA and interleukin 6 receptor mRNA in rat brain. Eur J Neurosci. 1993;5:1426–35.
Carlson NG, Wieggel WA, Chen J, Bacchi A, Rogers SW, Gahring LC. Inflammatory cytokines IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α impart neuroprotection to an excitotoxin through distinct pathways. J Immunol. 1999;163:3963–8.
Hirano T, Yasukawa K, Harada H, et al. Complementary DNA for a novel human interleukin (BSF-2) that induces B lymphocytes to produce immunoglobulin. Nature. 1986;324:73–6.
Spooren A, Kolmus K, Laureys G, et al. Interleukin-6, a mental cytokine. Brain Res Rev. 2011;67:157–83.
Tadamitsu K. Interleukin-6 and its receptor in autoimmunity. J Autoimmun. 1992;5(Supplement A):123–32.
Xing Z, Gauldie J, Cox G, et al. IL-6 is an anti-inflammatory cytokine required for controlling local or systemic acute inflammatory responses. J Clin Invest. 1998;101:311–20.
Uyttenhove C, Coulie PG, Van Snick J. T cell growth and differentiation induced by interleukin-HP1/IL-6, the murine hybridoma/plasmacytoma growth factor. J Exp Med. 1988;167:1417–27.
Lotz M, Jirik F, Kabouridis P, et al. B cell stimulating factor 2/interleukin 6 is a costimulant for human thymocytes and T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1988;167:1253–8.
Zheng H, Fletcher D, Kozak W, et al. Resistance to fever induction and impaired acute-phase response in interleukin-1β-deficient mice. Immunity. 1995;3:9–19.
Tilg H, Trehu E, Atkins MB, Dinarello CA, Mier JW. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) as an anti-inflammatory cytokine: induction of circulating IL-1 receptor antagonist and soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor p55. Blood. 1994;83:113–8.
Dinarello CA. Immunological and inflammatory functions of the interleukin-1 family. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:519–50.
Dinarello CA. Biologic basis for interleukin-1 in disease. Blood. 1996;87:2095–147.
Marlin SD, Springer TA. Purified intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) is a ligand for lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1). Cell. 1987;51:813–9.
Dustin ML, Rothlein R, Bhan AK, Dinarello CA, Springer TA. Induction by IL 1 and interferon-gamma: tissue distribution, biochemistry, and function of a natural adherence molecule (ICAM-1). J Immunol. 1986;137:245–54.
Sironi M, Breviario F, Proserpio P, et al. IL-1 stimulates IL-6 production in endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1989;142:549–53.
Wang CC, Fu CL, Yang YH, et al. Adenovirus expressing interleukin-1 receptor antagonist alleviates allergic airway inflammation in a murine model of asthma. Gene Ther. 2006;13:1414–21.
Nakae S, Asano M, Horai R, Iwakura Y. Interleukin-1β, but not interleukin-1α, is required for T-cell-dependent antibody production. Immunology. 2001;104:402–9.
Pfeffer K. Biological functions of tumor necrosis factor cytokines and their receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2003;14:185–91.
McCoy M, Tansey M. TNF signaling inhibition in the CNS: implications for normal brain function and neurodegenerative disease. J Neuroinflamm. 2008;5:1–13.
Cairns CB, Panacek EA, Harken AH, Banerjee A. Bench to bedside tumor necrosis factor-alpha: from inflammation to resuscitation. Acad Emerg Med. 2000;7:930–41.
Graham AL, Allen JE, Read AF. Evolutionary causes and consequences of immunopathology. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst. 2005;36:373–97.
Deeks J, Higgins J, Altman D. Cochrane reviewer’s handbook 4.2.2 [Updated March 2004] In: The Cochrane library. Chinchester: Wiley; 2004.
Brambilla F, Perna G, Bellodi L, et al. Plasma interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor concentrations in obsessive-compulsive disorders. Biol Psychiatry. 1997;42:976–81.
Maes M, Meltzer HY, Bosmans E. Psychoimmune investigation in obsessive-compulsive disorder: assays of plasma transferrin, IL-2 and IL-6 receptor, and IL-1β and IL-6 concentrations. Neuropsychobiology. 1994;30:57–60.
Monteleone P, Catapano F, Fabrazzo M, Tortorella A, Maj M. Decreased blood levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Neuropsychobiology. 1998;37:182–5.
Leckman JF, Katsovich L, Kawikova I, et al. Increased serum levels of interleukin-12 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in Tourette’s syndrome. Biol Psychiatry. 2005;57:667–73.
Gabbay V, Coffey BJ, Guttman LE, et al. A cytokine study in children and adolescents with Tourette’s disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2009;33:967–71.
Bos-Veneman NGP, Bijzet J, Limburg PC, Minderaa RB, Kallenberg CG, Hoekstra PJ. Cytokines and soluble adhesion molecules in children and adolescents with a tic disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2010;34:1390–5.
Weizman R, Laor N, Barber Y, et al. Cytokine production in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 1996;40:908–12.
Denys D, Fluitman S, Kavelaars A, Heijnen C, Westenberg H. Decreased TNF-α and NK activity in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2004;29:945–52.
Denys D, Fluitman S, Kavelaars A, Heijnen C, Westenberg HGM. Effects of paroxetine and venlafaxine on immune parameters in patients with obsessive compulsive disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2006;31:355–60.
Fluitman S, Denys D, Vulink N, Schutters S, Heijnen C, Westenberg H. Lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine production in obsessive-compulsive disorder and generalized social anxiety disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2010;178:313–6.
Fluitman SBAHA, Denys DAJP, Heijnen CJ, Westenberg HGM. Disgust affects TNF-alpha, IL-6 and noradrenalin levels in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2010;35:906–11.
Carpenter LL, Heninger GR, McDougle CJ, Tyrka AR, Epperson CN, Price LH. Cerebrospinal fluid interleukin-6 in obsessive-compulsive disorder and trichotillomania. Psychiatry Res. 2002;112:257–62.
Mittleman BB, Castellanos FX, Jacobsen LK, Rapoport JL, Swedo SE, Shearer GM. Cerebrospinal fluid cytokines in pediatric neuropsychiatric disease. J Immunol. 1997;159:2994–9.
Elenkov IJ, Chrousos GP. Stress hormones, proinflammatory and antiinflammatory cytokines, and autoimmunity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002;966:290–303.
Vgontzas AN, Bixler EO, Lin HM, Prolo P, Trakada G, Chrousos GP. IL-6 and Its Circadian Secretion in Humans. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2005;12:131–40.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the National Institute of Mental Health support of the Yale Child Study Center Research Training Program (Dr. Bloch), the National Institutes of Health (NIH) 1K23MH091240 (Dr. Bloch), the APIRE/Eli Lilly Psychiatric Research Fellowship (Dr. Bloch), the AACAP/Eli Lilly Junior Investigator Award (Dr. Bloch), the Trichotillomania Learning Center (Dr. Bloch), NARSAD (Dr. Bloch), and UL1 RR024139 from the National Center for Research Resources, a component of the NIH, and NIH roadmap for Medical Research (Dr. Bloch).
Disclosure
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gray, S.M., Bloch, M.H. Systematic Review of Proinflammatory Cytokines in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Curr Psychiatry Rep 14, 220–228 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-012-0272-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-012-0272-0