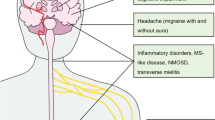
Abstract
Purpose of Review
Understanding of antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS), associated neurological manifestations, and disease-directed treatment has grown considerably over the last decade. Herein, we critically review the current and high-yield literature related to the pathophysiology, neurological presentations, and management of APS with particular emphasis on the rare and more fatal subset of APS, catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome (CAPS).
Recent Findings
APS may manifest with a variety of neurologic syndromes, with cerebrovascular disease representing the most commonly encountered presentation. Diagnostic evaluation and treatment are often tailored to the specific presentation, with suspicion and testing for antiphospholipid antibodies recommended when neurologic presentations occur atypically or in younger individuals. In CAPS, which is more rapidly progressive with multiorgan involvement, potential alternative microangiopathic syndromes should be carefully considered in the differential diagnosis. To date, anticoagulation with vitamin K antagonists remains the mainstay of therapy in APS while triple therapy with anticoagulation, corticosteroids, and plasma exchange is standard of care in CAPS. Immunotherapy has shown early promise in refractory cases.
Summary
APS is an autoimmune clinical syndrome with neurologic presentations classically characterized by vascular thrombosis, though recent understandings suggest additional direct immune-mediated phenomena. Our understanding of the underlying pathogenic mechanisms of APS continues to grow and will continue to influence our therapeutic approaches.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AIS:
-
Acute ischemic stroke
- APS:
-
Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome
- aPL:
-
Antiphospholipid antibodies
- CAPS:
-
Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CSF:
-
Cerebrospinal fluid
- CVT:
-
Cerebral venous thrombosis
- DOAC:
-
Direct oral anticoagulant
- EEG:
-
Electroencephalogram
- ICH:
-
Intracerebral hemorrhage
- INR:
-
International normalized ratio
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- MS:
-
Multiple sclerosis
- NAION:
-
Non-arteritic ischemic optic neuropathy
- NMOSD:
-
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders
- SAH:
-
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
- SLE:
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus
- TIA:
-
Transient ischemic attack
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
• Sciascia S, Radin M, Cecchi I, Levy RA, Erkan D. 16th International congress on antiphospholipid antibodies task force report on clinical manifestations of antiphospholipid syndrome. Lupus. 2021;30(8):1314–26. https://doi.org/10.1177/09612033211020361. Most recent guideline report on clinical manifestations of APS from the 16thth International congress on antiphospholipid antibodies task force.
Xourgia E, Tektonidou MG. An update on antiphospholipid syndrome. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2022;23(12):84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-021-01051-5.
Duarte-Garcia A, Pham MM, Crowson CS, Amin S, Moder KG, Pruthi RK, et al. The epidemiology of antiphospholipid syndrome: a population-based study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(9):1545–52. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.40901.
Radin M, Sciascia S, Bazzan M, Bertero T, Carignola R, Montabone E, et al. Antiphospholipid syndrome is still a rare disease-estimated prevalence in the Piedmont and Aosta Valley Regions of Northwest Italy: comment on the article by Duarte-Garcia et al. Rheumatol. 2020;72(10):1774–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.41401.
Miyakis S, Lockshin MD, Atsumi T, Branch DW, Brey RL, Cervera R, et al. International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4(2):295–306. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2006.01753.x.
Rato IR, Barbosa AR, Afonso DJ, Beca S. Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome presented as ruptured papillary muscle during puerperium in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2021;30(6):1017–21. https://doi.org/10.1177/09612033211002273.
•• Asherson RA, Cervera R. Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2003;5(5):395–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-003-0031-7. Seminal description of CAPS and proposed preliminary classification criteria.
Asherson RA, Cervera R. The antiphospholipid syndrome: multiple faces beyond the classical presentation. Autoimmun Rev. 2003;2(3):140–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1568-9972(02)00147-7.
Asherson RA, Cervera R, de Groot PG, Erkan D, Boffa MC, Piette JC, et al. Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome: international consensus statement on classification criteria and treatment guidelines. Lupus. 2003;12(7):530–4. https://doi.org/10.1191/0961203303lu394oa.
Erkan D, Cervera R, Asherson RA. Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome: where do we stand? Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(12):3320–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.11359.
•• Cervera R, Rodriguez-Pinto I, Legault K, Erkan D. 16th International Congress on Antiphospholipid Antibodies Task Force Report on Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Lupus. 2020;29(12):1594–600. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203320951260. Most recent guideline report on CAPS from the 16thth International congress on antiphospholipid antibodies task force.
Cervera R, Rodriguez-Pinto I, Espinosa G. The diagnosis and clinical management of the catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome: a comprehensive review. J Autoimmun. 2018;92:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2018.05.007.
Lim W. Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2009:233–9. https://doi.org/10.1182/asheducation-2009.1.233
Ricarte IF, Dutra LA, Abrantes FF, Toso FF, Barsottini OGP, Silva GS, et al. Neurologic manifestations of antiphospholipid syndrome. Lupus. 2018;27(9):1404–14. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203318776110.
Man YL, Sanna G. Neuropsychiatric manifestations of antiphospholipid syndrome-a narrative review. Brain Sci. 2022;12(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12010091
Arnson Y, Shoenfeld Y, Alon E, Amital H. The antiphospholipid syndrome as a neurological disease. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2010;40(2):97–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2009.05.001.
• Cervera R, Piette JC, Font J, Khamashta MA, Shoenfeld Y, Camps MT, et al. Antiphospholipid syndrome: clinical and immunologic manifestations and patterns of disease expression in a cohort of 1,000 patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46(4):1019–27. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.10187. The Euro-Phospholipid Project Group Study highlighting 1000 patients with APS and detailed prevalence of various neurologic and non-neurologic clinical manifestations.
Cervera R, Serrano R, Pons-Estel GJ, Ceberio-Hualde L, Shoenfeld Y, de Ramon E, et al. Morbidity and mortality in the antiphospholipid syndrome during a 10-year period: a multicentre prospective study of 1000 patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(6):1011–8. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204838.
• Garcia-Grimshaw M, Posadas-Pinto DR, Jimenez-Ruiz A, Valdes-Ferrer SI, Cadena-Fernandez A, Torres-Ruiz JJ, et al. Antiphospholipid syndrome-mediated acute cerebrovascular diseases and long-term outcomes. Lupus. 2022;31(2):228–37. https://doi.org/10.1177/09612033221074178. A recent retrospective cohort study describing the spectrum of cerebrovascular disease among patients with APS.
Valdes-Ferrer SI, Vega F, Cantu-Brito C, Ceballos-Ceballos J, Estanol B, Garcia-Ramos G, et al. Cerebral changes in SLE with or without antiphospholipid syndrome a case-control MRI study. J Neuroimaging. 2008;18(1):62–5. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1552-6569.2007.00183.x.
Fleetwood T, Cantello R, Comi C. Antiphospholipid syndrome and the neurologist: from pathogenesis to therapy. Front Neurol. 2018;9:1001. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2018.01001.
Rodrigues CE, Carvalho JF, Shoenfeld Y. Neurological manifestations of antiphospholipid syndrome. Eur J Clin Invest. 2010;40(4):350–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2362.2010.02263.x.
Hughes GR. Migraine, memory loss, and “multiple sclerosis” Neurological features of the antiphospholipid (Hughes’) syndrome. Postgrad Med J. 2003;79(928):81–3. https://doi.org/10.1136/pmj.79.928.81.
Sciascia S, Sanna G, Khamashta MA, Cuadrado MJ, Erkan D, Andreoli L, et al. The estimated frequency of antiphospholipid antibodies in young adults with cerebrovascular events: a systematic review. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(11):2028–33. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205663.
Provenzale JM, Barboriak DP, Allen NB, Ortel TL. Patients with antiphospholipid antibodies: CT and MR findings of the brain. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996;167(6):1573–8. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.167.6.8956600.
de Amorim LC, Maia FM, Rodrigues CE. Stroke in systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome: risk factors, clinical manifestations, neuroimaging, and treatment. Lupus. 2017;26(5):529–36. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203316688784.
Silvis SM, de Sousa DA, Ferro JM, Coutinho JM. Cerebral venous thrombosis. Nat Rev Neurol. 2017;13(9):555–65. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2017.104.
Burch R, Rizzoli P, Loder E. The prevalence and impact of migraine and severe headache in the United States: updated age, sex, and socioeconomic-specific estimates from government health surveys. Headache. 2021;61(1):60–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/head.14024.
Cavestro C, Micca G, Molinari F, Bazzan M, DIP C, Aloi R, et al. Migraineurs show a high prevalence of antiphospholipid antibodies. J Thromb Haemost. 2011;9(7):1350–4. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2011.04348.x.
Cavestro C, Degan D, Micca G, Aloi R, Mandrino S, Frigeri MC, et al. Thrombophilic alterations, migraine, and vascular disease: results from a case-control study. Neurol Sci. 2021;42(9):3821–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-05006-z.
Schofield JR, Hughes HN, Birlea M, Hassell KL. A trial of antithrombotic therapy in patients with refractory migraine and antiphospholipid antibodies: a retrospective study of 75 patients. Lupus. 2021;30(4):568–77. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203320983913.
de Carvalho JF, Pasoto SG, Appenzeller S. Seizures in primary antiphospholipid syndrome: the relevance of smoking to stroke. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012;2012: 981519. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/981519.
Shoenfeld Y, Lev S, Blatt I, Blank M, Font J, von Landenberg P, et al. Features associated with epilepsy in the antiphospholipid syndrome. J Rheumatol. 2004;31(7):1344–8.
Noureldine MH, Harifi G, Berjawi A, Haydar AA, Nader M, Elnawar R, et al. Hughes syndrome and epilepsy: when to test for antiphospholipid antibodies? Lupus. 2016;25(13):1397–411. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203316651747.
Cimaz R, Guerrini R. Epilepsy in lupus. Lupus. 2008;17(9):777–9. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203308094362.
Rosati A, Guerrini R, Cimaz R. Lupus, antiphospholipid syndrome and epilepsy: an update. Lupus. 2017;26(1):3–5. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203316666961.
Yelnik CM, Kozora E, Appenzeller S. Non-stroke central neurologic manifestations in antiphospholipid syndrome. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2016;18(2):11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-016-0568-x.
Brey RL, Muscal E, Chapman J. Antiphospholipid antibodies and the brain: a consensus report. Lupus. 2011;20(2):153–7. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203310396748.
Cervera R, Boffa MC, Khamashta MA, Hughes GR. The Euro-Phospholipid project: epidemiology of the antiphospholipid syndrome in Europe. Lupus. 2009;18(10):889–93. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203309106832.
Chapman J, Abu-Katash M, Inzelberg R, Yust I, Neufeld MY, Vardinon N, et al. Prevalence and clinical features of dementia associated with the antiphospholipid syndrome and circulating anticoagulants. J Neurol Sci. 2002;203–204:81–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-510x(02)00271-x.
Tektonidou MG, Varsou N, Kotoulas G, Antoniou A, Moutsopoulos HM. Cognitive deficits in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome: association with clinical, laboratory, and brain magnetic resonance imaging findings. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166(20):2278–84. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.166.20.2278.
Appenzeller S, Lapa AT, Guirau CR, de Carvalho JF, Shoenfeld Y. Cognitive impairment in antiphospholipid syndrome: evidence from animal models. Clin Rheumatol. 2012;31(3):403–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-011-1922-z.
Fernandez-Fernandez FJ, Rivera-Gallego A, de la Fuente-Aguado J, Perez-Fernandez S, Munoz-Fernandez D. Antiphospholipid syndrome mimicking multiple sclerosis in two patients. Eur J Intern Med. 2006;17(7):500–2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2006.02.018.
Mayer M, Cerovec M, Rados M, Cikes N. Antiphospholipid syndrome and central nervous system. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2010;112(7):602–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2010.03.023.
Ij JW, Conti-Kelly AM, Greco P, Abedi M, Amos M, Provenzale JM, et al. Anti-phospholipid antibodies in patients with multiple sclerosis and MS-like illnesses MS or APS? Lupus. 1999;8(2):109–15. https://doi.org/10.1191/096120399678847461.
Collard RC, Koehler RP, Mattson DH. Frequency and significance of antinuclear antibodies in multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 1997;49(3):857–61. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.49.3.857.
Ferreira S, D’Cruz DP, Hughes GR. Multiple sclerosis, neuropsychiatric lupus and antiphospholipid syndrome: where do we stand? Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005;44(4):434–42. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keh532.
Sherer Y, Hassin S, Shoenfeld Y, Levy Y, Livneh A, Ohry A, et al. Transverse myelitis in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies–the importance of early diagnosis and treatment. Clin Rheumatol. 2002;21(3):207–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-002-8287-2.
Lennon VA, Wingerchuk DM, Kryzer TJ, Pittock SJ, Lucchinetti CF, Fujihara K, et al. A serum autoantibody marker of neuromyelitis optica: distinction from multiple sclerosis. Lancet. 2004;364(9451):2106–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(04)17551-X.
Wingerchuk DM, Weinshenker BG. Neuromyelitis optica (Devic’s syndrome). Handb Clin Neurol. 2014;122:581–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-52001-2.00025-X.
Lee EJ, Lim YM, Kim SY, Lee J, Kim H, Jin JY, et al. The clinical and prognostic value of antinuclear antibodies in NMO-IgG seropositive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. J Neuroimmunol. 2019;328:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2018.11.012.
Long Y, He Y, Zheng Y, Chen M, Zhang B, Gao C. Serum anticardiolipin antibodies in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. J Neurol. 2013;260(12):3150–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-013-7128-3.
Iyer A, Elsone L, Appleton R, Jacob A. A review of the current literature and a guide to the early diagnosis of autoimmune disorders associated with neuromyelitis optica. Autoimmunity. 2014;47(3):154–61. https://doi.org/10.3109/08916934.2014.883501.
Martino D, Chew NK, Mir P, Edwards MJ, Quinn NP, Bhatia KP. Atypical movement disorders in antiphospholipid syndrome. Mov Disord. 2006;21(7):944–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.20842.
Orzechowski NM, Wolanskyj AP, Ahlskog JE, Kumar N, Moder KG. Antiphospholipid antibody-associated chorea. J Rheumatol. 2008;35(11):2165–70. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.080268.
Reitblat T, Polishchuk I, Dorodnikov E, Aladjem Z, Turiansky L, Zamir D, et al. Primary antiphospholipid antibody syndrome masquerading as progressive supranuclear palsy. Lupus. 2003;12(1):67–9. https://doi.org/10.1191/0961203303lu242CR.
Huang YC, Lyu RK, Chen ST, Chu YC, Wu YR. Parkinsonism in a patient with antiphospholipid syndrome–case report and literature review. J Neurol Sci. 2008;267(1–2):166–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2007.10.003.
Appenzeller S, Yeh S, Maruyama M, Barros SM, de Carvalho JF. Chorea in primary antiphospholipid syndrome is associated with rheumatic fever. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(9):2857–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-011-2120-7.
Peluso S, Antenora A, De Rosa A, Roca A, Maddaluno G, Brescia Morra V, et al. Antiphospholipid-related chorea Front Neurol. 2012;3:150. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2012.00150.
Cervera R, Asherson RA, Font J, Tikly M, Pallares L, Chamorro A, et al. Chorea in the antiphospholipid syndrome Clinical, radiologic, and immunologic characteristics of 50 patients from our clinics and the recent literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 1997;76(3):203–12. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005792-199705000-00006.
Safarpour D, Buckingham S, Jabbari B. Chorea associated with high titers of antiphospholipid antibodies in the absence of antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. Tremor Other Hyperkinet Mov (N Y). 2015;5:294. https://doi.org/10.7916/D8DB80M9.
Sanna G, D’Cruz D, Cuadrado MJ. Cerebral manifestations in the antiphospholipid (Hughes) syndrome. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2006;32(3):465–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rdc.2006.05.010.
Suvajac G, Stojanovich L, Milenkovich S. Ocular manifestations in antiphospholipid syndrome. Autoimmun Rev. 2007;6(6):409–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2006.11.005.
Giorgi D, Gabrieli CB, Bonomo L. The clinico-ophthalmological spectrum of antiphospholipid syndrome. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 1998;6(4):269–73. https://doi.org/10.1076/ocii.6.4.269.4025.
Vaphiades MS, Brock W, Brown HH, Petursson G, Westfall CT. Catastrophic antiphospholipid antibody syndrome manifesting as an orbital ischemic syndrome. J Neuroophthalmol. 2001;21(4):260–3. https://doi.org/10.1097/00041327-200112000-00006.
Santos MS, de Carvalho JF, Brotto M, Bonfa E, Rocha FA. Peripheral neuropathy in patients with primary antiphospholipid (Hughes’) syndrome. Lupus. 2010;19(5):583–90. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203309354541.
Jeruc J, Popovic M, Vizjak A, Jurcic V, Lestan B, Ferluga D. Multiple mononeuropathy due to vasculitis associated with anticardiolipin antibodies: a case report. Folia Neuropathol. 2006;44(2):140–3.
Sanna G, Bertolaccini ML, Cuadrado MJ, Khamashta MA, Hughes GR. Central nervous system involvement in the antiphospholipid (Hughes) syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003;42(2):200–13. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keg080.
Gilburd B, Stein M, Tomer Y, Tanne D, Abramski O, Chapman Y, et al. Autoantibodies to phospholipids and brain extract in patients with the Guillain-Barre syndrome: cross-reactive or pathogenic? Autoimmunity. 1993;16(1):23–7. https://doi.org/10.3109/08916939309010644.
Schofield JR. Autonomic neuropathy-in its many guises-as the initial manifestation of the antiphospholipid syndrome. Immunol Res. 2017;65(2):532–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-016-8889-4.
George JN, Nester CM. Syndromes of thrombotic microangiopathy. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(19):1847–8. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc1410951.
Bayraktar UD, Erkan D, Bucciarelli S, Espinosa G, Asherson R, Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome Project Group. The clinical spectrum of catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome in the absence and presence of lupus. J Rheumatol. 2007;34(2):346–52.
Chaturvedi S, Braunstein EM, Yuan X, Yu J, Alexander A, Chen H, et al. Complement activity and complement regulatory gene mutations are associated with thrombosis in APS and CAPS. Blood. 2020;135(4):239–51. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2019003863.
Chaturvedi S, Brodsky RA, McCrae KR. Complement in the pathophysiology of the antiphospholipid syndrome. Front Immunol. 2019;10:449. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00449.
Provenzale JM, Heinz ER, Ortel TL, Macik BG, Charles LA, Alberts MJ. Antiphospholipid antibodies in patients without systemic lupus erythematosus: neuroradiologic findings. Radiology. 1994;192(2):531–7. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.192.2.8029427.
Rovaris M, Pedroso C, Filippi M. Neuroimaging techniques in the diagnostic work-up of patients with the antiphospholipid syndrome. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2001;3(4):301–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-001-0034-1.
Kim JH, Choi CG, Choi SJ, Lee HK, Suh DC. Primary antiphospholipid antibody syndrome: neuroradiologic findings in 11 patients. Korean J Radiol. 2000;1(1):5–10. https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2000.1.1.5.
Hachulla E, Michon-Pasturel U, Leys D, Pruvo JP, Queyrel V, Masy E, et al. Cerebral magnetic resonance imaging in patients with or without antiphospholipid antibodies. Lupus. 1998;7(2):124–31. https://doi.org/10.1191/096120398678919868.
Pereira FR, Macri F, Jackowski MP, Kostis WJ, Gris JC, Beregi JP, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging in patients with obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome without neuropsychiatric symptoms. Eur Radiol. 2016;26(4):959–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-015-3922-x.
Garcia D, Erkan D. Diagnosis and management of the antiphospholipid syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(13):1290. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc1808253.
Arnaud L, Mathian A, Ruffatti A, Erkan D, Tektonidou M, Cervera R, et al. Efficacy of aspirin for the primary prevention of thrombosis in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies: an international and collaborative meta-analysis. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13(3):281–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2013.10.014.
• Tektonidou MG, Andreoli L, Limper M, Amoura Z, Cervera R, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of antiphospholipid syndrome in adults. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(10):1296–304. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215213. The most recent European League Against Rheumatism guidelines regarding the management of APS.
•• Cohen H, Cuadrado MJ, Erkan D, Duarte-Garcia A, Isenberg DA, Knight JS, et al. 16th International Congress on Antiphospholipid Antibodies Task Force report on antiphospholipid syndrome treatment trends. Lupus. 2020;29(12):1571–93. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203320950461. The most recent guidelines from the 16thth International Congress on Antiphospholipid Antibodies Task Force regarding recent treatment trends in APS.
• Cohen H, Hunt BJ, Efthymiou M, Arachchillage DR, Mackie IJ, Clawson S, et al. Rivaroxaban versus warfarin to treat patients with thrombotic antiphospholipid syndrome, with or without systemic lupus erythematosus (RAPS): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 2/3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Haematol. 2016;3(9):e426–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2352-3026(16)30079-5. A randomized controlled, open-label, non-inferiority trial that failed to show non-inferiority of rivaroxaban compared with warfarin.
• Pengo V, Denas G, Zoppellaro G, Jose SP, Hoxha A, Ruffatti A, et al. Rivaroxaban vs warfarin in high-risk patients with antiphospholipid syndrome. Blood. 2018;132(13):1365–71. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2018-04-848333. Another trial that failed to show the benefit of rivaroxaban compared with warfarin, and instead increased risk.
Bala MM, Celinska-Lowenhoff M, Szot W, Padjas A, Kaczmarczyk M, Swierz MJ, et al. Antiplatelet and anticoagulant agents for secondary prevention of stroke and other thromboembolic events in people with antiphospholipid syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020;10:CD012169. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD012169.pub3.
• Woller SC, Stevens SM, Kaplan D, Wang TF, Branch DW, Groat D, et al. Apixaban compared with warfarin to prevent thrombosis in thrombotic antiphospholipid syndrome: a randomized trial. Blood Adv. 2022;6(6):1661–70. https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2021005808. A recent multicenter prospective, randomized open-label study comparing apixaban to warfarin that ended prematurely due to protocol modifications and low patient accrual. Nonetheless, preliminary results failed to show the benefit of apixaban compared to warfarin.
Woller SC, Stevens SM, Kaplan DA, Branch DW, Aston VT, Wilson EL, et al. Apixaban for the secondary prevention of thrombosis among patients with antiphospholipid syndrome: study rationale and design (ASTRO-APS). Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2016;22(3):239–47. https://doi.org/10.1177/1076029615615960.
• Ordi-Ros J, Saez-Comet L, Perez-Conesa M, Vidal X, Riera-Mestre A, Castro-Salomo A, et al. Rivaroxaban versus vitamin K antagonist in antiphospholipid syndrome: a randomized noninferiority trial. Ann Intern Med. 2019;171(10):685–94. https://doi.org/10.7326/M19-0291. A recent open-label, randomized non-inferiority trial that failed to show non-inferiority of rivaroxaban to vitamin K antagonists and in fact showed a non-statistically significant near doubling of the risk for recurrent thrombosis.
Julkunen H, Hedman C, Kauppi M. Thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke in the primary antiphospholipid syndrome. J Rheumatol. 1997;24(1):181–3.
Camara-Lemarroy CR, Infante-Valenzuela A, Andrade-Vazquez CJ, Enriquez-Noyola RV, Garcia-Valadez EA, Gongora-Rivera F. Successful intravenous thrombolysis in a patient with antiphospholipid syndrome, acute ischemic stroke and severe thrombocytopenia. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2016;27(3):354–6. https://doi.org/10.1097/MBC.0000000000000432.
Stadler K, Mutzenbach JS, Kalss G, Sellner J, Al-Schameri AR, Trinka E, et al. Therapeutic challenges after successful thrombectomy in a patient with an antiphospholipid syndrome associated M1-occlusion: a case report. Interv Neuroradiol. 2015;21(5):598–602. https://doi.org/10.1177/1591019915590371.
Rosa RF, Ugolini-Lopes MR, Zeinad-Valim AK, D’Amico E, Andrade D. Difficult clinical situations in the antiphospholipid syndrome. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2015;17(4):29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-015-0502-7.
Nalli C, Andreoli L, Casu C, Tincani A. Management of recurrent thrombosis in antiphospholipid syndrome. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2014;16(3):405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-013-0405-4.
Erkan D, Willis R, Murthy VL, Basra G, Vega J, Ruiz-Limon P, et al. A prospective open-label pilot study of fluvastatin on proinflammatory and prothrombotic biomarkers in antiphospholipid antibody positive patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(6):1176–80. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203622.
Nuri E, Taraborelli M, Andreoli L, Tonello M, Gerosa M, Calligaro A, et al. Long-term use of hydroxychloroquine reduces antiphospholipid antibodies levels in patients with primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Immunol Res. 2017;65(1):17–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-016-8812-z.
Kravvariti E, Koutsogianni A, Samoli E, Sfikakis PP, Tektonidou MG. The effect of hydroxychloroquine on thrombosis prevention and antiphospholipid antibody levels in primary antiphospholipid syndrome: a pilot open label randomized prospective study. Autoimmun Rev. 2020;19(4):102491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102491.
Tumian NR, Hunt BJ. Clinical management of thrombotic antiphospholipid syndrome. J Clin Med. 2022;11(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030735
•• Rodriguez-Pinto I, Espinosa G, Erkan D, Shoenfeld Y, Cervera R, Group CRP. The effect of triple therapy on the mortality of catastrophic anti-phospholipid syndrome patients. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018;57(7):1264–70. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/key082. Report of the CAPS Registry cohort demonstrating that triple therapy (anticoagulation, corticosteroids, and plasma exchange and/or IVIG) was associated with a higher survival rate among patients with CAPS.
Legault K, Schunemann H, Hillis C, Yeung C, Akl EA, Carrier M, et al. McMaster RARE-Bestpractices clinical practice guideline on diagnosis and management of the catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome. J Thromb Haemost. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1111/jth.14192.
Berman H, Rodriguez-Pinto I, Cervera R, Morel N, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Erkan D, et al. Rituximab use in the catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome: descriptive analysis of the CAPS registry patients receiving rituximab. Autoimmun Rev. 2013;12(11):1085–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2013.05.004.
Unlu O, Erkan D. Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome: candidate therapies for a potentially lethal disease. Annu Rev Med. 2017;68:287–96. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-med-042915-102529.
Faguer S, Ribes D. Early use of eculizumab for catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome. Br J Haematol. 2022;196(2):e12–4. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.17783.
Lopez-Benjume B, Rodriguez-Pinto I, Amigo MC, Erkan D, Shoenfeld Y, Cervera R, et al. Eculizumab use in catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome (CAPS): descriptive analysis from the “CAPS Registry.” Autoimmun Rev. 2022;21(4):103055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2022.103055.
Yazici A, Yazirli B, Erkan D. Belimumab in primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Lupus. 2017;26(10):1123–4. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203316682102.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Rafid Mustafa declares no potential conflicts of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Neurology of Systemic Disease
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mustafa, R. Neurologic Manifestations of Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 22, 589–600 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-022-01228-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-022-01228-0