Abstract
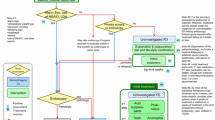
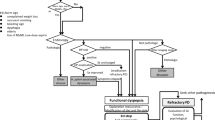
Nonulcer dyspepsia is a common condition in clinical practice. It is a heterogeneous disorder, and no single therapeutic agent is effective in all patients. The treatment of nonulcer dyspepsia is still dissatisfactory. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori organisms has a limited role and little effect. Antisecretory therapy has a modest effect in alleviating symptoms. Prokinetic agents may be effective, but selection bias in the trials performed to date may exaggerate their benefit. Partial 5-HT4 agonists stimulate gastric emptying and may also affect gastric accommodation. They are promising but need further study. Data are limited on 5-HT3 antagonists and hypnotherapy. New treatment approaches are necessary for this common and often chronic condition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: Of importance Of major importance
Talley NJ, Stanghellii V, Heading RC, et al.: Functional gastroduodenal disorders. Gut 1999, 45(Suppl II):1137–1142.
Talley NJ, Zinsmeister AR, Schleck CD, Melton LJ: Dyspepsia and dyspepsia subgroups: a population-based study. Gastroenterology 1992, 102:1259–1268.
Jones R, Lydeard S: Prevalence of symptoms of dyspepsia in the community. BMJ 1989, 298:30–32.
Marsland DW, Wood M, Mayo F: Content of family practice. Part I. Rank order of diagnoses by frequency. Part II. Diagnosis by disease category and age/sex distribution. J Fam Pract 1976, 3:37–68.
Kagevi I, Lofstedt S, Persson L-G: Endoscopic findings and diagnoses in unselected dyspeptic patients at a primary health care center. Scand J Gastroenterol 1989, 24:145–150.
Gear MWL, Barnes RJ: Endoscopic studies of dyspepsia in general practice. BMJ 1980, 1:1136–1137.
Health and Policy Committee of the American College of Physicians: Endoscopy in the evaluation of dyspepsia. Ann Intern Med 1985, 102:266–269.
Bytzer P, Hansen J, de Muckadell O: Empirical H2 blocker therapy or prompt endoscopy in management of dyspepsia. Lancet 1994, 343:811–815.
Silverstein M, Petterson T, Talley N: Initial endoscopy or empirical therapy with or without testing for H. Pylori for dyspepsia: a decision analysis. Gastroenterology 1996, 110:72–83.
Spiegel BM, Vakil NB, Ofman JJ: Dyspepsia management in primary care: a decision analysis of competing strategies. Gastroenterology 2002, 122:1270–1285. A PPI trial interposed between test and treat and endoscopy saves costs.
Blum AL, Talley NJ, O’Morain C, et al.: Lack of effect of treating Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with nonulcer dyspepsia. N Engl J Med 1998, 339:1875–1881. H. pylori eradication does not cure nonulcer dyspepsia.
Talley NJ, Jenssens J, Lauritsen K, et al.: Eradication of Helicobacter pylori in functional dyspepsia-randomized double blind placebo controlled trial with 12 months follow up. BMJ 1999, 318:833–837. H. pylori eradication does not cure nonulcer dyspepsia in European study.
Talley NJ, Vakil N, Ballard ED, Fennerty B: Absence of benefit of eradicating Helicobacter pylori in patients with nonulcer dyspepsia. N Engl J Med 1999, 341:1106–1111. H. pylori eradication does not cure nonulcer dyspepsia in US patients.
McColl K, Murray L, El-Omar E, et al.: Symptomatic benefit from eradicating H. pylori in patients with nonulcer dyspepsia. N Engl J Med 1998, 339:1869–1874. Only study to show therapeutic efficacy for H. pylori eradication in nonulcer dyspepsia.
Greenberg P, Cello J: Lack of effect of treatment for Helicobacter pylori on symptoms of non-ulcer dyspepsia. Arch Intern Med 1999, 159:2283–2288.
Malfertheiner P, Fischbach W, Layer P, et al.: ELAN study proves symptomatic benefit of Helicobacter pylori eradication in functional dyspepsia [abstract]. Gastroenterology 2000, 118:A440.
Moayyedi P, Soo S, Deeks J, et al.: Systematic review and economic evaluation of Helicobacter pylori eradication treatment for non-ulcer dyspepsia. BMJ 2000, 321:659–664. Meta-analysis suggesting a modest benefit for H. pylori eradication in nonulcer dyspepsia.
Laine L, Schoenfeld P, Fennerty MB: H pylori therapy is not effective for treatment of non-ulcer dyspepsia: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ann Intern Med 2001, 134:361–369. Meta-analysis suggesting no benefit for H. pylori eradication in nonulcer dyspepsia.
Finney JS, Kinnersley N, Hughes M, et al.: Meta-analysis of anti-secretory and gastrokinetic compounds in functional dyspepsia. J Clin Gastroenterol 1998, 26:312–320.
Soo S: Pharmacological interventions for non-ulcer dyspepsia [review]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2000, 2:CD001960.
Talley N, Meineche-Schmidt V, Pare P, et al.: Effect of omeprazole in functional dyspepsia: double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trials (the BOND and OPERA studies). Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1998, 12:1055–1065. PPIs have modest efficacy in functional dyspepsia.
Peura D, Kovacs T, Metz D, et al.: Low-dose Lansoprazole: effective for non-ulcer dyspepsia (NUD) [abstract]. Gastroenterology 2000, 118:A439.
Tack J, Vos R, Janssens J, et al.: Influence of tegaserod on proximal gastric sensory and motor function in man [abstract]. Gastroenterology 2002, 122:A20. Early results on tegaserod, a 5-HT4 partial agonist in dyspepsia.
Tack J, Delia T, Ligozio G, et al.: A phase II placebo controlled randomized trial with tegaserod in functional dyspepsia patients with normal gastric emptying [abstract]. Gastroenterology 2002, 122:A453.
Kuo B, Camilleri M, Burton D, et al.: 5-HT3 antagonism of upper gastrointestinal symptoms after a dyspepsia inducing meal. Gastroenterology 2001, 120:A134.
Chiarioni G, Benini L, Bonfante F, et al.: Prokinetic effect of a single session of gut oriented hypnotherapy on gastric emptying in normal subjects and dyspeptic patients [abstract]. Gastroenterology 2001, 120:A133.
Holtmann G: Randomized double-blind comparison of simethicone with cisapride in functional dyspepsia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1999, 13:1459–1465.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vakil, N. Nonulcer dyspepsia. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 4, 455–458 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-002-0020-4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-002-0020-4