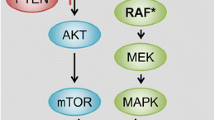
Abstract
Colorectal cancer (CRC) was the third leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States in 2012, and most patients eventually develop metastatic disease. The use of cytotoxic chemotherapy, the antiangiogenesis drug bevacizumab, and the anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies cetuximab and panitumumab have led to an improvement in median OS for metastatic CRC. Despite this improvement in survival, few agents have activity against CRC. Between 2006 and 2012, the FDA approved no new agents for patients with metastatic CRC (mCRC). Recently, the FDA has approved aflibercept and regorafenib for use in the treatment of patients with mCRC, and several new agents are currently in development. This paper reviews the use of new agents and new uses for established agents in mCRC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: •Of importance ••Of major importance
Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Neyman N, Aminou R, Altekruse SF, Kosary CL, Ruhl J, Tatalovich Z, Cho H, Mariotto A, Eisner MP, Lewis DR, Chen HS, Feuer EJ, Cronin KA (eds). SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2009 (Vintage 2009 Populations), National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD, http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2009_pops09/, based on November 2011 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site, 2012.
Van Cutsem E, Geboes K. The multidisciplinary management of gastrointestinal cancer: the integration of cytotoxics and biological in the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Best practice and research. Clin Gastroenterol. 2007;21:1089–108.
Takahashi Y, Kitadai Y, Bucana CD, Cleary KR, Ellis LM. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor, KDR, correlates with vascularity, metastasis, and proliferation of human colon cancer. Cancer Res. 1995;55:3964–8.
Takahashi Y, Tucker SL, Kitadai Y, Koura AN, Bucana CD, Cleary KR, Ellis LM. Vessel counts and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor as prognostic factors in node-negative colon cancer. Arch Surg. 1997;132:541–6.
Ellis LM, Hicklin DJ. VEGF-targeted therapy: mechanisms of anti-tumor activity. Nature reviews. Cancer. 2008;8:579–91.
Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, Cartwright T, Hainsworth J, Heim W, Berlin J, Baron A, Griffing S, Holmgren E, Ferrara N, Fyfe G, Rogers B, Ross R, Kabbinavar F. Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2335–42.
Saltz LB, Clarke S, Diaz-Rubio E, Scheithauer W, Figer A, Wong R, Koski S, Lichinitser M, Yang TS, Rivera F, Couture F, Sirzen F, Cassidy J. Bevacizumab in combination with oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy as first-line therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: a randomized phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:2013–9.
Giantonio BJ, Catalano PJ, Meropol NJ, O’Dwyer PJ, Mitchell EP, Alberts SR, Schwartz MA, Benson AB. Bevacizumab in combination with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin (FOLFOX4) for previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer: results from the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study E200. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:1539–44.
Tabernero J, Aranda E, Gomez A, Massuti B, Sastre J, Abad A, Valladares M, Rivera F, Safont M, Diaz-Rubio E. Phase II study of first line XELOX plus bevacizumab (BEV) for 6 cycles followed by XELOX plus BEV or single-agent (s/a) BEV as maintenance therapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: the MACRO Trial (Spanish Cooperative Group for the Treatment of Digestive Tumors). J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:15s. Abstract 3501.
Vaidyanathan G, Groman A, Wilding G, Fakih MG. Stop and go FOLFOX plus bevacizumab chemotherapy in the first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncology. 2010;79:67–71.
Grothey A, Sugrue MM, Purdie DM, Dong W, Sargent D, Hedrick E, Kozloff M. Bevacizumab beyond progression is associated with prolonged overall survival in metastatic colorectal cancer: results from a large observational cohort study (BRiTE). J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:5326–34.
•• Arnold D, Andre T, Bennouna J, Sastre J, Osterlund PJ, Greil R, Van Cutsem E, Von Moos R, Reyes-Rivera I, Bendahmane B, Kibicka S. Bevacizumab (BEV) plus chemotherapy (CT) continued beyond first progression in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) previously treated with BEV plus CT: results of a randomized phase III intergroup study (TML study). J Clin Oncol. 2012;Abstract CRA3503. The authors demonstrate the benefit of continuing bevacizumab in selected patients with mCRC who progress following frontline therapy with bevacizumab.
Masi G, Loupakis F, Salvatore L, Cremolini C, Fornaro L, Schirripa M, Fea E, Granetto C, Antonuzzo L, Giommoni E, Allegrini G, Cupini S, Boni C, Banzi M, Chiara S, Sonaglio C, Valsuani C, Bonetti A, Boni L, Falcone A. A randomized study evaluating the continuation of bevacizumab beyond progression in metastatic colorectal cancer patients who received bevacizumab as part of first-line treatment: results of the BEBYP trial by the Gruppo Oncologico Nord Ovest (GONO). Ann Oncol. 2012;23(Suppl 9):Abstract LBA17.
Chu QS. Aflibercept(AVE0005): an alternative for inhibiting tumour angiogenesis by vascular endothelial growth factors. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2009;9:263–71.
Holash J, Davis S, Papadopoulos N, Croll SD, Ho L, Russell M, Boland P, Leidich R, Hylton D, Burova E, Ioffe E, Huang T, Radziejewski C, Bailey K, Fandl JP, Daly T, Wiegand SJ, Yancopoulos GD, Rudge JS. VEGF-Trap: a VEGF blocker with potent antitumor effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:11393–8.
•• Van Cutsem E, Tabernero J, Lakomy R, Prenen H, Prausova J, Macarulla T, Ruff P, van Hazel GA, Moiseyenko V, Ferry D, McKendrick J, Polikoff J, Tellier A, Castan R, Allegra C. Addition of aflibercept to fluorouracil, leucovorin, and irinotecan improves survival in a phase III randomized trial in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer previously treated with an oxaliplatin-based regimen. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:3499–506. The authors demonstrate that Aflibercept, a new VEGF inhibitor is effective in mCRC, increasing the response rate and prolonging the median PFS and OS..
Shimizu T, Tolcher AW, Patnaik A, Papadopoulos K, Christensen O, Lin T, Blumenschein GR. Phase I dose escalation study of continuously administered regorafenib (BAY 73-4506), an inhibitor of oncogenic and angiogenic kinases, in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:Abstract3035.
•• Grothey A, Sobrero AF, Siena S, Falcone A, Ychou M, Lenz HJ, Yoshino T, Cihon F, Wagner A, Van Cutsem E. Results of a phase III randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial (CORRECT) of regorafenib plus best supportive care (BSC) versus placebo plus BSC in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) who have progressed after standard therapies. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:Abstract LBA385. The authors demonstrate that regorafenib, a small molecule is superior to placebo in patients with mCRC who are refractory to currently available agents.
Abrams TJ, Lee LB, Murray LJ, Pryer NK, Cherrington JM. SU11248 inhibits KIT and platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta in preclinical models of human small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2003;2:471–8.
Marzola P, Degrassi A, Calderan L, Farace P, Nicolato E, Crescimanno C, Sandri M, Giusti A, Presenti E, Terron A, Sbarbati A, Osculati F. Early antiangiogenic activity of SU11248 evaluated in vivo by dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in an experimental model of colon carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:5827–32.
Saltz LB, Rosen LS, Marshall JL, Belt RJ, Hurwitz HI, Eckhardt SG, Bergsland EK, Haller DG, Lockhart AC, Rocha Lima CM, Huag X, DePrimo SE, Chow-Maneval E, Chao RC, Lenz HJ. Phase II trial of sunitinib in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer after failure of standard therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:4793–9.
Tsuji Y, Satoh T, Tsuji A, Muro K, Yoshida M, Nishina T, Nagase M, Komatsu Y, Kato T, Miyata Y, Mizutani N, Hashigaki S, Lechuga MJ, Denda T. First-line sunitinib plus FOLFIRI in Japanese patients with unresectable/metastatic colorectal cancer. A phase II study. Cancer Sci. 2012;103:1502–7.
Carrato A, Swieboda-Sadlej A, Staszewska-Skurczynska M. Final results from a randomized double-blind phase III study of sunitinib plus FOLFIRI vs placebo plus FOLFIRI in first-line treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 2010;21:Abstract O-0026.
Chen E, Jonker D, Gauthier I, MacLean M, Wells J, Powers J, Seymour L. Phase I study of cediranib in combination with oxaliplatin and infusional 5-Fluorouracil in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:1481–6.
Hoff PM, Hochhaus A, Pestalozzi BC, Tebbutt NC, Li TJ, Kim TW, Koynov KD, Kurteva G, Pinter T, Cheng Y, Eyll BV, Pike L, Fielding A, Robertson JD, Saunders M. Cediranib plus FOLFOX/CAPOX versus placebo plus FOLFOX/CAPOX in patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer: a randomized, double-blind, phase III study (HORIZON II). J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:3596–603.
Schmoll HJ, Cunningham D, Sobrero A, Karapetis CS, Rougier P, Koski SL, Kocakova I, Bondarenko I, Bodoky G, Mainwaring P, Salazar R, Barker P, Mookerjee B, Robertson J, Van Cutsem E. Cediranib with mFOLFOX6 versus bevacizumab with mFOLFOX6 as first-line treatment for patients with advanced colorectal cancer: a double-blind, randomized phase III study (HORIZON III). J Clin Oncol. 2012;3588–95.
Garcia-Carbonero R, Rivera F, Maurel J, Ayoub JM, Moore MJ, Cervantes-Ruiperez A, Asmis TR, Schwartz JD, Ballal S, Tabernero J. A phase II, open-label study evaluating the safety and efficacy of ramucirumab combined with mFOLFOX-6 as first-line therapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: CP12-0709/NCT00862784. J Clin Oncol. 2012;Abstract 533.
Grothey A, Tabernero J, Rougier P, Ballal Shaila, Crane H, Rutstein MD. A randomized. Double-blind, phase III study of the irinotecan-based chemotherapy FOLFIRI plus ramucirumab or placebo in patients with metastatic colorectal carcinoma progressive during or following first-line therapy with bevacizumab, oxaliplatin, and a fluoropyrimidine (RAISE)(NCT01183780). J Clin Oncol. 2012;Abstract TPS3634.
Hess-Stumpp H, Haberey M, Thierauch KH. PTK787/ZK 222584, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor of all known VEGF receptors, represses tumor growth with high efficacy. ChemBioChem. 2005;6:550–7.
Mross K, Drevs J, Muller M, Medinger M, Marme D, Hennig J, Morgan B, Lebwohl D, Masson E, Ho YY, Gunther C, Laurent D, Unger C. Phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study of PTK/ZK, a multiple VEGF receptor inhibitor, in patients with liver metastases from solid tumours. Eur J Cancer. 2005;41:1291–9.
Thomas AL, Trarbach T, Bartel C, Laurent D, Henry A, Poethig M, Wang J, Masson E, Steward W, Vanhoefer U, Wiedenmann B. A phase IB, open-label dose-escalating study of the oral angiogenesis inhibitor PTK787/ZK 222584 (PTK/ZK), in combination with FOLFOX4 chemotherapy in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 2007;18:782–8.
Van Cutsem E, Bajetta E, Valle J, Kohne CH, Hecht JR, Moore M, Germond C, Berg W, Chen BL, Jalava T, Lebwohl D, Meinhardt G, Laurent D, Lin E. Randomized, placebo-controlled, phase III study of oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin with or without PTK787/ZK 222584 in patients with previously treated metastatic colorectal adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:2004–10.
Hecht JR, Trarbach T, Hainsworth JD, Major P, Jager E, Wolff RA, Lloyd-Salvant K, Bodoky G, Pendergrass K, Berg W, Chen BL, Jalava T, Meinhardt G, Laurent D, Lebwohl D, Kerr D. Randomized, placebo-controlled, phase III study of first-line oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy plus PTK787/ZK 222584, an oral vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor, in patients with metastatic colorectal adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:1997–2003.
Yarden Y, Slikowski MX. Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:127–37.
Mendelsohn J, Baselga J. Status of epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists in the biology and treatment of cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:2787–99.
Ng K, Zhu AX. Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor in metastatic colorectal cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2008;65:8–20.
Malumbres M, Barbacid M. RAS oncogenes: the first 30 years. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:459–65.
Lievre A, Bachet JB, Le Corre D, Boige V, Landi B, Emile JF, Cote JF, Tomasic G, Penna C, Ducreux M, Rougier P, Penault-Llorca F, Laurent-Puig P. KRAS mutation status is predictive of response to cetuximab therapy in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2006;66:3992–4005.
Benvenuti S, Sartore-Bianchi A, Di Nicolantonio F, Zanon C, Moroni M, Veronese S, Siena S, Bardelli A. Oncogenic activation of the RAS/RAF signaling pathway impairs the response of metastatic colorectal cancers to anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody therapies. Cancer Res. 2007;67:2643–58.
Goldstein NI, Prewett M, Zuklys K, Rockwell P, Mendelsohn J. Biological efficacy of a chimeric antibody to the epidermal growth factor receptor in a human tumor xenograft model. Clin Cancer Res. 1995;1:1311–8.
Jonker DJ, O’Callaghan CJ, Karapetis CS, Zalcberg JR, Tu D, Au HJ, Berry SR, Krahn M, Price T, Simes RJ, Tebbutt NC, van Hazel G, Wierzbicki R, Langer C, Moore MJ. Cetuximab for the treatment of colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:2040–8.
Karapetis CS, Khambata-Ford S, Jonker DJ, O’Callaghan CJ, Tu D, Tebbutt NC, Simes RJ, Chalchal H, Shapiro JD, Robitaille S, Price TJ, Sheperd L, Au HJ, Langer C, Moore MJ, Zalcberg JR. K-ras mutations and benefit from cetuximab in advanced colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1757–65.
Van Cutsem E, Köhne CH, Láng I, Folprecht G, Nowacki M, Cascinu S, Shchepotin I, Maurel J, Cunningham D, Tejpar S, Schlichting M, Zubel A, Celik I, Rougier P, Ciardiello F. Cetuximab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: updated analysis of overall survival according to tumor KRAS and BRAF mutation status. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:2011–9.
•• Maughan T, Adams R, Smith C, Meade A, Seymour M, Wilson R, Idziaszczyk S, Harris R, Fisher D, Kenny S, Kay E, Mitchell J, Madi A, Jasani B, James M, Bridgewater J, Kennedy M, Claes B, Lambrechts D, Kaplan R, Cheadle R, on behalf of the MRC COIN Trial Investigators. Addition of cetuximab to oxaliplatin-based first-line combination chemotherapy for treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: results of the randomised phase 3 MRC COIN trial. Lancet. 2011;377(9783):2103–14. The authors demonstrate that cetuximab in combination with oxaliplatin does not improve RR or PFS..
•• Tveit K, Curen T, Glimelius B, Pfeiffer P, Sorbye H, Pyrhonen S, Sigurdsson F, Kure E, Ikdahl T, Skovlund E, Fokstuen T, Hansen F, Hofsli E, Birkemeyer E, Johnsson A, Starkhammar H, Yilmaz MK, Keldsen N, Erdal AB, Dajani O, Dahl O, Christoffersen T. Phase III trial of cetuximab with continuous or intermittent fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin (Nordic FLOX) versus FLOX alone in first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: the NORDIC-VII study. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:1755–62. The authors also demonstrate that cetuximab in combination with oxaliplatin does not improve RR or PFS..
Sobrero AF, Maurel J, Fehrenbacher L, Scheithauer W, Abubakr YA, Lutz MP, Vega-Villegas ME, Eng C, Steinhauer EU, Prausova J, Lenz HJ, Borg C, Middleton G, Kroning H, Luppi G, Kisker O, Zubel A, Langer C, Kopit J, Burris HA. EPIC: phase III trial of cetuximab plus irinotecan after fluoropyrimidine and oxaliplatin failure in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:2311–9.
Van Cutsem E, Peeters M, Siena S, Humblet Y, Hendlisz A, Neyns B, Canon JL, Van Laethem JL, Maurel J, Richardson G, Wolf M, Amado RG. Open-label phase III trial of panitumumab plus best supportive care compared with best supportive care alone in patients with chemotherapy-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:1658–64.
Peeters M, Price TJ, Cervantes A, Sobrero AF, Ducreux M, Hotko Y, Andre T, Chan E, Lordick F, Punt CJ, Strickland AH, Wilson G, Ciuleanu TE, Roman L, Van Cutsem E, Tzekova V, Collins S, Oliner KS, Rong A, Gansert J. Randomized phase III study of panitumumab with fluorouracil, leucovorin, and irinotecan (FOLFIRI) compared with FOLFIRI alone as second-line treatment in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:4706–13.
Douillard JY, Siena S, Cassidy J, Tabernero J, Burkes R, Barugel M, Humblet Y, Bodoky G, Cunningham D, Jassem J, Rivera F, Kocakova I, Ruff P, Blasinska-Morawiec M, Smakal M, Canon JL, Rother M, Oliner KS, Wolf M, Gansert J. Randomized phase III trial of panitumumab with infusional fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin (FOLFOX4) versus FOLFOX4 alone as first-line treatment in patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer: the PRIME study. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:4697–705.
Hecht JR, Mitchell E, Chidiac T, Scroggin C, Hagenstad C, Spigel D, Marshall J, Cohn A, McCollum D, Stella P, Deeter R, Shahin S, Amado RG. A randomized phase IIIB trial of chemotherapy, bevacizumab, and panitumumab compared with chemotherapy and bevacizumab alone for metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:672–80.
Tol J, Koopman M, Cats A, Rodenburg CJ, Creemers GJ, Schrama JG, Erdkamp FL, Vos AH, Van Groeningen CJ, Sinnige HA, Richel DJ, Voest EE, Dijkstra JR, Vink-Borger ME, Antonini NF, Mol L, Van Krieken JH, Dalesio O, Punt CJ. Chemotherapy, bevacizumab, and cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:563–72.
Siu LL, Shapiro JD, Jonker DJ, Karapetis CS, Zalcberg JR, Simes J, Couture F, Moore MJ, Price TJ, Siddiqui J, Nott LM, Charpentier D, Liauw WS, Sawyer MB, Jefford M, Magoski NM, Haydon AM, Walters IB, Tu D, O’Callaghan CJ. Phase III randomized trial of cetuximab plus either brivanib alininate or placebo in patients with metastatic chemotherapy refractory K-RAS wild-type colorectal carcinoma: the NCIC clinical trials group and AGITG CO.20 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2012;Abstract 386.
Guertin DA, Sabatini DM. Defining the role of MTOR in cancer. Cancer Cell. 2007;12:9–22.
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Oudard S, Hutson TE, Porta C, Bracarda S, Grunwald V, Thompson JA, Figlin RA, Hollaender N, Kay A, Ravaud A. RECORD-1 Study group. Efficacy of everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase III trial. Lancet. 2008;372:449–56.
Bullock KE, Petros WP, Younis I, Uronis HE, Morse MA, Blobe GC, Zafar SY, Gockerman JP, Lager JJ, Truax R, Meadows KL, Howard LA, O’Neill MM, Broadwater G, Hurwitz HI, Bendell JC. A phase I study of bevacizumab(B) in combination with everolimus (E) and erlotinib (E) in advanced cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011;67:465–74.
Altomare I, Bendell JC, Bullock KE, Uronis HE, Morse MA, Hsu SD, Zafar SY, Blobe GC, Pang H, Honeycutt W, Sutton L, Hurwitz HI. Oncologist. 2011;16:1131–7.
Wolpin BM, Ng Kimmie, Zhu AX, Abrams TA, Enzinger PC, McCleary N, Meyerhardt JA, Schrag D, Kwak EL, Allen JN, Bhargava P, Chan JA, Goessling W, Blaszkowsky LS, Elliott M, Shellock M, Regan E, Fuchs CS. Multicenter phase Ib/II study of everolimus and tivozanib in patients with refractory, metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2012;Abstract 560.
Kondapaka SB, Singh SS, Dasmahapatra GP, Sausville EA, Roy KK. Perifosine, a novel alkylphospholipid, inhibits protein kinase B activation. Mol Cancer Ther. 2003;2:1093–103.
Chiarini F, Del Sole M, Mongiorgi S, Gaboardi GC, Cappellini A, Mantovani I, Follo MY, McCubrey JA, Martelli AM. The novel Akt inhinitor, perifosine, induces caspase-dependent apoptosis and downregulates P-glycoprotein expression in multidrug-resistant human T-acute leukemia cells by a JNK-dependent mechanism. Leukemia. 2008;22:1106–16.
De Siervi A, Marinissen M, Diggs J, Wang XF, Pages G, Senderowicz A. Transcriptional activation of the p21(waf1/cip1) by alkylphospholipids: role of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in the transactivation of the human p21(waf1/cip1) promoter by Sp1. Cancer Res. 2004;64:743–50.
Greco FA, Infante JR, Burris HA, et al. Safety and pharmacokinetic (PK) study of perifosine plus capecitabine (P-CAP) in patients with refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28: Abstract e14086.
Bendell JC, Nemunaitis J, Vukelja SJ, Hagenstad C, Campos LT, Hermann RC, Sportelli P, Gardner L, Richards DA. Randomized placebo-controlled phase II trial of perifosine plus capecitabine as second or third-line therapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:4394–400.
Bendell JC, Ervin TJ, Senzer NN, Richards DA, Firdaus I, Lockhart AC, Cohn AL, Saleh MN, Gardner LR, Sportelli P, Eng C, Cannon S. Results of the X-PECT study: a phase III randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study of perifosine plus capecitabine (P-CAP) versus placebo plus capecitabine (CAP) in patients (pts) with refractory metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). ASCO Meeting Abstracts 30:LBA3501, 2012.
Graff JR, McNulty AM, Hanna KR, Konicek BW, Lynch RL, Bailey SN, Banks C, Capen A, Goode R, Lewis JE, Sams L, Huss KL, Campbell RM, Iversen PW, Neubauer BL, Brown TJ, Musib L, Geeganage S, Thornton D. The protein kinase C beta-selective inhibitor, Enzastaurin (LY317615.HCL), suppresses signaling through AKT pathway, induces apoptosis, and suppresses growth of human colon cancer, and glioblastoma xenografts. Cancer Res. 2005;65:7462–9.
Resta LP, Ermisch S, Collins C, et al. Phase I study of enzastaurin and bevacizumab in patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:Abstract3529.
• Wolff RA, Fuchs M, Bartolomeo MD, Hossain AM, Stoffregen C, Nicol S, Heinemann V. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study of maintenance enzastaurin with 5-Fluorouracil/leucovorin plus bevacizumab after first-line therapy for metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer. 2012;118:4132–8. Maintenance enzaustarin increases toxicity in mCRC..
Disclosure
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Belisario A. Arango and Ikechukwu Akunyili contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arango, B.A., Akunyili, I. Newer Agents in Colon Cancer: What’s Next?. Curr Colorectal Cancer Rep 9, 74–84 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11888-012-0157-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11888-012-0157-y