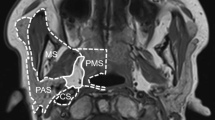
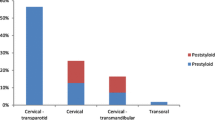
Abstract
Purpose of Review
Management of parapharyngeal tumors is challenging due to the complex anatomic nature of the space and the wide range of pathologies encountered. This article will review the anatomy, common pathologies, and management of parapharyngeal masses. Surgical strategies are also reviewed.
Recent Findings
Masses of the parapharyngeal space are most commonly benign (80%). More recent longitudinal studies have shown that observation and non-surgical therapy are indicated in many cases. When surgery is indicated, innovative endoscopic and robotic-assisted techniques allow for improved visualization and complete tumor removal while avoiding significant blood loss, tumor spillage, and injury to surrounding nerves and vessels.
Summary
Management of parapharyngeal masses should consider morbidity of surgical resection versus the natural course of the disease. Surgical strategy is determined by location, size, and pathology. Adequate access is needed surgically to ensure complete resection and avoid tumor rupture.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Locketz GD, et al. Histopathologic classification of parapharyngeal space tumors: a case series and review of the literature. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;273(3):727–34.
Sun F, et al. Surgical management of primary parapharyngeal space tumors in 103 patients at a single institution. Acta Otolaryngol. 2018;138(1):85–9.
Colen TY, et al. Catecholamine-secreting paragangliomas: recent progress in diagnosis and perioperative management. Skull Base. 2009;19(6):377–85.
Jansen JC, et al. Estimation of growth rate in patients with head and neck paragangliomas influences the treatment proposal. Cancer. 2000;88(12):2811–6.
Mendenhall WM, et al. Head and neck paragangliomas. Head Neck. 2011;33(10):1530–4.
Sato Y, et al. Clinical diagnosis and treatment outcomes for parapharyngeal space schwannomas: a single-institution review of 21 cases. Head Neck. 2018;40(3):569–76.
Riffat F, et al. A systematic review of 1143 parapharyngeal space tumors reported over 20 years. Oral Oncol. 2014;50(5):421–30.
Gupta A, Chazen JL, Phillips CD. Imaging evaluation of the parapharyngeal space. Otolaryngol Clin N Am. 2012;45(6):1223–32.
Saito DM, et al. Parapharyngeal space schwannomas: preoperative imaging determination of the nerve of origin. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007;133(7):662–7.
Stambuk HE, Patel SG. Imaging of the parapharyngeal space. Otolaryngol Clin N Am. 2008;41(1):77–101.
Iglesias-Moreno MC, et al. Parapharyngeal space tumors: fifty-one cases managed in a single tertiary care center. Acta Otolaryngol. 2016;136(3):298–303.
Oliai BR, et al. "Parapharyngeal space" tumors: a cytopathological study of 24 cases on fine-needle aspiration. Diagn Cytopathol. 2005;32(1):11–5.
Bradley PJ, Bradley PT, Olsen KD. Update on the management of parapharyngeal tumours. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011;19(2):92–8.
•• Moore MG, et al. Head and neck paragangliomas: an update on evaluation and management. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016;154(4):597–605. This article is a review of the contemporary published literature on the management of head and neck paragangliomas, which are commonly encountered in the parapharyngeal space. Traditionally, management of paraganglioms invovled surgical removal. However, as this review highlights, more recently, the literature supports that up-front non-surgical management is often appropriate for paragangliomas of the head and neck. The authors offer recommendations on instances when surgery should be considered.
Carlson ML, et al. Natural history of glomus jugulare: a review of 16 tumors managed with primary observation. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015;152(1):98–105.
Eisele DW, Richmon JD. Contemporary evaluation and management of parapharyngeal space neoplasms. J Laryngol Otol. 2013;127(6):550–5.
Mendenhall WM, et al. Radiotherapy for parapharyngeal space tumors. Am J Otolaryngol. 2019;40(2):289–91.
Cohen SM, Burkey BB, Netterville JL. Surgical management of parapharyngeal space masses. Head Neck. 2005;27(8):669–75.
Carrau RL, Myers EN, Johnson JT. Management of tumors arising in the parapharyngeal space. Laryngoscope. 1990;100(6):583–9.
Carrau RL, Johnson JT, Myers EN. Management of tumors of the parapharyngeal space. Oncology (Williston Park). 1997;11(5):633–40 discussion 640, 642.
Bozza F, et al. Surgical management of parapharyngeal space tumours: results of 10-year follow-up. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2009;29(1):10–5.
Hussain A, Ah-See KW, Shakeel M. Trans-oral resection of large parapharyngeal space tumours. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2014;271(3):575–82.
Dimitrijevic MV, et al. Parapharyngeal space tumors: 61 case reviews. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;39(10):983–9.
Ducic Y, Oxford L, Pontius AT. Transoral approach to the superomedial parapharyngeal space. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006;134(3):466–70.
Betka J, et al. Transoral and combined transoral-transcervical approach in the surgery of parapharyngeal tumors. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2010;267(5):765–72.
Chan JY, et al. Transoral robotic surgery of the parapharyngeal space: a case series and systematic review. Head Neck. 2015;37(2):293–8.
Panda S, et al., Transoral robotic surgery for the parapharyngeal space: expanding the transoral corridor. J Robot Surg, 2019.
Meng LZ, et al. Early experience in endoscopic transoral resection for parapharyngeal space tumors. Ear Nose Throat J. 2018;97(4–5):E5–e9.
Mendelsohn AH. Transoral robotic assisted resection of the parapharyngeal space. Head Neck. 2015;37(2):273–80.
Markou K, et al. Transoral resection of giant parapharyngeal space tumors via a combined surgical approach. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2019;31(103):87–96.
Basaran B, et al. Parapharyngeal space tumours: the efficiency of a transcervical approach without mandibulotomy through review of 44 cases. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2014;34(5):310–6.
Ijichi K, Murakami S. Surgical treatment of parapharyngeal space tumors: a report of 29 cases. Oncol Lett. 2017;14(3):3249–54.
Singh M, Gupta SC, Singla A. Our experiences with parapharyngeal space tumors and systematic review of the literature. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009;61(2):112–9.
Kuet ML, et al. Management of tumors arising from the parapharyngeal space: a systematic review of 1,293 cases reported over 25 years. Laryngoscope. 2015;125(6):1372–81.
Pradhan P, et al. Surgical management of parapharyngeal space tumours in a single tertiary care center. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018;70(4):531–7.
van Hees T, et al. Tumors of the parapharyngeal space: the VU University medical center experience over a 20-year period. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2018;275(4):967–72.
•• Ferrari M, et al. Surgical anatomy of the parapharyngeal space: multiperspective, quantification-based study. Head Neck. 2019;41(3):642–56. This anatomic study of human cadavers compares the main surgical approaches to the parapharyngeal space. This provides a comprehensive review of the objective strengths and limitations of each approach, with detailed human cadaver pictures. This study can be helpful in facilitating preoperative planning for the head and neck surgeon.
Shahinian H, Dornier C, Fisch U. Parapharyngeal space tumors: the infratemporal fossa approach. Skull Base Surg. 1995;5(2):73–81.
Poletti AM, et al. Surgical management of parapharyngeal space tumors: the role of cervical and lateral skull base approaches. Ear Nose Throat J. 2016;95(12):E1–e6.
Jungehuelsing M, et al. Modifications of the midline mandibulotomy for access to the parapharyngeal space. Laryngoscope. 2010;120(8):1557–62.
Kolokythas A, et al. Mandibular osteotomies for access to select parapharyngeal space neoplasms. Head Neck. 2009;31(1):102–10.
Benet A, Plata Bello J, El-Sayed I. Combined endonasal-transcervical approach to a metastatic parapharyngeal space papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cureus. 2015;7(7):e285.
• Duek I, et al. Minimally invasive surgery for resection of parapharyngeal space tumors. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2018;79(3):250–6. This article reviews 11 patients who underwent surgery for parapharyngeal space masses using a transcervical endoscopic, transoral robotic, or combined endoscopic-robotic approach. This study provides a thorough explanation of how the new technologies (endoscopes and robot) result in improved visualizaation, safe vascular control, and complete tumor removal without spillage.
Pilolli F, et al. Parapharyngeal space tumours: video-assisted minimally invasive transcervical approach. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2016;36(4):259–64.
Li SY, Hsu CH, Chen MK. Minimally invasive endoscope-assisted trans-oral excision of huge parapharyngeal space tumors. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2015;42(2):179–82.
Chen Z, et al. Excision of tumors in the parapharyngeal space using an endoscopically assisted transoral approach: a case series and literature review. J Int Med Res. 2019;47(3):1103–13.
Dallan I, et al. Endoscopic-assisted transoral-transpharyngeal approach to parapharyngeal space and infratemporal fossa: focus on feasibility and lessons learned. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;273(11):3965–72.
Sun X, et al. A comparative analysis of endoscopic-assisted transoral and transnasal approaches to Parapharyngeal space: a cadaveric study. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2018;79(3):229–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Head and Neck Cancers
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strohl, M.P., El-Sayed, I.H. Contemporary Management of Parapharyngeal Tumors. Curr Oncol Rep 21, 103 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-019-0853-8
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-019-0853-8