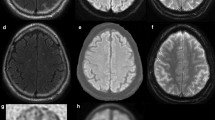
Abstract
Mitochondrial diseases are multisystem disorders that frequently involve the central nervous system. The clinical presentation of these disorders may be challenging to differentiate from cerebrovascular disorders. Various imaging techniques are now available that provide a wide range of imaging modalities during initial clinical evaluation and throughout the disease course. Recent technological advancements have introduced advanced neuroimaging modalities that provide detailed information of metabolic disorders at the tissue level. Imaging findings, though diverse, usually have characteristic features that support differentiating these disorders from vascular syndromes. This article provides an overview of various neuroimaging modalities available along with the advent of new imaging techniques being utilized in these disorders.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Pavlakis SG, Phillips PC, DiMauro S, De Vivo DC, Rowland LP. Mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and strokelike episodes: a distinctive clinical syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1984;16(4):481–8. doi:10.1002/ana.410160409.
DiMauro S, Schon EA. Mitochondrial disorders in the nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2008;31:91–123. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.30.051606.094302.
DiMauro S, Schon EA. Mitochondrial respiratory-chain diseases. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(26):2656–68. doi:10.1056/NEJMra022567.
Iizuka T, Sakai F. Pathogenesis of stroke-like episodes in MELAS: analysis of neurovascular cellular mechanisms. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2005;2(1):29–45.
Malhotra K, Liebeskind DS. Imaging in Endovascular Stroke Trials. J Neuroimaging. 2015;25(4):517–27. doi:10.1111/jon.12272.
Goto Y, Horai S, Matsuoka T, Koga Y, Nihei K, Kobayashi M, et al. Mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes (MELAS): a correlative study of the clinical features and mitochondrial DNA mutation. Neurology. 1992;42(3 Pt 1):545–50.
Yoshida T, Ouchi A, Miura D, Shimoji K, Kinjo K, Sueyoshi T, et al. MELAS and reversible vasoconstriction of the major cerebral arteries. Int Med (Tokyo, Japan). 2013;52(12):1389–92.
Yeh HL, Chen YK, Chen WH, Wang HC, Chiu HC, Lien LM, et al. Perfusion status of the stroke-like lesion at the hyperacute stage in MELAS. Brain Dev. 2013;35(2):158–64. doi:10.1016/j.braindev.2012.03.017.
Ito H, Mori K, Kagami S. Neuroimaging of stroke-like episodes in MELAS. Brain Dev. 2011;33(4):283–8. doi:10.1016/j.braindev.2010.06.010.
Haas R, Dietrich R. Neuroimaging of mitochondrial disorders. Mitochondrion. 2004;4(5–6):471–90. doi:10.1016/j.mito.2004.07.008.
Ito H, Mori K, Harada M, Minato M, Naito E, Takeuchi M, et al. Serial brain imaging analysis of stroke-like episodes in MELAS. Brain Dev. 2008;30(7):483–8. doi:10.1016/j.braindev.2008.01.003.
Allard JC, Tilak S, Carter AP. CT and MR of MELAS syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1988;9(6):1234–8.
Johnson EC, West TW, Ko NU, Strober JB. A 41-year-old man with new headache and altered mental status. Neurohospitalist. 2011;1(1):48–54. doi:10.1177/1941875210385948.
Lazzaro MA, Malhotra K, Mohammad YM. The role of antithrombotics in secondary stroke prevention. Semin Neurol. 2010;30(5):492–500. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1268860.
Finsterer J, Barton P. Regression of stroke-like lesions in MELAS-syndrome after seizure control. Epileptic Disord. 2010;12(4):330–4. doi:10.1684/epd.2010.0338.
Carolei A, Sacco S. Headache attributed to arteritis, cerebral venous thrombosis, and other vascular intracranial disturbances. Handb Clin Neurol. 2010;97:529–40. doi:10.1016/s0072-9752(10)97048-6.
Jamieson DG, Cheng NT, Skliut M. Headache and acute stroke. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2014;18(9):444. doi:10.1007/s11916-014-0444-1.
Wang YX, Le WD. Progress in Diagnosing Mitochondrial Myopathy, Encephalopathy, Lactic Acidosis, and Stroke-like Episodes. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015;128(13):1820–5. doi:10.4103/0366-6999.159360.
Kim IO, Kim JH, Kim WS, Hwang YS, Yeon KM, Han MC. Mitochondrial myopathy-encephalopathy-lactic acidosis-and strokelike episodes (MELAS) syndrome: CT and MR findings in seven children. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996;166(3):641–5. doi:10.2214/ajr.166.3.8623642.
Chung SH, Chen SC, Chen WJ, Lee CC. Symmetric basal ganglia calcification in a 9-year-old child with MELAS. Neurology. 2005;65(9), E19. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000184112.34211.d1.
Hirano M, Pavlakis SG. Mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and strokelike episodes (MELAS): current concepts. J Child Neurol. 1994;9(1):4–13.
Davis PC, Hoffman Jr JC, Braun IF, Ahmann P, Krawiecki N. MR of Leigh’s disease (subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy). AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1987;8(1):71–5.
Goodfellow JA, Dani K, Stewart W, Santosh C, McLean J, Mulhern S, et al. Mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis and stroke-like episodes: an important cause of stroke in young people. Postgrad Med J. 2012;88(1040):326–34. doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2011-130326.
Gire C, Girard N, Nicaise C, Einaudi MA, Montfort MF, Dejode JM. Clinical features and neuroradiological findings of mitochondrial pathology in six neonates. Childs Nerv Syst. 2002;18(11):621–8. doi:10.1007/s00381-002-0621-0.
Moroni I, Bugiani M, Bizzi A, Castelli G, Lamantea E, Uziel G. Cerebral white matter involvement in children with mitochondrial encephalopathies. Neuropediatrics. 2002;33(2):79–85. doi:10.1055/s-2002-32372.
Pauli W, Zarzycki A, Krzysztalowski A, Walecka A. CT and MRI imaging of the brain in MELAS syndrome. Pol J Radiol. 2013;78(3):61–5. doi:10.12659/pjr.884010.
Wang XY, Noguchi K, Takashima S, Hayashi N, Ogawa S, Seto H. Serial diffusion-weighted imaging in a patient with MELAS and presumed cytotoxic oedema. Neuroradiology. 2003;45(9):640–3. doi:10.1007/s00234-003-1029-6.
Yoneda M, Maeda M, Kimura H, Fujii A, Katayama K, Kuriyama M. Vasogenic edema on MELAS: a serial study with diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Neurology. 1999;53(9):2182–4.
Jian-Ren L. Precipitation of stroke-like event by chickenpox in a child with MELAS syndrome. Neurol India. 2005;53(3):323–5.
Yonemura K, Hasegawa Y, Kimura K, Minematsu K, Yamaguchi T. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in a case of mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and strokelike episodes. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001;22(2):269–72.
Tzoulis C, Bindoff LA. Serial diffusion imaging in a case of mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes. Stroke. 2009;40(2):e15–7. doi:10.1161/strokeaha.108.523118.
Kim JH, Lim MK, Jeon TY, Rha JH, Eo H, Yoo SY, et al. Diffusion and perfusion characteristics of MELAS (mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episode) in thirteen patients. Korean J Radiol. 2011;12(1):15–24. doi:10.3348/kjr.2011.12.1.15.
Chinnery PF. Mitochondrial Disorders Overview. In: Pagon RA, Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, Bean LJH, editors. GeneReviews(R). Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993. All rights reserved.
Dindyal S, Mistry K, Angamuthu N, Smith G, Hilton D, Arumugam P, et al. MELAS syndrome presenting as an acute surgical abdomen. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2014;96(1):101e–3e. doi:10.1308/003588414x13824511649733.
Saneto RP, Friedman SD, Shaw DW. Neuroimaging of mitochondrial disease. Mitochondrion. 2008;8(5–6):396–413. doi:10.1016/j.mito.2008.05.003.
Wilichowski E, Pouwels PJ, Frahm J, Hanefeld F. Quantitative proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of cerebral metabolic disturbances in patients with MELAS. Neuropediatrics. 1999;30(5):256–63. doi:10.1055/s-2007-973500.
Moller HE, Kurlemann G, Putzler M, Wiedermann D, Hilbich T, Fiedler B. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy in patients with MELAS. J Neurol Sci. 2005;229–230:131–9. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2004.11.014.
Osborn AG, Salzman KL, Jhaveri MD, Barkovich AJ. Diagnostic imaging: brain. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2015
Abe K, Yoshimura H, Tanaka H, Fujita N, Hikita T, Sakoda S. Comparison of conventional and diffusion-weighted MRI and proton MR spectroscopy in patients with mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like events. Neuroradiology. 2004;46(2):113–7. doi:10.1007/s00234-003-1138-2.
Kaufmann P, Engelstad K, Wei Y, Kulikova R, Oskoui M, Sproule DM, et al. Natural history of MELAS associated with mitochondrial DNA m.3243A>G genotype. Neurology. 2011;77(22):1965–71. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e31823a0c7f.
Weiduschat N, Kaufmann P, Mao X, Engelstad KM, Hinton V, DiMauro S, et al. Cerebral metabolic abnormalities in A3243G mitochondrial DNA mutation carriers. Neurology. 2014;82(9):798–805. doi:10.1212/wnl.0000000000000169.
Virtanen SM, Lindroos MM, Majamaa K, Nuutila P, Borra RJ, Parkkola R. Voxelwise analysis of diffusion tensor imaging and structural MR imaging in patients with the m.3243A>G mutation in mitochondrial DNA. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011;32(3):522–6. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A2309.
Noguchi A, Shoji Y, Matsumori M, Komatsu K, Takada G. Stroke-like episode involving a cerebral artery in a patient with MELAS. Pediatr Neurol. 2005;33(1):70–1. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2005.01.013.
Iizuka T, Goto Y, Miyakawa S, Sato M, Wang Z, Suzuki K, et al. Progressive carotid artery stenosis with a novel tRNA phenylalanine mitochondrial DNA mutation. J Neurol Sci. 2009;278(1–2):35–40. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2008.11.016.
Ooiwa Y, Uematsu Y, Terada T, Nakai K, Itakura T, Komai N, et al. Cerebral blood flow in mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and strokelike episodes. Stroke. 1993;24(2):304–9.
Molnar MJ, Valikovics A, Molnar S, Tron L, Dioszeghy P, Mechler F, et al. Cerebral blood flow and glucose metabolism in mitochondrial disorders. Neurology. 2000;55(4):544–8.
Ikawa M, Okazawa H, Arakawa K, Kudo T, Kimura H, Fujibayashi Y, et al. PET imaging of redox and energy states in stroke-like episodes of MELAS. Mitochondrion. 2009;9(2):144–8. doi:10.1016/j.mito.2009.01.011.
Nishioka J, Akita Y, Yatsuga S, Katayama K, Matsuishi T, Ishibashi M, et al. Inappropriate intracranial hemodynamics in the natural course of MELAS. Brain Dev. 2008;30(2):100–5. doi:10.1016/j.braindev.2007.06.008.
Thajeb P, Wu MC, Shih BF, Tzen CY, Chiang MF, Yuan RY. Brain single photon emission computed tomography in patients with A3243G mutation in mitochondrial DNA tRNA. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005;1042:48–54. doi:10.1196/annals.1338.005.
Koga Y, Akita Y, Junko N, Yatsuga S, Povalko N, Fukiyama R, et al. Endothelial dysfunction in MELAS improved by l-arginine supplementation. Neurology. 2006;66(11):1766–9. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000220197.36849.1e.
Koga Y, Povalko N, Nishioka J, Katayama K, Kakimoto N, Matsuishi T. MELAS and L-arginine therapy: pathophysiology of stroke-like episodes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1201:104–10. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05624.x.
Iizuka T, Sakai F, Kan S, Suzuki N. Slowly progressive spread of the stroke-like lesions in MELAS. Neurology. 2003;61(9):1238–44.
Tsujikawa T, Yoneda M, Shimizu Y, Uematsu H, Toyooka M, Ikawa M, et al. Pathophysiologic evaluation of MELAS strokes by serially quantified MRS and CASL perfusion images. Brain Dev. 2010;32(2):143–9. doi:10.1016/j.braindev.2008.12.003.
Ikawa M, Yoneda M, Muramatsu T, Matsunaga A, Tsujikawa T, Yamamoto T, et al. Detection of preclinically latent hyperperfusion due to stroke-like episodes by arterial spin-labeling perfusion MRI in MELAS patients. Mitochondrion. 2013;13(6):676–80. doi:10.1016/j.mito.2013.09.007.
Huppi PS, Inder TE. Magnetic resonance techniques in the evaluation of the perinatal brain: recent advances and future directions. Semin Neonatol. 2001;6(2):195–210. doi:10.1053/siny.2001.0039.
Majoie CB, Akkerman EM, Blank C, Barth PG, Poll-The BT, den Heeten GJ. Mitochondrial encephalomyopathy: comparison of conventional MR imaging with diffusion-weighted and diffusion tensor imaging: case report. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002;23(5):813–6.
Xie S. MR OEF, imaging in MELAS. Methods Enzymol. 2014;547:433–44. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-801415-8.00021-7.
De Volder A, Ghilain S, de Barsy T, Goffinet AM. Brain metabolism in mitochondrial encephalomyopathy: a PET study. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1988;12(5):854–7.
Yu L, Xie S, Xiao J, Wang Z, Zhang X. Quantitative measurement of cerebral oxygen extraction fraction using MRI in patients with MELAS. PLoS One. 2013;8(11):e79859. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0079859.
Malhotra K, Conners JJ, Lee VH, Prabhakaran S. Relative changes in transcranial Doppler velocities are inferior to absolute thresholds in prediction of symptomatic vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2014;23(1):31–6. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2012.08.004.
Kodaka R, Itagaki Y, Matsumoto M, Nagai T, Okada S. A transcranial doppler ultrasonography study of cerebrovascular CO2 reactivity in mitochondrial encephalomyopathy. Stroke. 1996;27(8):1350–3.
Ganslandt O, Steinmeier R, Kober H, Vieth J, Kassubek J, Romstock J, et al. Magnetic source imaging combined with image-guided frameless stereotaxy: a new method in surgery around the motor strip. Neurosurgery. 1997;41(3):621–7. discussion 7–8.
Rossini PM, Tecchio F, Pizzella V, Lupoi D, Cassetta E, Pasqualetti P, et al. On the reorganization of sensory hand areas after mono-hemispheric lesion: a functional (MEG)/anatomical (MRI) integrative study. Brain Res. 1998;782(1–2):153–66.
Kamada K, Takeuchi F, Houkin K, Kitagawa M, Kuriki S, Ogata A, et al. Reversible brain dysfunction in MELAS: MEG, and (1)H MRS analysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2001;70(5):675–8.
Tschampa HJ, Urbach H, Greschus S, Kunz WS, Kornblum C. Neuroimaging characteristics in mitochondrial encephalopathies associated with the m.3243A>G MTTL1 mutation. J Neurol. 2013;260(4):1071–80. doi:10.1007/s00415-012-6763-4.
Lax NZ, Pienaar IS, Reeve AK, Hepplewhite PD, Jaros E, Taylor RW, et al. Microangiopathy in the cerebellum of patients with mitochondrial DNA disease. Brain. 2012;135(Pt 6):1736–50. doi:10.1093/brain/aws110.
Renard D, Taieb G. Neurological picture. Cortical susceptibility-weighted imaging hypointensity after stroke-like episode in MELAS. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2014;85(9):1055–6. doi:10.1136/jnnp-2013-306933.
Betts J, Jaros E, Perry RH, Schaefer AM, Taylor RW, Abdel-All Z, et al. Molecular neuropathology of MELAS: level of heteroplasmy in individual neurones and evidence of extensive vascular involvement. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2006;32(4):359–73. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.2006.00731.x.
Ramanathan RS, Malhotra K, Scott T. Teaching NeuroImages: diffuse cerebral neurosarcoidosis mimicking gliomatosis cerebri. Neurology. 2013;81(7):e46. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182a08d47.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Konark Malhotra declares no conflict of interest.
David S. Liebeskind declares NIH-NINDS grant support and being a consultant for Imaging Core Lab for Stryker and Medtronic.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Imaging
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malhotra, K., Liebeskind, D.S. Imaging of MELAS. Curr Pain Headache Rep 20, 54 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-016-0583-7
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-016-0583-7