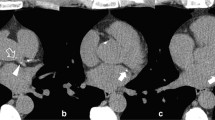
Abstract
Purpose of Review
In this review, we aim to summarize state-of-the-art artificial intelligence (AI) approaches applied to cardiovascular CT and their future implications.
Recent Findings
Recent studies have shown that deep learning networks can be applied for rapid automated segmentation of coronary plaque from coronary CT angiography, with AI-enabled measurement of total plaque volume predicting future heart attack. AI has also been applied to automate assessment of coronary artery calcium on cardiac and ungated chest CT and to automate the measurement of epicardial fat. Additionally, AI-based prediction models integrating clinical and imaging parameters have been shown to improve prediction of cardiac events compared to traditional risk scores.
Summary
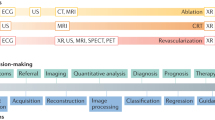
Artificial intelligence applications have been applied in all aspects of cardiovascular CT — in image acquisition, reconstruction and denoising, segmentation and quantitative analysis, diagnosis and decision assistance and to integrate prognostic risk from clinical data and images. Further incorporation of artificial intelligence in cardiovascular imaging holds important promise to enhance cardiovascular CT as a precision medicine tool.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Dey D, Slomka PJ, Leeson P, Comaniciu D, Shrestha S, Sengupta PP, et al. Artificial intelligence in cardiovascular imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73:1317–35.
Hoffmann U, Massaro JM, D’Agostino RB, Kathiresan S, Fox CS, O’Donnell CJ. Cardiovascular event prediction and risk reclassification by coronary, aortic, and valvular calcification in the Framingham Heart Study. J Am Heart Assoc Cardiovasc Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016;5: e003144.
Chiles C, Duan F, Gladish GW, Ravenel JG, Baginski SG, Snyder BS, et al. Association of coronary artery calcification and mortality in the national lung screening trial: a comparison of three scoring methods. Radiology. 2015;276:82–90.
Lin A, Kolossváry M, Motwani M, Išgum I, Maurovich-Horvat P, Slomka PJ, et al. Artificial intelligence in cardiovascular imaging for risk stratification in coronary artery disease. Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging. 2021;3: e200512.
Green M, Marom EM, Konen E, Kiryati N, Mayer A. 3-D Neural denoising for low-dose coronary CT angiography (CCTA). Comput Med Imaging Graph Off J Comput Med Imaging Soc. 2018;70:185–91.
Lossau T, Nickisch H, Wissel T, Bippus R, Schmitt H, Morlock M, et al. Motion artifact recognition and quantification in coronary CT angiography using convolutional neural networks. Med Image Anal. 2019;52:68–79.
Wolterink JM, van Hamersvelt RW, Viergever MA, Leiner T, Išgum I. Coronary artery centerline extraction in cardiac CT angiography using a CNN-based orientation classifier. Med Image Anal. 2019;51:46–60.
Kang E, Koo HJ, Yang DH, Seo JB, Ye JC. Cycle-consistent adversarial denoising network for multiphase coronary CT angiography. Med Phys. 2019;46:550–62.
López-Linares K, Aranjuelo N, Kabongo L, Maclair G, Lete N, Ceresa M, et al. Fully automatic detection and segmentation of abdominal aortic thrombus in post-operative CTA images using deep convolutional neural networks. Med Image Anal. 2018;46:202–14.
Cao L, Shi R, Ge Y, Xing L, Zuo P, Jia Y, et al. Fully automatic segmentation of type B aortic dissection from CTA images enabled by deep learning. Eur J Radiol. 2019;121:108713.
Lee J-G, Kim H, Kang H, Koo HJ, Kang J-W, Kim Y-H, et al. Fully automatic coronary calcium score software empowered by artificial intelligence technology: validation study using three CT cohorts. Korean J Radiol. 2021;22:1764–76.
Lin A, Kolossváry M, Motwani M, Išgum I, Maurovich-Horvat P, Slomka PJ, et al. Artificial intelligence in cardiovascular CT: current status and future implications. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2021;15:462–9.
•• Lin A, Manral N, McElhinney P, Killekar A, Matsumoto H, Kwiecinski J, et al. Deep learning-enabled coronary CT angiography for plaque and stenosis quantification and cardiac risk prediction: an international multicentre study. Lancet Digit Health. 2022;4:e256–65. Findings from this study showed that a deep learning network can be applied to rapidly segment and characterize coronary plaque from coronary CT angiography; with AI-enabled measurement of total plaque volume predicting future heart attack in the multicenter SCOT-HEART trial.
Baskaran L, Maliakal G, Al’Aref SJ, Singh G, Xu Z, Michalak K, et al. Identification and quantification of cardiovascular structures from CCTA: an end-to-end, rapid, pixel-wise, deep-learning method. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020;13:1163–71.
Koo HJ, Lee JG, Ko JY, Lee G, Kang JW, Kim YH, et al. Automated segmentation of left ventricular myocardium on cardiac computed tomography using deep learning. Korean J Radiol. 2020;21:660–9.
• Commandeur F, Goeller M, Razipour A, Cadet S, Hell MM, Kwiecinski J, et al. Fully automated CT quantification of epicardial adipose tissue by deep learning: a multicenter study. Radiol Artif Intell. 2019;1:e190045. This study demonstrated the feasibility of using deep learning to automate epicardial fat quantification with high accuracy compared to expert reader measurement.
Grbic S, Ionasec R, Vitanovski D, Voigt I, Wang Y, Georgescu B, et al. Complete valvular heart apparatus model from 4D cardiac CT. Med Image Anal. 2012;16:1003–14.
Liang L, Kong F, Martin C, Pham T, Wang Q, Duncan J, et al. Machine learning-based 3-D geometry reconstruction and modeling of aortic valve deformation using 3-D computed tomography images. Int J Numer Methods Biomed Eng. 2017;33.
Zheng Y, Barbu A, Georgescu B, Scheuering M, Comaniciu D. Four-chamber heart modeling and automatic segmentation for 3-D cardiac CT volumes using marginal space learning and steerable features. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2008;27:1668–81.
Yeboah J, McClelland RL, Polonsky TS, Burke GL, Sibley CT, O’Leary D, et al. Comparison of novel risk markers for improvement in cardiovascular risk assessment in intermediate-risk individuals. JAMA. 2012;308:788–95.
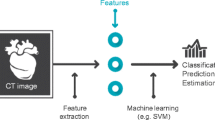
Singh G, Al’Aref SJ, Van Assen M, Kim TS, van Rosendael A, Kolli KK, et al. Machine learning in cardiac CT: basic concepts and contemporary data. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2018;12:192–201.
Yang DH. Application of artificial intelligence to cardiovascular computed tomography. Korean J Radiol. 2021;22:1597.
Isgum I, Rutten A, Prokop M, van Ginneken B. Detection of coronary calcifications from computed tomography scans for automated risk assessment of coronary artery disease. Med Phys. 2007;34:1450–61.
Brunner G, Chittajallu DR, Kurkure U, Kakadiaris IA. Toward the automatic detection of coronary artery calcification in non-contrast computed tomography data. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2010;26:829–38.
Shahzad R, van Walsum T, Schaap M, Rossi A, Klein S, Weustink AC, et al. Vessel specific coronary artery calcium scoring: an automatic system. Acad Radiol. 2013;20:1–9.
Wolterink JM, Leiner T, de Vos BD, van Hamersvelt RW, Viergever MA, Išgum I. Automatic coronary artery calcium scoring in cardiac CT angiography using paired convolutional neural networks. Med Image Anal. 2016;34:123–36.
Wang W, Wang H, Chen Q, Zhou Z, Wang R, Wang H, et al. Coronary artery calcium score quantification using a deep-learning algorithm. Clin Radiol. 2020;75:237.e11-237.e16.
Cano-Espinosa C, González G, Washko GR, Cazorla M, Estépar RSJ. Automated Agatston score computation in non-ECG gated CT scans using deep learning. Proc SPIE-- Int Soc Opt Eng. 2018;10574:105742K.
Lessmann N, Išgum I, Setio AAA, de Vos BD, Ciompi F, de Jong PA, et al. Deep convolutional neural networks for automatic coronary calcium scoring in a screening study with low-dose chest CT. In: Tourassi GD, Armato SG, editors. San Diego, California, United States; 2016 [cited 2022 Apr 16]. p. 978511. Available from: https://proceedings.spiedigitallibrary.org/proceeding.aspx?doi=10.1117/12.2216978
van Velzen SGM, Lessmann N, Velthuis BK, Bank IEM, van den Bongard DHJG, Leiner T, et al. Deep learning for automatic calcium scoring in CT: validation using multiple cardiac CT and chest CT protocols. Radiology. 2020;295:66–79.
Zeleznik R, Foldyna B, Eslami P, Weiss J, Alexander I, Taron J, et al. Deep convolutional neural networks to predict cardiovascular risk from computed tomography. Nat Commun. 2021;12:715.
Eng D, Chute C, Khandwala N, Rajpurkar P, Long J, Shleifer S, et al. Automated coronary calcium scoring using deep learning with multicenter external validation. Npj Digit Med Nature Publishing Group. 2021;4:1–13.
Choi AD, Marques H, Kumar V, Griffin WF, Rahban H, Karlsberg RP, et al. CT evaluation by artificial intelligence for atherosclerosis, stenosis and vascular morphology (CLARIFY): a multi-center, international study. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2021;15:470–6.
Kang D, Dey D, Slomka PJ, Arsanjani R, Nakazato R, Ko H, et al. Structured learning algorithm for detection of nonobstructive and obstructive coronary plaque lesions from computed tomography angiography. J Med Imaging. 2015;2: 014003.
Dey D, Gaur S, Ovrehus KA, Slomka PJ, Betancur J, Goeller M, et al. Integrated prediction of lesion-specific ischaemia from quantitative coronary CT angiography using machine learning: a multicentre study. Eur Radiol. 2018;28:2655–64.
Tesche C, De Cecco CN, Albrecht MH, Duguay TM, Bayer RR, Litwin SE, et al. Coronary CT angiography-derived fractional flow reserve. Radiology. 2017;285:17–33.
Coenen A, Kim Y-H, Kruk M, Tesche C, De Geer J, Kurata A, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of a machine-learning approach to coronary computed tomographic angiography-based fractional flow reserve: result from the MACHINE Consortium. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018;11: e007217.
Alizadehsani R, Hosseini MJ, Khosravi A, Khozeimeh F, Roshanzamir M, Sarrafzadegan N, et al. Non-invasive detection of coronary artery disease in high-risk patients based on the stenosis prediction of separate coronary arteries. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2018;162:119–27.
van Hamersvelt RW, Zreik M, Voskuil M, Viergever MA, Išgum I, Leiner T. Deep learning analysis of left ventricular myocardium in CT angiographic intermediate-degree coronary stenosis improves the diagnostic accuracy for identification of functionally significant stenosis. Eur Radiol. 2019;29:2350–9.
Zreik M, Lessmann N, van Hamersvelt RW, Wolterink JM, Voskuil M, Viergever MA, et al. Deep learning analysis of the myocardium in coronary CT angiography for identification of patients with functionally significant coronary artery stenosis. Med Image Anal. 2018;44:72–85.
Wu D, Wang X, Bai J, Xu X, Ouyang B, Li Y, et al. Automated anatomical labeling of coronary arteries via bidirectional tree LSTMs. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2019;14:271–80.
Hong Y, Commandeur F, Cadet S, Goeller M, Doris MK, Chen X, et al. Deep learning-based stenosis quantification from coronary CT angiography. Proc SPIE-- Int Soc Opt Eng. 2019;10949:109492I.
Zreik M, van Hamersvelt RW, Khalili N, Wolterink JM, Voskuil M, Viergever MA, et al. Deep learning analysis of coronary arteries in cardiac CT angiography for detection of patients requiring invasive coronary angiography. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2020;39:1545–57.
Kumamaru KK, Fujimoto S, Otsuka Y, Kawasaki T, Kawaguchi Y, Kato E, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of 3D deep-learning-based fully automated estimation of patient-level minimum fractional flow reserve from coronary computed tomography angiography. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020;21:437–45.
Mahabadi AA, Berg MH, Lehmann N, Kälsch H, Bauer M, Kara K, et al. Association of epicardial fat with cardiovascular risk factors and incident myocardial infarction in the general population: the Heinz Nixdorf Recall Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;61:1388–95.
Rodrigues ÉO, Morais FFC, Morais N a. OS, Conci LS, Neto LV, Conci A. A novel approach for the automated segmentation and volume quantification of cardiac fats on computed tomography. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2016;123:109–28.
Pérez-Pelegrí M, Monmeneu JV, López-Lereu MP, Pérez-Pelegrí L, Maceira AM, Bodí V, et al. Automatic left ventricle volume calculation with explainability through a deep learning weak-supervision methodology. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021;208: 106275.
Asif A, Charters PFP, Thompson CAS, Komber HMEI, Hudson BJ, Rodrigues JCL. Artificial intelligence can detect left ventricular dilatation on contrast-enhanced thoracic computer tomography relative to cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. Br J Radiol. 2022;20210852.
Aquino GJ, Chamberlin J, Yacoub B, Kocher MR, Kabakus I, Akkaya S, et al. Diagnostic accuracy and performance of artificial intelligence in measuring left atrial volumes and function on multiphasic CT in patients with atrial fibrillation. Eur Radiol [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2022 Apr 4]; Available from: https://link.springer.com/ https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-022-08657-y
Jin C, Feng J, Wang L, Yu H, Liu J, Lu J, et al. Left atrial appendage segmentation and quantitative assisted diagnosis of atrial fibrillation based on fusion of temporal-spatial information. Comput Biol Med. 2018;96:52–68.
Mannil M, von Spiczak J, Manka R, Alkadhi H. Texture analysis and machine learning for detecting myocardial infarction in noncontrast low-dose computed tomography: unveiling the invisible. Invest Radiol. 2018;53:338–43.
O’Brien H, Williams MC, Rajani R, Niederer S. Radiomics and machine learning for detecting scar tissue on CT delayed enhancement imaging. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:847825.
Motwani M, Dey D, Berman DS, Germano G, Achenbach S, Al-Mallah MH, et al. Machine learning for prediction of all-cause mortality in patients with suspected coronary artery disease: a 5-year multicentre prospective registry analysis. Eur Heart J. 2017;38:500–7.
van Rosendael AR, Maliakal G, Kolli KK, Beecy A, Al’Aref SJ, Dwivedi A, et al. Maximization of the usage of coronary CTA derived plaque information using a machine learning based algorithm to improve risk stratification; insights from the CONFIRM registry. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2018;12:204–9.
Nakanishi R, Slomka PJ, Rios R, Betancur J, Blaha MJ, Nasir K, et al. Machine learning adds to clinical and CAC assessments in predicting 10-year CHD and CVD deaths. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2021;14:615–25.
• Tamarappoo BK, Lin A, Commandeur F, McElhinney PA, Cadet S, Goeller M, et al. Machine learning integration of circulating and imaging biomarkers for explainable patient-specific prediction of cardiac events: a prospective study. Atherosclerosis. 2021;318:76–82. This study found that use of machine learning integration of clinical features, circulating, and imaging biomarkers from non-contrast CT improved long-term prediction of cardiac events compared to traditional risk scores such as ASCVD risk scores.
Funding
This work is supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute [1R01HL148787-01A1 and 1R01HL151266]. MCW (FS/ICRF/20/26002) is supported by the British Heart Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Outside the current work, Dr. Dey and Dr. Slomka may receive software royalties from Cedars-Sinai Medical Center. Dr. Williams also reports personal fees from Canon Medical Systems, Siemens Healthineers, and Novartis, outside the submitted work. The remaining authors have no relevant financial interests to disclose.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Mugdha Joshi and Diana Patricia Melo are co-first authors of this manuscript.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Cardiac PET, CT, and MRI
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Joshi, M., Melo, D.P., Ouyang, D. et al. Current and Future Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Cardiac CT. Curr Cardiol Rep 25, 109–117 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11886-022-01837-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11886-022-01837-8