Abstract
Significant improvement of neuropathic pain has been achieved with studies that have demonstrated efficacy of newer anticonvulsants in relieving this type of pain, by having a neuromodulatory effect on the hyperexcitable damaged nervous system. Two drugs from this class, gabapentin and lamotrigine, have been submitted to a number of clinical trials. Ease of use and broad therapeutic range, in addition to demonstrated efficacy, make gabapentin the drug of choice for most neuropathic pain disorders. Lamotrigine is well tolerated when it is titrated slowly, which also is the way to avoid the development of a rash. Pregabalin, the newest agent that has demonstrated efficacy in the treatment of post-herpetic neuralgia, is awaiting approval. A number of available anticonvulsants are undergoing clinical trials and many drugs with neuromodulatory properties are being considered for further development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Backonja M, Glanzman RL: Gabapentin dosing for neuropathic pain: evidence from randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials. Clin Ther 2003, 25:81–104.
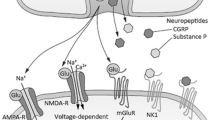
Basbaum AI, Woolf CJ: Pain. Curr Biol 1999, 9:R429-R431.
Backonja M, Beydoun A, Edwards KR, et al.: Gabapentin for the symptomatic treatment of painful neuropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 1998, 280:1831–1836.
Rowbotham M, Harden N, Stacey B, et al.: Gabapentin for the treatment of post-herpetic neuralgia: a randomized, controlled trial. JAMA 1998, 280:1837–1842.
Rice AS, Maton S, Post-herpetic Neuralgia Study Group: Gabapentin in post-herpetic neuralgia: a randomized, doubleblind, placebo-controlled study. Pain 2001, 94:215–224.
Serpell MG, Neuropathic Pain Study Group: Gabapentin in neuropathic pain syndromes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Pain 2002, 99:557–566.
Backonja MM: Defining neuropathic pain. Anesth Anal 2003, 97:785–790.
Wiffen P, Collins S, McQuay H, et al.: Anticonvulsant drugs for acute and chronic pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2000, 3:CD001133. This is an evolving method of literature review.
McCleane G: 200 mg daily of lamotrigine has no analgesic effect in neuropathic pain: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Pain 1999, 83:105–107.
Simpson DM, Olney R, McArthur JC, et al.: A placebo-controlled trial of lamotrigine for painful HIV-associated neuropathy. Neurology 2000, 54:2115–2119.
Simpson DM, McArthur JC, Olney R, et al.: Lamotrigine for HIV-associated painful sensory neuropathies: a placebocontrolled trial. Neurology 2003, 60:1508–1514.
Eisenberg E, Lurie Y, Braker C, et al.: Lamotrigine reduces painful diabetic neuropathy: a randomized, controlled study. Neurology 2001, 57:505–509.
Vestergaard K, Andersen G, Gottrup H, et al.: Lamotrigine for central post-stroke pain: a randomized, controlled trial. Neurology 2001, 56:184–190. Two studies (references 9 and 19) were done in a patient population that has been neglected in clinical trials. It is encouraging that a single agent, lamotrigine, relieves pain in both of these central neuropathic pain disorders.
Finnerup NB, Sindrup SH, Bach FW, et al.: Lamotrigine in spinal cord injury pain: a randomized, controlled trial. Pain 2002, 96:375–383.
Tremont-Lukats IW, Megeff C, Backonja MM: Anticonvulsants for neuropathic pain syndromes: mechanisms of action and place in therapy. Drugs 2001, 60:1029–1052. This is a comprehensive review of randomized clinical trials and open-label studies.
Tanelian DL, Brose WG: Neuropathic pain can be relieved by drugs that are use-dependent sodium channel blockers: lidocaine, carbamazepine, and mexiletine. Anesthesiology 1991, 74:949–951.
Tanelian DL, MacIver MB: Analgesic concentrations of lidocaine suppress tonic A-delta and C fiber discharges produced by acute injury. Anesthesiology 1991, 74:934–936.
Wallace MS, Dyck JB, Rossi SS, Yaksh TL: Computer-controlled lidocaine infusion for the evaluation of neuropathic pain after peripheral nerve injury. Pain 1996, 66:69–77.
Wallace MS, Ridgeway BM, Leung AY, et al.: Concentration-effect relationship of intravenous lidocaine on the allodynia of complex regional pain syndrome types I and II. Anesthesiology 2000, 92:75–83.
Attal N, Gaude V, Brasseur L, et al.: Intravenous lidocaine in central pain: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, psychophysical study. Neurology 2000, 54:564–574.
Backonja M: Anticonvulsants and antiarrythmics in the treatment of neuropathic pain syndromes. In Neuropathic Pain: Pathophysiology and Treatment. Edited by Hansson PT, Fields HL, Hill RG, Marchettini P. Seattle: IASP Press; 2001:185–202.
Dworkin RH, Corbin AE, Young JP Jr, et al.: Pregabalin for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia: a randomized, placebocontrolled trial. Neurology 2003, 60:1274–1283.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Backonja, M. Neuromodulating drugs for the symptomatic treatment of neuropathic pain. Current Science Inc 8, 212–216 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-004-0054-4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-004-0054-4