Abstract
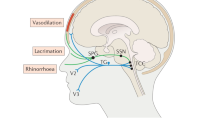
The cerebral circulation is innervated by sympathetic, parasympathetic, and sensory nerves, which store a considerable number of neurotransmitters. The role of these has been evaluated in primary headaches. A clear association between head pain and the release of calcitonin gene-related peptide was demonstrated. In cluster headache and in a case of chronic paroxysmal headache there was in addition the release of vasoactive intestinal peptide, which was associated with the facial symptoms (nasal congestion, rhinorrhea). In parallel with sumatriptan treatment, head pain subsided and neuropeptide release normalized. These data show the involvement of sensory and parasympathetic mechanisms in the pathophysiology of primary headaches.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Willis T, ed: Cerebri Anatome. London: Martin Allestry; 1664.
Liveing E, ed: On Migraine, Sick-Headache, and Some Allied Disorders: A Contribution To the Pathology of Nerve Storms. London: Churchill; 1873:1–512.
Ray BS, Wolff HG: Experimental studies on headaches, pain sensitive structures of the head and their significance in headaches. Arch Surg 1940, 41:813–856.
Radner S: Intracranial angiography via the vertebral artery. Acta Radiol 1947, 28:838–843.
Hauge T: Catheter vertebral angiography. Acta Radiol 1954, 109:1–219.
Olesen J, Iversen HK, Thomsen LL: Nitric oxide supersensitivity. A possible molecular mechanisms of migraine pain. Neuroreport 1993, 4:1027–1030.
Fanciullacci M, Alessandri M, Figini M, et al.: Increases in plasma calcitonin gene-related peptide from extracerebral circulation during nitroglycerin-induced cluster attack. Pain 1995, 60:119–123.
Edvinsson L, Owman C, Sjöberg N-O: Autonomic nerves, mast cells and amine receptors in human brain vessles. A histochemical and pharmacological study. Brain Res 1976, 115:337–393.
Edvinsson L, MacKenzie ET, McCulloch J, eds: Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism. New York: Raven Press; 1993:1–683.
Goadsby PJ, Zagami AS: Stimulation of the superior sagittal sinus increases metabolic activity and blood flow in certain regions of the brainstem and upper cervical spinal cord of the cat. Brain 1991, 114:1001–1004.
McCulloch J, Uddman R, Kingman TA, Edvinsson L: Calcitonin gene-related peptide. Functional role in cerebrovascular regulation. Proc Nat Acad Sci U S A 1986, 83:5731–5735.
Edvinsson L, McCulloch J, Kingman TA, Uddman R: On the functional role of the trigemino-cerebrovascular system in the regulation of cerebral circulation. In Neural Regulations of the Cerebral Circulation. Edited by Owman C, Hardebo JE. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 1986:407–418.
Goadsby PJ, Lambert GA, Lance JW: Stimulation of the trigeminal ganglion increases flow in the extra cerebral but not the cerebral circulation of the monkey. Brain Res 1986, 381:63–67.
Tran-Dinh YR, Thurei C, Cunin G, et al.: Cerebral vasodilation after the thermocoagulation of the trigeminal ganglion in humans. Neurosurgery 1992, 31:658–662.
Goadsby PJ, Edvinsson L, Ekman R: Vasoactive peptide release in the extracerebral circulation of human during migraine headache. Ann Neurol 1990, 28:183–197.
Edvinsson L, Hara H, Uddman R: Retrograde tracing of nerve fibers to the rat middle cerebral artery with True Blue: localization with different peptides. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1989, 9:212–218.
Gallai V, Sarchielli P, Floridi A, et al.: Vasoactive peptide levels in the plasma of young migraine patients with and without aura assessed both interictally and ictally. Cephalalgia 1995, 15:384–390.
Goadsby PJ, Edvinsson L: The trigeminovascular system and migraine: studies characterizing cerebrovascular and neuropeptide changes seen in humans and cats. Ann Neurol 1993, 33:48–56.
Goadsby PJ, Edvinsson L: Human in vivo evidence for trigeminovascular activation in cluster headache. Neuropeptide changes and effects of acute attacks therapies. Brain 1994, 117:427–434.
Goadsby PJ, Edvinsson L, Ekman R: Release of vasoactive peptides in the extracerebral circulation of humans and the cat during activation of the trigeminovascular system. Ann Neurol 1988, 23:193–196.
Goadsby PJ, Edvinsson L, Ekman R: Cutaneous sensory stimulation leading to facial flushing and release of calcitonin gene-related peptide. Cephalalgia 1992, 12:53–56.
Goadsby PJ, Edvinsson L: Neuropeptide changes in a case of chronic paroxysmal hemicrania: evidence for trigeminoparasympathetic activation. Cephalalgia 1996, 16:448–450.
Goadsby PJ, Edvinsson L: Peripheral and central trigeminovascular activation in cat is blocked by the serotonin (HT)-ID receptor agonist 311C90. Headache 1994, 34:394–399.
Martin GR: Pre-clinical pharmacology of zolmitriptan (Zomig; formerly 311C90), a centrally and peripherally acting 5-HT 1B/1D agonist for migraine. Cephalalgia 1997, 17(suppl 18):4–14.
Ophoff RA, Terwindt GM, Vergouve MN, et al.: Familial hemiplegic migraine and episodic ataxia type 2 are caused by mutation in the Ca2+ channel gene CACNL1A4. Cell 1996, 87:543–552.
Weiller C, May A, Limmroth V, et al.: Brain stem activation in spontaneous human migraine attacks. Nat Med 1995, 1:658–660.
Olesen J, Friberg L, Skyhöj OT: Timing and topography of cerebral blood flow, aura and headache during migraine attacks. Ann Neurol 1990, 28:791–798.
Woods RP, Iacoboni M, Mazziotta JC: Bilateral spreading cerebral hypoperfusion during spontaneous migraine headache. New Engl J Med 1994, 31:1689–1692.
Edvinsson L, Degueurce A, Duverger D, et al.: Central serotonergic nerves project to the pial vessels of the brain. Nature 1983, 306:55–57.
Reinhard JF Jr, Liebmann JR, Schlosberg AJ, Moskowits MA: Serotonin neurons project to small blood vessels in the brain. Science 1979, 206:85–87.
Lauritzen M: Pathophysiology of migraine aura: the spreading depression theory. Brain 1994, 117:199–210.
May A, Bahra A, Büchel C, et al.: Hypothalamic activation in cluster headache attacks. Lancet 1998, 351:275–278. Recent demonstration that in cluster headache there is activation of the hypothalamic center, putatively linked with symptomatology.
May A, Kaube H, Buechel C, et al.: Experimental cranial pain elicited by capsaicin: a PET study. Pain 1998, 74:61–66.
Edvinsson L, Goadsby PJ: Neuropeptides in headache. Eur J Neurol 1998, 5:329–341. A convenient review providing a wealth of information of the neuropeptides in headache.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Edvinsson, L. Pathophysiology of primary headaches. Current Science Inc 5, 71–78 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-001-0013-2
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-001-0013-2