Abstract
Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) is an idiopathic inflammatory hepatic disorder characterized by granulomatous destruction of small bile ducts and formation of antimitochondrial antibodies. Having found that most patients with PBC have antibody reactivity to retroviral proteins, we recently cloned a retroviral sequence directly from biliary epithelium extracted from PBC livers. Further evidence for an infectious etiology of PBC has been derived from an in vitro model using normal biliary epithelial cells in culture with lymph node extracts from patients with chronic liver disease. In this model, biliary epithelial cells cocultivated with PBC lymph nodes developed a specific phenotype of PBC with immunohistochemical evidence of antimitochondrial antibody reactivity. This model has been used to show that patients with PBC harbor a transmissible agent that may be related to the cloned retrovirus. Pilot studies using antiretroviral treatment for patients with PBC have also supported the involvement of a retrovirus in the disease process. Because the antiretroviral therapy was tolerated without undue adverse events, a multicenter controlled trial is being established to determine whether patients with PBC derive significant benefit from this new line of investigation and management.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Gershwin ME, Rowley M, Davis PA, et al.: Molecular biology of the 2-oxo-acid fehydrogenase vomplexes and anti-mitochondrial antibodies. In Progress in Liver Disease. Edited by Boyer JL and Ockner RK. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1992:47–61.
Joplin R, Gershwin ME: Ductular expression of autoantigens in primary biliary cirrhosis. Semin Liver Dis 1997, 17:97–103.
Joplin RE, Wallace LL, Lindsay JG, et al.: The human biliary epithelial cell plasma membrane antigen in primary biliary cirrhosis: pyruvate dehydrogenase X? Gastroenterology 1997, 113:1727–1733.
Lazaridis KN, Lindor KD: Management of primary biliary cirrhosis: from diagnosis to end-stage disease. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 2000, 2:94–98. A recent update detailing standard therapy and management for patients with PBC.
Liermann-Garcia RF, Evangelista-Garcia C, McMaster P, Neuberger J: Transplantation for primary biliary cirrhosis: retrospective analysis of 400 patients in a single center. Hepatology 2001, 33:22–27.
Poupon RE, Balkau B, Eschwége E, Poupon R: A multicenter, controlled trial of ursodiol for the treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis. N Engl J Med 1991, 324:1548–1554.
Neuberger J, Thompson R: PBC and AMA: what is the connection? Hepatology 1999, 29:271–277.
Haydon G, Neuberger J: PBC: an infectious disease? Gut 2000, 47:586–588.
Metcalf J, Howel D, James O: Primary biliary cirrhosis: epidemiology helping the clinician. BMJ 1996, 312:1181–1182.
Neuberger J: Primary biliary cirrhosis. Lancet 1997, 350:875–879.
Neuberger JM, Portmann B, MacDougall B, et al.: Recurrence of primary biliary cirrhosis after liver transplantation. N Engl J Med 1982, 306:1–4.
Van-de-Water J, Gerson LB, Ferrell LD, et al.: Immunohistochemical evidence of disease recurrence following liver transplantation for primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology 1996, 24:1079–1084.
Sadamoto T, Joplin R, Keogh A, et al.: Expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex PDC-E2 on biliary epithelial cells induced by lymph nodes from primary biliary cirrhosis. Lancet 1998, 352:1595–1596. This was the first study to demonstrate the presence of a transmissible agent in periportal lymph nodes derived from patients with PBC capable of inducing the phenotypic manifestation of disease in normal biliary epithelial cells.
Keogh A, Sadamoto T, Joplin R, et al.: Expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex PDC-E2 on biliary epithelial cells induced by incubation with lymph nodes from primary biliary cirrhosis [abstract]. Hepatology 1999, 30:469A.
Tanaka A, Prindiville TP, Gish R, et al.: Are infectious agents involved in primary biliary cirrhosis? A PCR approach. J Hepatol 1999, 31:664–671.
Lisitsyn N, Lisitsyn N, Wigler M: Cloning the difference between two complex genomes. Science 1993, 259:946–951.
Xu L, Guo L, Joplin R, et al.: Viral induction of primary biliary cirrhosis [abstract]. J Hepatol 1997, 26:61.
Conrad B, Weissmahr RN, Boni J, et al.: A human endogenous retroviral superantigen as candidate autoimmune gene in type I diabetes. Cell 1997, 90:303–313.
Lan MS, Mason A, Chen QY, et al.: HERV-K10s and immunemediated (type1) diabetes. Cell 1998, 95:14–16.
Mason AL, Xu L, Guo L, Garry RF: Retroviruses in autoimmune liver disease: genetic or environment agents? Arch Immuno ther Exp 1999, 47:289–297.
Garry RF, Fermin CD, Hart DJ, et al.: Detection of a human intracisternal A-type retroviral particle antigenically related to HIV. Science 1990, 250:1127–1129. A landmark coculture experiment documenting the isolation of a novel human retrovirus, the human intracisternal A-type particle, from salivary glands of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome.
Garry RF, Krieg AM, Cheevers WP, et al.: Retroviruses and their role in chronic inflammatory diseases and autoimmunity. In The Retroviridae. Edited by Levy JA. New York: Plenum Press; 1995:491–602. This book chapter presents a thorough discussion of animal models, human disorders, retroviral infections and immunologic mechanisms that link retroviruses with autoimmune disease.
Talal N, Dauphinee M, Dang H, et al.: Detection of serum antibodies to retroviral proteins in patients with Sjögrens syndrome. Arthritis Rheum 1990, 33:741–781.
Talal N, Garry R, Alexander S, et al.: A conserved idiotype and antibodies to retroviral proteins in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest 1990, 85:1866–1871.
Mason A, Xu L, Guo L, et al.: Detection of retroviral antibodies in primary biliary cirrhosis and other idiopathic biliary disorders. Lancet 1998, 351:1620–1624. This Western blot study shows that the majority of patients with PBC have antibody reactivity with the human intracisternal A-type particle, a retrovirus isolated from patients with Sjögren’s syndrome.
Xu L, Guo L, Keogh A, et al.: Isolation and characterization of a novel virus associated with primary biliary cirrhosis [abstract]. Hepatology 2000, 32:297A. A preliminary abstract reporting the cloning of a novel exogenous β-retrovirus from a PBC cDNA library and the detection of viral sequences in the in vitro coculture model for PBC.
Lee Y, Kaplan M: Treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis and primary sclerosing cholangitis: use of ursodeoxycholic acid. Curr Gastrenterol Rep 1999, 1:38–41. A recent update discussing the use of UDCA in patients with PBC.
Goulis J, Leandro G, Burroughs A: Randomised controlled trials of ursodeoxycholic acid therapy for primary biliary cirrhosis: a meta analysis. Lancet 1999, 354:1053–1060.
Mason A, Farr G, Xu L, et al.: Pilot study of lamivudine for patients with primary biliary cirrhosis [abstract]. J Hepatol 2001, 34:205.
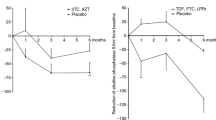
Mason A, Neuberger J: Pilot study of anti-retroviral therapy for patients with primary biliary cirrhosis [abstract]. Hepatology 2001, 34:527A. A preliminary abstract reporting significant improvements in hepatic biochemistry in patients with PBC receiving combination antiretroviral treatment with Combivir.
Degott C, Zafrani ES, Callard P, et al.: Histopathological study of primary biliary cirrhosis and the effect of ursodeoxycholic acid treatment on histology progression. Hepatology 1999, 29:1007–1012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mason, A., Nair, S. Primary biliary cirrhosis: New thoughts on pathophysiology and treatment. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 4, 45–51 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-002-0037-8
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-002-0037-8