Abstract
Purpose of Review
From a physiological point of view, VEGFs (vascular endothelial growth factors) and their receptors (VEGFR) play a critical role in vascular development angiogenesis, endothelial function, and vascular tone. On the pathological side, VEGF–VEGFR signaling may induce dysregulated angiogenesis, which contributes to the growth and to the spread of tumors, being essential for neoplastic proliferation and invasion.
Recent Findings
Pharmacological inhibition of VEGF–VEGFR is now a cornerstone in the treatment of many malignancies; however, treatment with VEGF inhibitors is commonly associated with an increase in blood pressure values. This side effect is strictly connected with the mechanism of action of these medications and might represent an index of therapy efficacy.
Summary
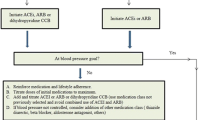
The optimal management of this form of hypertension is, at present, not clear. Calcium channel blockers and renin-angiotensin system inhibitors probably represent the most appropriate classes of hypertensive dugs for the treatment of this condition; however, no conclusive data are presently available.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major Importance
Svilaas T, Lefrandt JD, Gietema JA, Kamphuisen PW. Long-term arterial complications of chemotherapy in patients with cancer. Thromb Res. 2016;140S1:S109–18.
De Santis CE, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, Siegel RL, Stein KD, Kramer JL, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:252–71.
Strumberg D, Brugge S, Korn MW, et al. Evaluation of long-term toxicity in patients after cisplatin-based chemotherapy for non-seminomatous testicular cancer. Ann Oncol. 2002;13:229–36.
De Vos F, Nuver J, Willemse P. Long-term survivors of ovarian malig- nancies after cisplatin-based chemotherapy: cardiovascular risk factors and signs of vascular damage. Eur J Cancer. 2004;40:696–700.
Yeh ET, Tong AT, Lenihan DJ, Yusuf SW, Swafford J, Champion C, et al. Cardiovascular complications of cancer therapy: diagnosis, pathogenesis, and management. Circulation. 2004;109:3122–31.
Barrett-Lee PJ, Dixon JM, Farrell C, Jones A, Leonard R, Murray N, et al. Expert opinion on the use of anthracyclines in patients with advanced breast cancer at cardiac risk. Ann Oncol. 2009;20:816–27.
Oeffinger KC, Mertens AC, Sklar CA, Kawashima T, Hudson MM, Meadows AT, et al. Chronic health conditions in adult survivors of childhood cancer—Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1572–82.
Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, Cartwright T, Hainsworth J, Heim W, et al. Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2335–42.
Ranpura V, Pulipati B, Chu D, Zhu X, Wu S. Increased risk of high-grade hypertension with bevacizumab in cancer patients: a meta-analysis. Am J Hypertens. 2010;23:460–8.
Allen JA, Adlakha A, Bergethon PR. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome after bevacizumab/FOLFIRI regimen for metastatic colon cancer. Arch Neurol. 2006;63:1475–8.
Ozcan C, Wong SJ, Hari P. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome and bevacizumab. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:980–2.
Zhu X, Wu S, Dahut WL, Parikh CR. Risks of proteinuria and hypertension with bevacizumab, an antibody against vascular endothelial growth factor: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007;49:186–93.
Faruque LI, Lin M, Battistella M, Wiebe N, Reiman T, Hemmelgarn B, et al. Systematic review of the risk of adverse outcomes associated with vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitors for the treatment of cancer. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e101145.
Zhu X, Stergiopoulos K, Wu S. Risk of hypertension and renal dysfunction with an angiogenesis inhibitor sunitinib: systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Oncol. 2009;48:9–17.
Qi WX, Shen Z, Lin F, Sun YJ, Min DL, Tang LN, et al. Incidence and risk of hypertension with vandetanib in cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013;75:919–30.
Qi WX, Lin F, Sun YJ, Tang LN, He AN, Yao Y, et al. Incidence and risk of hypertension with pazopanib in patients with cancer: a meta-analysis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013;71:431–9.
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, et al. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors: European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92:205–16.
Rixe O, Billemont B, Izzedine H. Hypertension as a predictive factor of Sunitinib activity. Ann Oncol. 2007;18:1117.
Fukuda N, Takahari D, Wakatsuk T. Early hypertension is associated with better clinical outcomes in gastric cancer patients treated with ramucirumab plus paclitaxel. Oncotarget. 2018;9:15219–27.
Hurwitz HI, Douglas PS, Middleton JP, Sledge GW, Johnson DH, Reardon DA, et al. Analysis of early hypertension and clinical outcome with bevacizumab: results from seven phase III studies. Oncologist. 2013;18:273–80.
Harper SJ, Bates DO. VEGF-A splicing: the key to anti-angiogenic therapeutics? Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:880–7.
Takahashi S. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), VEGF receptors and their inhibitors for antiangiogenic tumor therapy. Biol Pharm Bull. 2011;34:1785–8.
Ferrara N, Kerbel RS. Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target. Nature. 2005;438:967–74.
Storkebaum E, Ruiz de Almodovar C, Meens M, Zacchigna S, Mazzone M, Vanhoutte G, et al. Impaired autonomic regulation of resistance arteries in mice with low vascular endothelial growth factor or upon vascular endothelial growth factor trap delivery. Circulation. 2010;122:273–81.
Lee S, Chen TT, Barber CL, Jordan MC, Murdock J, Desai S, et al. Autocrine VEGF signaling is required for vascular homeostasis. Cell. 2007;130:691–703.
Sela S, Itin A, Natanson-Yaron S, Greeneld C, Goldman-Wohl D, Yagel S, et al. A novel human-specific soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1: cell-type-specific splicing and implications to vascular endothelial growth factor homeostasis and preeclampsia. Circ Res. 2008;102:1566–74.
Safran M, Kaelin WG Jr. HIF hydroxylation and the mammalian oxygen-sensing pathway. J Clin Invest. 2003;111:779–83.
Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med. 1971;285:1182–6.
Morabito A, De Maio E, Di Maio M, Normanno N, Perrone F. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors in clinical trials: current status and future directions. Oncologist. 2006;11:753–64.
Force T, Krause DS, Van Etten RA. Molecular mechanisms of cardiotoxicity of tyrosine kinase inhibition. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:332–44.
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:378–90.
Spratlin JL, Cohen RB, Eadens M, Gore L, Camidge DR, Diab S, et al. Phase I pharmacologic and biologic study of ramucirumab (IMC-1121B), a fully human immunoglobulin G1 monoclonal antibody targeting the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:780–7.
Syed YY, McKeage K. Aflibercept: a review in metastatic colorectal cancer. Drugs. 2015;75:1435–45.
•• de Jesus-Gonzalez N, Robinson E, Moslehi J, Humphreys BD. Management of antiangiogenic therapy-induced hypertension. Hypertension. 2012;60:607–15. A comprehensive review, taking into account available data about the development and management of hypertension during treatment with antiangiogenic drugs.
•• Lankhorst S, Kappers MH, van Esch JH, Danser AH, van den Meiracker AH. Mechanism of hypertension and proteinuria during angiogenesis inhibition: evolving role of endothelin-1. J Hypertens. 2013;31:444–54. An updated review dealing with mechanism underlying the development of hypertension and proteinuria during treatment with antiangiogenic drugs, again focusing on the possible role of endothelin-1.
Dimmeler S, Fleming I, Fisslthaler B, Hermann C, Busse R, Zeiher AM. Activation of nitric oxide synthase in endothelial cells by Akt-dependent phosphorylation. Nature. 1999;399:601–5.
Shen BQ, Lee DY, Zioncheck TF. Vascular endothelial growth factor governs endothelial nitric-oxide synthase expression via a KDR/ Flk-1 receptor and a protein kinase C signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:33057–63.
Facemire CS, Nixon AB, Grif ths R, Hurwitz H, Coffman TM. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 controls blood pressure by regulating nitric oxide synthase expression. Hypertension. 2009;54:652–8.
Robinson ES, Khankin EV, Choueiri TK, Dhawan MS, Rogers MJ, Karumanchi SA, et al. Suppression of the nitric oxide pathway in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients receiving vascular endothelial growth factor-signaling inhibitors. Hypertension. 2010;56:1131–6.
Thijs AM, van Herpen CM, Sweep FC, Geurts-Moespot A, Smits P, van der Graaf WT, et al. Role of endogenous vascular endothelial growth factor in endothelium-dependent vasodilation in humans. Hypertension. 2013;61:1060–5.
Thijs AM, van Herpen CM, Verweij V, Pertijs J, van den Broek PH, van der Graaf WT, et al. Impaired endothelium-dependent vasodilation does not initiate the development of sunitinib-associated hypertension. J Hypertens. 2015;33:2075–82.
Kappers MH, Smedts FM, Horn T, van Esch JH, Sleijfer S, Leijten F, et al. The vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor sunitinib causes a preeclampsia-like syndrome with activation of the endothelin system. Hypertension. 2011;58:295–302.
Kappers MH, van Esch JH, Sluiter W, Sleijfer S, Danser AH, van den Meiracker AH. Hypertension induced by the tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinib is associated with increased circulating endothelin-1 levels. Hypertension. 2010;56:675–81.
Kappers MH, de Beer VJ, Zhou Z, Danser AH, Sleijfer S, Duncker DJ, et al. Sunitinib-induced systemic vasoconstriction in swine is endothelin mediated and does not involve nitric oxide or oxidative stress. Hypertension. 2012;59:151–7.
de Jesus-Gonzalez N, Robinson E, Penchev R, von Mehren M. Regorafenib induces rapid and reversible changes in plasma nitric oxide and endothelin-1. Am J Hypertens. 2012;25:1118–23.
Lankhorst S, Kappers MH, van Esch JH, Smedts FM, Sleijfer S, Mathijssen RH, et al. Treatment of hypertension and renal injury induced by the angiogenesis inhibitor sunitinib: preclinical study. Hypertension. 2014;64:1282–9.
Agabiti-Rosei E, Rizzoni D. Microvascular structure as a prognostically relevant endpoint. J Hypertens. 2017;35:914–21.
Rizzoni D, Paini A, Salvetti M, Rossini C, De Ciuceis C, Agabiti-Rosei C, et al. Inhibitors of angiogenesis and blood pressure. Curr Cardiovasc Risk Rep. 2013;7:244–7.
Mourad JJ d, Guetz G, Debbabi H, Levy BI. Blood pressure rise following angiogenesis inhibition by bevacizumab: a crucial role for microcirculation. Ann Oncol. 2008;19:927–34.
Steeghs N, Gelderblom H, Roodt JO, Christensen O, Rajagopalan P, Hovens M, et al. Hypertension and rarefaction during treatment with telatinib, a small molecule angiogenesis inhibitor. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:3470–6.
Chen DD, Dong YG, Yuan H, Chen AF. Endothelin 1 activation of endothelin A receptor/NADPH oxidase pathway and diminished anti- oxidants critically contribute to endothelial progenitor cell reduction and dysfunction in salt-sensitive hypertension. Hypertension. 2012;59:1037–43.
Neves KB, Rios FJ, van der Mey L, Alves-Lopes R, Cameron AC, Volpe M, et al. VEGFR (vascular endothelial growth factor receptor) inhibition induces cardiovascular damage via redox-sensitive processes. Hypertension. 2018;71:638–47.
•• Touyz RM, Lang NN, Herrmann J, van den Meiracker AH, Danser AHJ. Recent advances in hypertension and cardiovascular toxicities with vascular endothelial growth factor inhibition. Hypertension. 2017;70:220–6. A very recent contribution that provides an up- to-date assessment of the “state of the art.”
Gu JW, Manning RD Jr, Young E, Shparago M, Sartin B, Bailey AP. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor enhances dietary salt-induced hypertension in Sprague-Dawley rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009;297:R142–8.
Lankhorst S, Baelde HJ, Clahsen-van Groningen MC, Smedts FM, Danser AH, van den Meiracker AH. Effect of high salt diet on blood pressure and renal damage during vascular endothelial growth factor inhibition with sunitinib. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2016;31:914–21.
•• Boursiquot BC, Zabor EC, Glezerman IG, Jaimes EA. Hypertension and VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) receptor tyrosine kinase inhibition: effects on renal function. Hypertension. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.09275. This recent interesting paper provides evidence that the use of VEGF tyrosine kinase inhibitors does not adversely affect long-term renal function.
Curwen JO, Musgrove HL, Kendrew J, Richmond GH, Ogilvie DJ, Wedge SR. Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-a signaling induces hypertension: examining the effect of cediranib (recentin; azd2171) treatment on blood pressure in rat and the use of concomitant antihypertensive therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:3124–31.
• Moslehi J, Pandey AK, Cardio-Oncology BN. Vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitors, salt, and macrophages: a complicated interaction. Hypertension. 2017;69:785–6. An interesting editorial comment on reference 59.
Lankhorst S, Severs D, Markó L, Rakova N, Titze J, Müller DN, et al. Salt sensitivity of angiogenesis inhibition-induced blood pressure rise: role of interstitial sodium accumulation? Hypertension. 2017;69:919–26.
Maitland ML, Bakris GL, Black HR, Chen HX, Durand JB, Elliott WJ, et al. Initial assessment, surveillance, and management of blood pressure in patients receiving vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway inhibitors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010;102:596–604.
Steingart RM, Bakris GL, Chen HX, Chen MH, Force T, Ivy SP, et al. Management of cardiac toxicity in patients receiving vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway inhibitors. Am Heart J. 2012;163:156–63.
Bair SM, Choueiri TK, Moslehi J. Cardiovascular complications associated with novel angiogenesis inhibitors: emerging evidence and evolving perspectives. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2013;23:104–13.
•• Cameron AC, Touyz RM, Lang NN. Vascular complications of cancer chemotherapy. Can J Cardiol. 2016;32:852–62. A landmark contribution on the issue addressed by the present review.
• Kalaitzidis RG, Elisaf MS. Uncontrolled hypertension and oncology: clinical tips. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2017;16:23–9. Clinical tips on the management of uncontrolled hypertension in oncology.
•• Touyz RM, Herrmann SMS, Herrmann J. Vascular toxicities with VEGF inhibitor therapies-focus on hypertension and arterial thrombotic events. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2018. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2018 Jun;12(6):409-425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jash.2018.03.008. A most recent contribution on the issue, also providing some practical hints.
Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, Casey DE Jr, Collins KJ, Dennison Himmelfarb C, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Hypertension. 2018;71:1269–324.
Rizzoni D, De Ciuceis C, Porteri E, Agabiti-Rosei C, Agabiti-Rosei E. Use of antihypertensive drugs in neoplastic patients. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2017;24:127–32.
Pande A, Lombardo J, Spangenthal E, Javle M. Hypertension secondary to anti-angiogenic therapy: experience with bevacizumab. Anticancer Res. 2007;27:3465–70.
Mir OCR, Ropert S, Cabanes L, Blanchet B, Camps S, Billemont B, et al. Treatment of bevacizumab-induced hypertension by amlodipine. Investig New Drugs. 2012;30:702–7.
des Guetz G, Uzzan B, Chouahnia K, Morere JF. Cardiovascular toxicity of anti-angiogenic drugs. Target Oncol. 2011;6:197–202.
Keizman D, Huang P, Eisenberger MA, Pili R, Kim JJ, Antonarakis ES, et al. Angiotensin system inhibitors and outcome of sunitinib treatment in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a retrospective examination. Eur J Cancer. 2011;47:1955–61.
Derosa L, Izzedine H, Albiges L, Escudier B. Hypertension and angiotensin system inhibitors in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Oncol Rev. 2016;10(2):298.
McKay RR, Rodriguez GE, Lin X, Kaymakcalan MD, Hamnvik OP, Sabbisetti VS, et al. Angiotensin system inhibitors and survival outcomes in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21:2471–9.
Sorich MJ, Rowland A, Kichenadasse G, Woodman RJ, Mangoni AA. Risk factors of proteinuria in renal cell carcinoma patients treated with VEGF inhibitors: a secondary analysis of pooled clinical trial data. Br J Cancer. 2016;114:1313–7.
Kruzliak P, Kovacova G, Pechanova O. Therapeutic potential of nitric oxide donors in the prevention and treatment of angiogenesis-inhibitor-induced hypertension. Angiogenesis. 2013;16:289–95.
Hayman SR, Leung N, Grande JP, Garovic VD. VEGF inhibition, hypertension, and renal toxicity. Curr Oncol Rep. 2012;14:285–94.
Langenberg MH, van Herpen CM, De Bono J, Schellens JH, Unger C, Hoekman K, et al. Effective strategies for management of hyper tension after vascular endothelial growth factor signaling inhibition therapy: results from a phase II randomized, factorial, double-blind study of cediranib in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:6152–9.
•• van den Meiracker AH, Danser AH. Mechanisms of hypertension and renal injury during vascular endothelial growth factor signaling inhibition. Hypertension. 2016;68:17–23. The article provides a description of the mechanisms possibly involved in the development of hypertension and renal injury during VEGF signalling inhibition.
Miura S, Fujino M, Matsuo Y, Tanigawa H, Saku K. Nifedipine-induced vascular endothelial growth factor secretion from coronary smooth muscle cells promotes endothelial tube formation via the kinase insert domain-containing receptor/fetal liver kinase-1/NO pathway. Hypertens Res. 2005;28:147–53.
Miyajima A, Yazawa S, Kosaka T, Tanaka N, Shirotake S, Mizuno R, et al. Prognostic impact of renin-angiotensin system blockade on renal cell carcinoma after surgery. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22:3751–9.
Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, Redón J, Zanchetti A, Böhm M, et al. Task force members. 2013 ESH/ESC guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. The task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens. 2013;31:1281–357.
Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, Casey DE Jr, Collins KJ, Dennison Himmelfarb C, et al. ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71:e127–248.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Antihypertensive Agents: Mechanisms of Drug Action
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caletti, S., Paini, A., Coschignano, M.A. et al. Management of VEGF-Targeted Therapy-Induced Hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep 20, 68 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11906-018-0871-1
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11906-018-0871-1