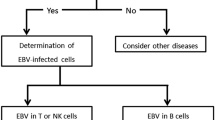
Abstract
Esptein-Barr virus (EBV) is a ubiquitous gammaherpesvirus that persists in carriers as a lifelong, mostly asymptomatic infection. EBV is associated with a variety of lymphomas and lymphoproliferative disorders. In this review we provide an update of the relevant literature on EBV-associated lymphoproliferative disorders, with particular emphasis on epidemiology, pathogenesis, and novel treatment approaches.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Parkin DM: The global health burden of infection-associated cancers in the year 2002. Int J Cancer 2006, 118:3030–3044.
Ushiku T, Chong JM, Uozaki H, et al.: p73 gene promoter methylation in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma. Int J Cancer 2007, 120:60–66.
Hjalgrim H, Smedby KE, Rostgaard K, et al.: Infectious mononucleosis, childhood social environment, and risk of Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer Res 2007, 67:2382–2388.
Landgren O, Engels EA, Pfeiffer RM, et al.: Autoimmunity and susceptibility to Hodgkin lymphoma: a population-based case-control study in Scandinavia. J Natl Cancer Inst 2006, 98:1321–1330.
Gandhi MK, Lambley E, Burrows J, et al.: Plasma Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA is a biomarker for EBV-positive Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 2006, 12:460–464.
Musacchio JG, Carvalho Mda G, Morais JC, et al.: Detection of free circulating Epstein-Barr virus DNA in plasma of patients with Hodgkin’s disease. Sao Paulo Med J 2006, 124:154–157.
Hirose Y, Masaki Y, Sawaki T, et al.: Association of Epstein-Barr virus with human immunodeficiency virus-negative peripheral T-cell lymphomas in Japan. Eur J Haematol 2006, 76:109–118.
Biggar RJ, Jaffe ES, Goedert JJ, et al.: Hodgkin lymphoma and immunodeficiency in persons with HIV/AIDS. Blood 2006, 108:3786–3791.
Engels EA, Pfeiffer RM, Goedert JJ, et al.: Trends in cancer risk among people with AIDS in the United States 1980–2002. AIDS 2006, 20:1645–1654.
Newton R, Carpenter L, Casabonne D, et al.: A prospective study of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus and Epstein-Barr virus in adults with human immunodeficiency virus-1. Br J Cancer 2006, 94:1504–1509.
Fellner MD, Durand K, Correa RM, et al.: Circulating Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in HIV-infected patients and its relation with primary brain lymphoma. Int J Infect Dis 2007, 11:172–178.
Bonnet F, Jouvencel AC, Parrens M, et al.: A longitudinal and prospective study of Epstein-Barr virus load in AIDS-related non-Hodgkin lymphoma. J Clin Virol 2006, 36:258–263.
Lee TC, Savoldo B, Barshes NR, et al.: Use of cytokine polymorphisms and Epstein-Barr virus viral load to predict development of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder in paediatric liver transplant recipients. Clin Transplant 2006, 20:389–393.
Lee TC, Goss JA, Rooney CM, et al.: Quantification of a low cellular immune response to aid in identification of pediatric liver transplant recipients at high-risk for EBV infection. Clin Transplant 2006, 20:689–694.
Brauninger A, Schmitz R, Bechtel D, et al.: Molecular biology of Hodgkin’s and Reed/Sternberg cells in Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Int J Cancer 2006, 118:1853–1861.
Diepstra A, van Imhoff GW, Karim-Kos HE, et al.: HLA class II expression by Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg cells is an independent prognostic factor in classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2007, 25:3101–3108.
Gandhi MK, Lambley E, Duraiswamy J, et al.: Expression of LAG-3 by tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes is coincident with the suppression of latent membrane antigen-specific CD8+ T-cell function in Hodgkin lymphoma patients. Blood 2006, 108:2280–2289.
Marshall NA, Culligan DJ, Tighe J, et al.: The relationships between Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 and regulatory T cells in Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Exp Hematol 2007, 35:596–604.
Sauce D, Larsen M, Curnow SJ, et al.: EBV-associated mononucleosis leads to long-term global deficit in T-cell responsiveness to IL-15. Blood 2006, 108:11–18.
Asada H: Hypersensitivity to mosquito bites: a unique pathogenic mechanism linking Epstein-Barr virus infection, allergy and oncogenesis. J Dermatol Sci 2007, 45:153–160.
Cho JH, Kim HS, Ko YH, Park CS: Epstein-Barr virus infected natural killer cell lymphoma in a patient with hypersensitivity to mosquito bite. J Infect 2006, 52:e173–e176.
Iwatsuki K, Satoh M, Yamamoto T, et al.: Pathogenic link between hydroa vacciniforme and Epstein-Barr virus-associated hematologic disorders. Arch Dermatol 2006, 142:587–595.
Asano N, Oshiro A, Matsuo K, et al.: Prognostic significance of T-cell or cytotoxic molecules phenotype in classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma: a clinicopathologic study. J Clin Oncol 2006, 24:4626–4633.
Dutton A, Woodman CB, Chukwuma MB, et al.: Bmi-1 is induced by the Epstein-Barr virus oncogene LMP1 and regulates the expression of viral target genes in Hodgkin lymphoma cells. Blood 2007, 109:2597–2603.
Kim LH, Peh SC, Poppema S: Expression of retino-blastoma protein and P16 proteins in classic Hodgkin lymphoma: relationship with expression of p53 and presence of Epstein-Barr virus in the regulation of cell growth and death. Hum Pathol 2006, 37:92–100.
Smith C, Cooper L, Burgess M, et al.: Functional reversion of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells from patients with Hodgkin lymphoma following in vitro stimulation with recombinant polyepitope. J Immunol 2006, 177:4897–4906.
Savoldo B, Rooney CM, Di Stasi A, et al.: Epstein Barr virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes expressing the anti-CD30(zeta) artificial chimeric T-cell receptor for immunotherapy of Hodgkin’s disease. Blood 2007, In press.
Cho HI, Hong YS, Lee MA, et al.: Adoptive transfer of Epstein-Barr virus-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocytes for the treatment of angiocentric lymphomas. Int J Hematol 2006, 83:66–73.
Demachi-Okamura A, Ito Y, Akatsuka Y, et al.: Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latent membrane protein-1-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes targeting EBV-carrying natural killer cell malignancies. Eur J Immunol 2006, 36:593–602.
Choquet S, Leblond V, Herbrecht R, et al.: Efficacy and safety of rituximab in B-cell post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorders: results of a prospective multicenter phase 2 study. Blood 2006, 107:3053–3057.
Savoldo B, Goss JA, Hammer MM, et al.: Treatment of solid organ transplant recipients with autologous Epstein Barr virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). Blood 2006, 108:2942–2949.
Humar A, Hebert D, Davies HD, et al.: A randomized trial of ganciclovir versus ganciclovir plus immune globulin for prophylaxis against Epstein-Barr virus related posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder. Transplantation 2006, 81:856–861.
Green M, Michaels MG, Katz BZ, et al.: CMV-IVIG for prevention of Epstein Barr virus disease and posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease in pediatric liver transplant recipients. Am J Transplant 2006, 6:1906–1912.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wagner-Johnston, N.D., Ambinder, R.F. Epstein-Barr virus-related lymphoproliferative disorders. Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2, 249–254 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11899-007-0034-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11899-007-0034-y