Abstract
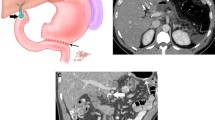
Percutaneous transhepatic intraportal pancreatic islet transplantation is an experimental treatment for patients with type 1 diabetes. The radiologic aspects of pancreatic islet transplantation are described, including a review of interventional radiology, ultrasound, and fluoroscopy image-guided, minimally invasive techniques and procedure-related complications and their avoidance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Williams P: Notes on diabetes treated with extract and by grafts of sheep's pancreas. BMJ 1894, 2:1303–1304.
Ryan EA, Lakey JR, Paty BW, et al.: Successful islet transplantation: continued insulin reserve provides long-term glycemic control. Diabetes 2002, 51:2148–2157.
Shapiro AM, Ricordi C: Unraveling the secrets of single donor success in islet transplantation. Am J Transplant 2004, 4:296–298.
Shapiro AM, Lakey JR, Ryan EA, et al.: Islet transplantation in seven patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus using a glucocorticoid-free immunosuppressive regimen. N Engl J Med 2000, 343:230–238. Landmark paper describing the preliminary success with islet cell transplantation using a glucocorticoid-free immunosuppressive regimen, providing proof of the principle that islet transplantation can be reproducibly successful for at least 1 year..
Hirshberg B, Rother KI, Digon BJ 3rd, et al.: Benefits and risks of solitary islet transplantation for type 1 diabetes using steroid-sparing immunosuppression: the National Institutes of Health experience. Diabetes Care 2003, 26:3288–3295.
Bucher P, Mathe Z, Bosco D, et al.: Morbidity associated with intraportal islet transplantation. Transplant Proc 2004, 36:1119–1120.
Ryan EA, Paty BW, Senior PA, Shapiro AM: Risks and side effects of islet transplantation. Curr Diab Rep 2004, 4:304–309.
Owen RJ, Ryan EA, O'Kelly K, et al.: Percutaneous transhepatic pancreatic islet cell transplantation in type 1 diabetes mellitus: radiologic aspects. Radiology 2003, 229:165–170.
Villiger P, Ryan EA, Owen R, et al.: Prevention of bleeding after islet transplantation: lessons learned from a multivariate analysis of 132 cases at a single institution. Am J Transplant 2005, 5:2992–2998.
Froud T, Yrizarry JM, Alejandro R, Ricordi C: Use of D-STAT to prevent bleeding following percutaneous transhepatic intraportal islet transplantation. Cell Transplant 2004, 13:55–59. [Published erratum appears in Cell Transplant 2004, 13:475.]
Lakey JR, Burridge PW, Shapiro AM: Technical aspects of islet preparation and transplantation. Transpl Int 2003, 6:613–632.
Ryan EA, Bigam D, Shapiro AM: Current indications for pancreas or islet transplant. Diabetes Obes Metab 2006, 8:1–7.
Gaglia JL, Shapiro AM, Weir GC: Islet transplantation: progress and challenge. Arch Med Res 2005, 36:273–280.
Shapiro AM, Lakey JR, Paty BW, et al.: Strategic opportunities in clinical islet transplantation. Transplantation 2005, 79:1304–1307.
Ryan EA, Paty BW, Senior PA, et al.: Five-year followup after clinical islet transplantation. Diabetes 2005, 54:2060–2069. This paper addresses the longer-term follow-up data of islet transplant recipients, including short- and long-term complications. Most recipients who are rendered free from insulin therapy at 1 year after transplantation need to reinstitute insulin therapy within 5 years after transplantation..
Venturini M, Angeli E, Maf P, et al.: Technique, complications, and therapeutic ef.cacy of percutaneous transplantation of human pancreatic islet cells in type 1 diabetes: the role of US. Radiology 2005, 234:617–624.
Goss JA, Soltes G, Goodpastor SE, et al.: Pancreatic islet transplantation: the radiographic approach. Transplantation 2003, 76:199–203.
Moberg L, Johansson H, Lukinius A, et al.: Production of tissue factor by pancreatic islet cells as a trigger of detrimental thrombotic reactions in clinical islet transplantation. Lancet 2002, 360:2039–2045.
Arias-Diaz J, Vara E, Balibrea JL, et al.: CT-guided fine needle approach for intrathymic islet transplantation in a diabetic patient. Pancreas 1996, 12:100–103.
Shuliang S, Guang DY, Xun Q, et al.: Puncture guidance by two-dimensional ultrasonogram: new method of kidney capsule islet transplantation. Transplant Proc 1998, 30:3421–3422.
Weimar B, Rauber K, Brendel MD, et al.: Percutaneous transhepatic catheterization of the portal vein: a combined CT- and fluoroscopy-guided technique. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 1999, 22:342–344.
Osama Gaber A, Chamsuddin A, Fraga D, et al.: Insulin independence achieved using the transmesenteric approach to the portal vein for islet transplantation. Transplantation 2004, 77:309–311.
Paty BW, Bonner-Weir S, Laughlin MR, et al.: Toward development of imaging modalities for islets after transplantation: insights from the National Institutes of Health Workshop on Beta Cell Imaging. Transplantation 2004, 77:1133–1137. This paper summarizes the consensus among investigators in the field, that an accurate and reproducible in vivo measure of functional islet mass is critically needed in order to allow the assessment of islet engraftment and the early recognition of graft loss, leading potentially to greater improvements in islet graft survival and function..
Kriz J, Jirak D, Girman P, et al.: Magnetic resonance imaging of pancreatic islets in tolerance and rejection. Transplantation 2005, 80:1596–1603.
Evgenov NV, Medarova Z, Dai G, et al.: In vivo imaging of islet transplantation. Nat Med 2006, 12:144–148.
Koblas T, Girman P, Berkova Z, et al.: Magnetic resonance imaging of intrahepatically transplanted islets using paramagnetic beads. Transplant Proc 2005, 37:3493–3495.
Neeman Z, Hirshberg B, Tal MG, et al.: Pulmonary angiography for the diagnosis of thromboembolic events in the non-human primate. Transplantation 2004, 78:1025–1029.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neeman, Z., Hirshberg, B., Harlan, D. et al. Radiologic aspects of islet cell transplantation. Curr Diab Rep 6, 310–315 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-006-0066-z
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-006-0066-z