Abstract
Purpose of Review
The aim of this review is to summarize the current data available on the metabolic effects of fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) including obesity and glucose metabolism in humans.
Recent Findings
Gut microbiota dysbiosis is a frequent characteristic observed in obesity and related metabolic diseases. Pieces of evidence mostly generated in mouse models suggest that rescuing this dysbiosis associates with improved metabolism. In humans, dietary or bariatric surgery interventions are often accompanied by complete or partial restoration of this dysbiosis together with weight reduction and metabolic amelioration. FMT is an interesting option to modify gut microbiota and has been associated with improved clinical outcomes, albeit only used in routine care for Clostridium difficile infection. However, there are only limited data on using FMT in the metabolic context.
Summary
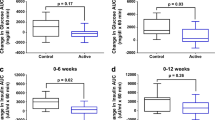
FMT from lean donors significantly improves insulin sensitivity in obese subjects with metabolic syndrome. However, there is a wide range of clinical responses. Interestingly in subjects with high microbial gene richness at baseline and when FMT donors that are metabolically compromised are used, no metabolic improvement is seen. Moreover, more studies evaluating the effect of FMT in patients with overt type 2 diabetes are warranted. Furthermore, interventions (in the receiver prior to FMT) aiming to enhance FMT response also need evaluation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Fouhy F, Ross RP, Fitzgerald GF, Stanton C, Cotter PD. Composition of the early intestinal microbiota: knowledge, knowledge gaps and the use of high-throughput sequencing to address these gaps. Gut Microbes. 2012;3(3):203–20.
Rastelli M, Knauf C, Cani PD. Gut microbes and health: a focus on the mechanisms linking microbes, obesity, and related disorders. Obes Silver Spring Md. 2018;26(5):792–800.
Karlsson FH, Tremaroli V, Nookaew I, Bergström G, Behre CJ, Fagerberg B, et al. Gut metagenome in European women with normal, impaired and diabetic glucose control. Nature. 2013;498(7452):99–103.
Pedersen HK, Gudmundsdottir V, Nielsen HB, Hyotylainen T, Nielsen T, Jensen BAH, et al. Human gut microbes impact host serum metabolome and insulin sensitivity. Nature. 2016;535(7612):376–81.
Le Chatelier E, Nielsen T, Qin J, Prifti E, Hildebrand F, Falony G, et al. Richness of human gut microbiome correlates with metabolic markers. Nature. 2013;500(7464):541–6.
Cotillard A, Kennedy SP, Kong LC, Prifti E, Pons N, Le Chatelier E, et al. Dietary intervention impact on gut microbial gene richness. Nature. 2013;500(7464):585–8.
Turnbaugh PJ, Bäckhed F, Fulton L, Gordon JI. Diet-induced obesity is linked to marked but reversible alterations in the mouse distal gut microbiome. Cell Host Microbe. 2008;3(4):213–23.
Yatsunenko T, Rey FE, Manary MJ, Trehan I, Dominguez-Bello MG, Contreras M, et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature. 2012;486(7402):222–7.
•• Aron-Wisnewsky J, Prifti E, Belda E, Ichou F, Kayser BD, Dao MC, et al. Major microbiota dysbiosis in severe obesity: fate after bariatric surgery. Gut. 2018 Jun 13. This study demonstrates that severe obesity is associated with a dramatic increased prevalence of low MGR. Bariatric surgery is able to partially restore gut microbiota dysbiosis.
Qin J, Li Y, Cai Z, Li S, Zhu J, Zhang F, et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2012;490(7418):55–60.
Allin KH, Tremaroli V, Caesar R, Jensen BAH, Damgaard MTF, Bahl MI, et al. Aberrant intestinal microbiota in individuals with prediabetes. Diabetologia. 2018;61(4):810–20.
Aydin Ö, Nieuwdorp M, Gerdes V. The gut microbiome as a target for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 2018;18(8):55.
Debédat J, Amouyal C, Aron-Wisnewsky J, Clément K. Impact of bariatric surgery on type 2 diabetes: contribution of inflammation and gut microbiome? Semin Immunopathol. 2019;
Cani PD, Possemiers S, Van de Wiele T, Guiot Y, Everard A, Rottier O, et al. Changes in gut microbiota control inflammation in obese mice through a mechanism involving GLP-2-driven improvement of gut permeability. Gut. 2009;58(8):1091–103.
Dewulf EM, Cani PD, Claus SP, Fuentes S, Puylaert PGB, Neyrinck AM, et al. Insight into the prebiotic concept: lessons from an exploratory, double blind intervention study with inulin-type fructans in obese women. Gut. 2013;62(8):1112–21.
Canfora EE, van der Beek CM, Hermes GDA, Goossens GH, Jocken JWE, Holst JJ, et al. Supplementation of diet with galacto-oligosaccharides increases bifidobacteria, but not insulin sensitivity, in obese prediabetic individuals. Gastroenterology. 2017;153(1):87–97.e3.
Koutnikova H, Genser B, Monteiro-Sepulveda M, Faurie J-M, Rizkalla S, Schrezenmeir J, et al. Impact of bacterial probiotics on obesity, diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease related variables: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ Open. 2019;9(3):e017995.
Liou AP, Paziuk M, Luevano J-M, Machineni S, Turnbaugh PJ, Kaplan LM. Conserved shifts in the gut microbiota due to gastric bypass reduce host weight and adiposity. Sci Transl Med. 2013;5(178):178ra41.
Tremaroli V, Karlsson F, Werling M, Ståhlman M, Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Olbers T, et al. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and vertical banded gastroplasty induce long-term changes on the human gut microbiome contributing to fat mass regulation. Cell Metab. 2015;22(2):228–38.
Brandt LJ, Aroniadis OC, Mellow M, Kanatzar A, Kelly C, Park T, et al. Long-term follow-up of colonoscopic fecal microbiota transplant for recurrent Clostridium difficile infection. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012;107(7):1079–87.
Hamilton MJ, Weingarden AR, Sadowsky MJ, Khoruts A. Standardized frozen preparation for transplantation of fecal microbiota for recurrent Clostridium difficile infection. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012;107(5):761–7.
Kelly CR, de Leon L, Jasutkar N. Fecal microbiota transplantation for relapsing Clostridium difficile infection in 26 patients: methodology and results. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2012;46(2):145–9.
Mattila E, Uusitalo-Seppälä R, Wuorela M, Lehtola L, Nurmi H, Ristikankare M, et al. Fecal transplantation, through colonoscopy, is effective therapy for recurrent Clostridium difficile infection. Gastroenterology. 2012;142(3):490–6.
Gough E, Shaikh H, Manges AR. Systematic review of intestinal microbiota transplantation (fecal bacteriotherapy) for recurrent Clostridium difficile infection. Clin Infect Dis Off Publ Infect Dis Soc Am. 2011;53(10):994–1002.
Cui B, Feng Q, Wang H, Wang M, Peng Z, Li P, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation through mid-gut for refractory Crohn’s disease: safety, feasibility, and efficacy trial results. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;30(1):51–8.
•• van Nood E, Vrieze A, Nieuwdorp M, Fuentes S, Zoetendal EG, de Vos WM, et al. Duodenal infusion of donor feces for recurrent Clostridium difficile. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(5):407–15. This RCT is the first to demonstrate the efficacy of FMT to cure Clostridium difficile infection.
•• Youngster I, Sauk J, Pindar C, Wilson RG, Kaplan JL, Smith MB, et al. Fecal microbiota transplant for relapsing Clostridium difficile infection using a frozen inoculum from unrelated donors: a randomized, open-label, controlled pilot study. Clin Infect Dis Off Publ Infect Dis Soc Am. 2014;58(11):1515–22. This study demonstrated for the first time the efficacy of capsulized oral fecal microbiota transplantation.
Cammarota G, Masucci L, Ianiro G, Bibbò S, Dinoi G, Costamagna G, et al. Randomised clinical trial: faecal microbiota transplantation by colonoscopy vs. vancomycin for the treatment of recurrent Clostridium difficile infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;41(9):835–43.
Lee CH, Steiner T, Petrof EO, Smieja M, Roscoe D, Nematallah A, et al. Frozen vs fresh fecal microbiota transplantation and clinical resolution of diarrhea in patients with recurrent Clostridium difficile infection: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016;315(2):142–9.
Quraishi MN, Widlak M, Bhala N, Moore D, Price M, Sharma N, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the efficacy of faecal microbiota transplantation for the treatment of recurrent and refractory Clostridium difficile infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;46(5):479–93.
Surawicz CM, Brandt LJ, Binion DG, Ananthakrishnan AN, Curry SR, Gilligan PH, et al. Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of Clostridium difficile infections. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108(4):478–98 quiz 499.
Debast SB, Bauer MP, Kuijper EJ. European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases: update of the treatment guidance document for Clostridium difficile infection. Clin Microbiol Infect Off Publ Eur Soc Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014;20(Suppl 2):1–26.
McDonald LC, Gerding DN, Johnson S, Bakken JS, Carroll KC, Coffin SE, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for Clostridium difficile infection in adults and children: 2017 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA). Clin Infect Dis Off Publ Infect Dis Soc Am. 2018;66(7):987–94.
König J, Siebenhaar A, Högenauer C, Arkkila P, Nieuwdorp M, Norén T, et al. Consensus report: faecal microbiota transfer - clinical applications and procedures. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;45(2):222–39.
Cammarota G, Ianiro G, Tilg H, Rajilić-Stojanović M, Kump P, Satokari R, et al. European consensus conference on faecal microbiota transplantation in clinical practice. Gut. 2017;66(4):569–80.
Borody TJ, Paramsothy S, Agrawal G. Fecal microbiota transplantation: indications, methods, evidence, and future directions. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2013;15(8):337.
Anderson JL, Edney RJ, Whelan K. Systematic review: faecal microbiota transplantation in the management of inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012;36(6):503–16.
Zhang F-M, Wang H-G, Wang M, Cui B-T, Fan Z-N, Ji G-Z. Fecal microbiota transplantation for severe enterocolonic fistulizing Crohn’s disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19(41):7213–6.
Rossen NG, MacDonald JK, de Vries EM, D’Haens GR, de Vos WM, Zoetendal EG, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation as novel therapy in gastroenterology: a systematic review. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(17):5359–71.
Lin SC, Alonso CD, Moss AC. Fecal microbiota transplantation for recurrent Clostridium difficile infection in patients with solid organ transplants: an institutional experience and review of the literature. Transpl Infect Dis Off J Transplant Soc. 2018;16:e12967.
Kassam Z, Lee CH, Yuan Y, Hunt RH. Fecal microbiota transplantation for Clostridium difficile infection: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108(4):500–8.
van Beurden YH, de Groot PF, van Nood E, Nieuwdorp M, Keller JJ, Goorhuis A. Complications, effectiveness, and long term follow-up of fecal microbiota transfer by nasoduodenal tube for treatment of recurrent Clostridium difficile infection. United Eur Gastroenterol J. 2017;5(6):868–79.
Smits LP, Bouter KEC, de Vos WM, Borody TJ, Nieuwdorp M. Therapeutic potential of fecal microbiota transplantation. Gastroenterology. 2013;145(5):946–53.
Drekonja D, Reich J, Gezahegn S, Greer N, Shaukat A, MacDonald R, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation for Clostridium difficile infection: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162(9):630–8.
Kelly CR, Kahn S, Kashyap P, Laine L, Rubin D, Atreja A, et al. Update on fecal microbiota transplantation 2015: indications, methodologies, mechanisms, and outlook. Gastroenterology. 2015;149(1):223–37.
Youngster I, Russell GH, Pindar C, Ziv-Baran T, Sauk J, Hohmann EL. Oral, capsulized, frozen fecal microbiota transplantation for relapsing Clostridium difficile infection. JAMA. 2014;312(17):1772–8.
Bircher L, Schwab C, Geirnaert A, Lacroix C. Cryopreservation of artificial gut microbiota produced with in vitro fermentation technology. Microb Biotechnol. 2018;11(1):163–75.
Kao D, Roach B, Silva M, Beck P, Rioux K, Kaplan GG, et al. Effect of oral capsule- vs colonoscopy-delivered fecal microbiota transplantation on recurrent Clostridium difficile infection: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;318(20):1985–93.
Cheminet G, Kapel N, Bleibtreu A, Sadou-Yaye H, Bellanger A, Duval X, et al. Faecal microbiota transplantation with frozen capsules for relapsing Clostridium difficile infections: the first experience from 15 consecutive patients in France. J Hosp Infect. 2018.
Gérard C, Vidal H. Impact of gut microbiota on host glycemic control. Front Endocrinol. 2019;10:29.
de Groot PF, Frissen MN, de Clercq NC, Nieuwdorp M. Fecal microbiota transplantation in metabolic syndrome: history, present and future. Gut Microbes. 2017;8(3):253–67.
Vrieze A, Van Nood E, Holleman F, Salojärvi J, Kootte RS, Bartelsman JFWM, et al. Transfer of intestinal microbiota from lean donors increases insulin sensitivity in individuals with metabolic syndrome. Gastroenterology. 2012;143(4):913–916.e7.
•• Kootte RS, Levin E, Salojärvi J, Smits LP, Hartstra AV, Udayappan SD, et al. Improvement of insulin sensitivity after lean donor feces in metabolic syndrome is driven by baseline intestinal microbiota composition. Cell Metab. 2017;26(4):611–619.e6. This study confirmed the efficacy of FMT to improve insulin sensitivity in a larger group of patients and demonstrated the major variability of response. The authors identified that low MGR before FMT was predictive of a good response to FMT.
Everard A, Belzer C, Geurts L, Ouwerkerk JP, Druart C, Bindels LB, et al. Cross-talk between Akkermansia muciniphila and intestinal epithelium controls diet-induced obesity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(22):9066–71.
Plovier H, Everard A, Druart C, Depommier C, Van Hul M, Geurts L, et al. A purified membrane protein from Akkermansia muciniphila or the pasteurized bacterium improves metabolism in obese and diabetic mice. Nat Med. 2017;23(1):107–13.
Dao MC, Everard A, Aron-Wisnewsky J, Sokolovska N, Prifti E, Verger EO, et al. Akkermansia muciniphila and improved metabolic health during a dietary intervention in obesity: relationship with gut microbiome richness and ecology. Gut. 2015.
Jumpertz R, Le DS, Turnbaugh PJ, Trinidad C, Bogardus C, Gordon JI, et al. Energy-balance studies reveal associations between gut microbes, caloric load, and nutrient absorption in humans. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011;94(1):58–65.
Bäckhed F, Ding H, Wang T, Hooper LV, Koh GY, Nagy A, et al. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(44):15718–23.
Ridaura VK, Faith JJ, Rey FE, Cheng J, Duncan AE, Kau AL, et al. Gut microbiota from twins discordant for obesity modulate metabolism in mice. Science. 2013;341(6150):1241214.
Aron-Wisnewsky J, Clément K. The gut microbiome, diet, and links to cardiometabolic and chronic disorders. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2015.
Kulecka M, Paziewska A, Zeber-Lubecka N, Ambrozkiewicz F, Kopczynski M, Kuklinska U, et al. Prolonged transfer of feces from the lean mice modulates gut microbiota in obese mice. Nutr Metab. 2016;13(1):57.
de Clercq NC, Frissen MN, Davids M, Groen AK, Nieuwdorp M. Weight gain after fecal microbiota transplantation in a patient with recurrent underweight following clinical recovery from anorexia nervosa. Psychother Psychosom. 2019;88(1):58–60.
Alang N, Kelly CR. Weight gain after fecal microbiota transplantation. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2015;2(1):ofv004.
Donor metabolic characteristics drive effects of faecal microbiota transplantation on recipient insulin sensitivity, energy expenditure and intesti... - PubMed - NCBI [Internet]. [cited 2019 Jun 3]. Available from: https://www-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.gate2.inist.fr/pubmed/31147381
Angelberger S, Reinisch W, Makristathis A, Lichtenberger C, Dejaco C, Papay P, et al. Temporal bacterial community dynamics vary among ulcerative colitis patients after fecal microbiota transplantation. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108(10):1620–30.
Seekatz AM, Aas J, Gessert CE, Rubin TA, Saman DM, Bakken JS, et al. Recovery of the gut microbiome following fecal microbiota transplantation. mBio. 2014;5(3):e00893–14.
Hamilton MJ, Weingarden AR, Unno T, Khoruts A, Sadowsky MJ. High-throughput DNA sequence analysis reveals stable engraftment of gut microbiota following transplantation of previously frozen fecal bacteria. Gut Microbes. 2013;4(2):125–35.
Li SS, Zhu A, Benes V, Costea PI, Hercog R, Hildebrand F, et al. Durable coexistence of donor and recipient strains after fecal microbiota transplantation. Science. 2016;352(6285):586–9.
Moayyedi P, Surette MG, Kim PT, Libertucci J, Wolfe M, Onischi C, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation induces remission in patients with active ulcerative colitis in a randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 2015;149(1):102–109.e6.
Paramsothy S, Paramsothy R, Rubin DT, Kamm MA, Kaakoush NO, Mitchell HM, et al. Faecal microbiota transplantation for inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Crohns Colitis. 2017;11(10):1180–99.
Vermeire S, Joossens M, Verbeke K, Wang J, Machiels K, Sabino J, et al. Donor species richness determines faecal microbiota transplantation success in inflammatory bowel disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2016;10(4):387–94.
Shin N-R, Lee J-C, Lee H-Y, Kim M-S, Whon TW, Lee M-S, et al. An increase in the Akkermansia spp. population induced by metformin treatment improves glucose homeostasis in diet-induced obese mice. Gut. 2014;63(5):727–35.
Lee H, Lee Y, Kim J, An J, Lee S, Kong H, et al. Modulation of the gut microbiota by metformin improves metabolic profiles in aged obese mice. Gut Microbes. 2017:1–11.
Forslund K, Hildebrand F, Nielsen T, Falony G, Le Chatelier E, Sunagawa S, et al. Disentangling type 2 diabetes and metformin treatment signatures in the human gut microbiota. Nature. 2015;528(7581):262–6.
Wu H, Esteve E, Tremaroli V, Khan MT, Caesar R, Mannerås-Holm L, et al. Metformin alters the gut microbiome of individuals with treatment-naive type 2 diabetes, contributing to the therapeutic effects of the drug. Nat Med. 2017;23(7):850–8.
David LA, Maurice CF, Carmody RN, Gootenberg DB, Button JE, Wolfe BE, et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature. 2014;505(7484):559–63.
Wu GD, Chen J, Hoffmann C, Bittinger K, Chen Y-Y, Keilbaugh SA, et al. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science. 2011;334(6052):105–8.
Kong LC, Holmes BA, Cotillard A, Habi-Rachedi F, Brazeilles R, Gougis S, et al. Dietary patterns differently associate with inflammation and gut microbiota in overweight and obese subjects. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e109434.
Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, Gordon JI. Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature. 2006;444(7122):1022–3.
Groen AK, Nieuwdorp M. An evaluation of the therapeutic potential of fecal microbiota transplantation to treat infectious and metabolic diseases. EMBO Mol Med. 2017;9(1):1–3.
SL et.al Effect of vegan fecal microbiota transplantation on carnitine- and choline-derived trimethylamine-N-oxide production and vascular inflammation in P... - PubMed - NCBI [internet] [cited 2019 Apr 25]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29581220
Arbel LT, Hsu E, McNally K. Cost-effectiveness of fecal microbiota transplantation in the treatment of recurrent clostridium difficile infection: a literature review. Cureus. 2017;9(8):e1599.
Zhang T, Xiang J, Cui B, He Z, Li P, Chen H, et al. Cost-effectiveness analysis of fecal microbiota transplantation for inflammatory bowel disease. Oncotarget. 2017;8(51):88894–903.
Gundling F, Roggenbrod S, Schleifer S, Sohn M, Schepp W. Patient perception and approval of faecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) as an alternative treatment option for obesity. Obes Sci Pract. 2019;5(1):68–74.
Funding
Grant supports in this field were obtained by Ministry of Health and Solidarity (Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris: to JAW/PHRC-N Drifter, to KC/PHRC Micronaria), by European Union (Metacardis to KC HEALTH-F4-2012-305312, JPI MICRODIET Grant (5290510105) to KC and MN, EU Horizon 2020 grant (LITMUS 777377) to KC and MN) and by LeDucq Foundation consortium grant (17CVD01) to KC and MN. MN is also supported by a ZONMW-VIDI grant 2013 (016.146.327). JAW and KC are part of ICAN (Institute of Cardiometabolism and Nutrition Institute).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Judith Aron-Wisnewsky declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Karine Clément is on the Scientific Advisory Board of LNC Therapeutics, France.
Max Nieuwdorp is on the Scientific Advisory Board of Caelus Pharmaceuticals, the Netherlands.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Immunology, Transplantation, and Regenerative Medicine
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aron-Wisnewsky, J., Clément, K. & Nieuwdorp, M. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation: a Future Therapeutic Option for Obesity/Diabetes?. Curr Diab Rep 19, 51 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-019-1180-z
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-019-1180-z