Abstract
Purpose of Review
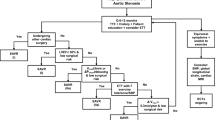
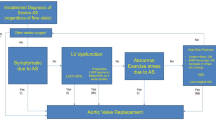
The optimal treatment for asymptomatic patients with severe aortic valve stenosis (AS) is not clearly known. Here, we review the available data on the management of such patients.
Recent Findings
Half of patients with severe AS are asymptomatic at the time of diagnosis, and are at risk for adverse events, including sudden cardiac death. A significant proportion of these patients develop AS-related symptoms within 1 or 2 years. Clinical and echocardiographic characteristics are predictors of poor outcomes and can guide treatment decisions. Several non-randomized studies and meta-analyses have suggested benefit from early AVR for asymptomatic severe AS, including improved all-cause, cardiovascular, and valve-related mortality. Based on the available information, current guidelines suggest aortic valve replacement in the presence of specific characteristic, including left ventricular dysfunction and very severe AS with significantly elevated gradients.
Summary
Although the available data suggests early AVR improves the clinical outcomes of these patients, most patients in current practice are managed conservatively. Six randomized trials are ongoing to better elucidate the ideal management of asymptomatic severe AS patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
•• Lindman BR, Clavel MA, Mathieu P, Lung B, Lancellotti P, Otto CM, et al. Calcific aortic stenosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16006 This is a comprehensive review on aortic stenosis, including epidemiology, pathophysiology, and treatment.
Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Blaha MJ, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics – 2014 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2014;129:e28–e292.
Jacobs JP, Shahian DM, D’Agostino R, Jacobs ML, Kozower BD, Badhwar V, et al. The Society of Thoracic Surgeons National Database 2017 annual report. Ann Thorac Surg. 2017;104:1774–81.
Nishimura RA, Otto CM, Bonow RO, Carabello BA, Erwin JP 3rd, Guyton RA, et al. AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with valvular heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63:e57–e185.
Varadarajan P, Kapoor N, Bansal RC, Pai RG. Clinical profile and natural history of 453 nonsurgical managed patients with severe aortic stenosis. Ann Thorac Surg. 2006;82:2111–5.
Carabello BA, Paulus WJ. Aortic stenosis. Lancet. 2009;373:956–66.
Baumgartner H, Falk V, Bax JJ, De Bonis M, Hamm C, Holm PJ, et al. 2017 ESC/EACTS guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease. Eur Heart J. 2017;38:2739–91.
Nishimura RA, Otto CM, Bonow RO, Carabello BA, Erwin JP 3rd, Fleisher LA, et al. 2017 AHA/ACC focused update of the 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with valvular heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70:252–89.
Pai RG, Kapoor N, Bansal RC, Varadarajan P. Malignant natural history of asymptomatic severe aortic valve stenosis: benefit of aortic valve replacement. Ann Thorac Surg. 2006;82:2116–22.
Pellikka PA, Nishimura RA, Bailey KR, Tajik AJ. The natural history of adults with asymptomatic, hemodynamically significant aortic stenosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1990;15:1012–7.
Pellikka PA, Sarano ME, Nishimura RA, Malouf JF, Bailey KR, Scott CG, et al. Outcomes of 622 adults with asymptomatic, hemodynamically significant aortic stenosis during prolonged follow-up. Circulation. 2005;111:3290–5.
•• Taniguchi T, Morimoto T, Shiommi H, Ando K, Kanamori N, Murata K, et al. Initial surgical versus conservative strategies in patients with asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;66:2827–38 This study is the largest non-randomized study comparing early surgery versus conservative management in patients with asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis.
Rafique AM, Biner S, Ray I, Forrester JS, Tolstrup K, Siegel RJ. Meta-analysis of prognostic value of stress testing in patients with asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis. Am J Cardiol. 2009;104:972–7.
Otto CM, Burwash IG, Legget ME, Munt BI, Fujioka M, Healy NL, et al. Prospective study of asymptomatic valvular stenosis. Clinical, echocardiographic, and exercise predictors of outcome. Circulation. 1997;95:2262–70.
Green P, Cohen DS, Genereux P, McAndrew T, Arnold SV, Alu M, et al. Relation between six-minute walk test performance and outcomes after transcatheter aortic valve implantation (from the PARTNER trial). Am J Cardiol. 2013;112:700–6.
Kitai T, Honda S, Okada Y, Tani T, Kim K, Kaji S, et al. Clinical outcomes in non-surgically managed patients with very severe versus severe aortic stenosis. Heart. 2011;97:2029–32.
Lancellotti P, Lebois F, Simon M, Tombeux C, Chauvel C, Pierard LA. Prognostic importance of quantitative exercise Doppler echocardiography in asymptomatic valvular stenosis. Circulation. 2005;112:I377–82.
Yingchoncharoen T, Gibby C, Rodriguez LL, Grimm RA, Marwick TH. Association of myocardial deformation with outcome in asymptomatic aortic stenosis with normal ejection fraction. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2012;5:719–25.
Saito T, Muro T, Takeda H, Hyodo E, Ehara S, Nakamura Y, et al. Prognostic value of aortic valve area index in asymptomatic patients with severe aortic stenosis. Am J Cardiol. 2012;110:93–7.
Marechaux S, Hachicha Z, Bellouin A, Dumesnil JG, Meimoun P, Pasquet A, et al. Usefulness of exercise-stress echocardiography for risk stratification of true asymptomatic patients with aortic valve stenosis. Eur Heart J. 2010;31:1309–97.
Rosenhek R, Zilberszac R, Schemper M, Czerny M, Mundigler G, Graf S, et al. Natural history of very severe aortic stenosis. Circulation. 2010;121:151–6.
Kang DH, Park SJ, Rim JH, Yun SC, Kim DH, Song JM, et al. Early surgery versus conventional treatment in asymptomatic very severe aortic stenosis. Circulation. 2010;121:1502–9.
Brown ML, Pellikka PA, Schaff HV, Scott CG, Mullany CJ, Sundt TM, et al. The benefits of early aortic valve replacement in asymptomatic patients with severe aortic stenosis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008;135:308–15.
Avakian SD, Grinberg M, Ramirex JAF, Mansur AP. Outcome of adults with asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis. Int J Cardiol. 2006;123:322–7.
Cioffi G, Faggiano P, Vizzardi E, Tarantini L, Cramariuc D, Gerdts E, et al. Prognostic effect of inappropriately high left ventricular mass in asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis. Heart. 2011;97:301–7.
Duncan AI, Lowe BS, Garcia MJ, Xu M, Gillinov AM, Mihaljevic T, et al. Influence of concentric left ventricular remodeling on early mortality after aortic valve replacement. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008;85:2030–9.
Lancellotti P, Donal E, Magne J, Moonen M, O’Connor K, Daubert JC, et al. Risk stratification in asymptomatic moderate to severe aortic stenosis: the importance of the valvular, arterial, and ventricular interplay. Heart. 2010;96:1364–71.
Zito C, Salvia J, Cusma-Piccione M, Antonini-Canterin F, Lentini S, Oreto G, et al. Prognostic significance of valvuloarterial impedance and left ventricular longitudinal function in asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis involving three-cuspid valves. Am J Cardiol. 2011;108:1463–9.
Hachicha Z, Dusmesnil JG, Pibarot P. Usefulness of the valvuloarterial impedance to predict adverse outcome in asymptomatic aortic stenosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54:1003–11.
Briand M, Dumesnil JG, Kadem L, Tongue AG, Rieu R, Garcia D, et al. Reduced systemic arterial compliance impacts significantly on left ventricular afterload and function in aortic stenosis: implication for diagnosis and treatment. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;46:291–8.
Rosenhek R, Binder T, Porenta G, Lang I, Christ G, Schemper M, et al. Predictors of outcomes in severe, asymptomatic aortic stenosis. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:611–7.
Lancellotti P, Magne J, Donal E, Davin L, O’Connor K, Rosca M, et al. Clinical outcome in asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis: insights from the new proposed aortic stenosis grading classification. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;59:235–43.
Das P, Rimington H, Chambers J. Exercise testing to stratify risk in aortic stenosis. Eur Heart J. 2005;26:1309–13.
Lung B, Baron G, Butchart EG, Delahaye F, Gohlke-Barwolf C, Levang OW, et al. A prospective survey of patients with valvular heart disease in Europe: the Euro Heart Survey on valvular heart disease. Eur Heart J. 2033;24:1231–43.
• Genereux P, Stone GW, O’Hara PT, Marquis-Glavel G, Redfors B, Giustino G, et al. Natural history, diagnostic approaches and therapeutic strategies for patients with asymptomatic aortic stenosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;67:2263–88 Meta-analysis of available non-randomized studies comparing conservative management versus early AVR for asymptomatic patients with severe aortic stenosis. This meta-analysis showed improved outcomes with early AVR.
Peidro R, Brion G, Angelino A. Exercise testing in asymptomatic aortic stenosis. Cardiology. 2007;108:258–64.
Lancellotti P, Magne J, Donal E, O’Connor K, Dulgheru R, Rosca M, et al. Determinants and prognostic significance of exercise pulmonary hypertension in asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis. Circulation. 2012;126:851–9.
Clavel MA, Messika-Zeitoun D, Capoulade R, Malouf J, Aggarval S, et al. Impact of aortic valve calcification, as measured by MDCT, on survival in patients with aortic stenosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64:1202–13.
Feuchtner GM, Muller S, Grander W, Alber HF, Bartel T, Friedrich GJ, et al. Aortic valve calcification as quantified with multislice computed tomography predicts short-term clinical outcome in patients with asymptomatic aortic stenosis. J Heart Valve Dis. 2006;15:494–8.
Clavel MA, Messika-Zeitoun D, Pibarot P, Aggarval S, Malouf J, Araoz P, et al. The complex nature of discordant severe calcified artic valve disease grading: new insights from combined Doppler echocardiographic and computed tomographic study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:2329–38.
Weidemann F, Herrmann S, Stork S, Niemann M, Frantz S, Lange V, et al. Impact of myocardial fibrosis in patients with symptomatic severe aortic stenosis. Circulation. 2009;120:577–84.
Azevedo CF, Nigri M, Higuchi ML, Pomerantzeff PM, Spina GC, Sampaio RO, et al. Prognostic significance of myocardial fibrosis quantification by histopathology and magnetic resonance imaging in patients with severe aortic valve disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;56:278–87.
Chin CW, Messika-Zeitoun D, Shah AS, Lefevre G, Bailleul S, Yeung EN, et al. A clinical risk score of myocardial fibrosis predicts adverse outcomes in aortic stenosis. Eur Heart J. 2016;37:713–23.
Kolasa-Trela R, Konieczynska M, Bazanek M, Undas A. Specific changes in circulating cytokines and growth factors induced by exercise stress testing in asymptomatic aortic valve stenosis. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0173787.
Hodges GW, Bang CN, Eugen-Olsen J, Olsen MH, Boman K, Ray S, et al. SuPAR predicts postoperative complications and mortality in patients with asymptomatic aortic stenosis. Open Heart. 2018;5:e000743.
Farre N, Gomez M, Molina L, Cladellas M, Ble M, Roqueta C, et al. Prognostic value of NT-proBNP and an adapted monin score in patients with asymptomatic aortic stenosis. Rev Esp Cardiol. 2014;67:52–7.
Lancellotti P, Moonen M, Magne J, O’Connor K, Cosyns B, Attena E, et al. Prognostic effect of long-axis ventricular dysfunction and B-type natriuretic peptide levels in asymptomatic aortic stenosis. Am J Cardiol. 2010;105:383–8.
Clavel MA, Malouf J, Michelena HI, Suri RM, Jaffe AS, Mahoney DW, et al. B-type natriuretic peptide clinical activation in aortic stenosis impact on long-term survival. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63:2016–25.
Capoudale R, Magne J, Dulgheru R, Hachida Z, Dumesnil JG, O’Connor K, et al. Prognostic value of plasma B-type natriuretic peptide levels after exercise in patients with severe asymptomatic aortic stenosis. Heart. 2014;100:1606–12.
Lund O, Nielsen TT, Emmertsen K, Flo C, Rasmunssen B, Jensen FT, et al. Mortality and worsening of prognostic profile during waiting time for valve replacement in aortic stenosis. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1996;44:289–95.
Zilberszac R, Gabriel H, Schemper M, Laufer G, Maurer G, Rosenhek A. Symptomatic severe aortic stenosis in the elderly. J Am Coll Cardiol Img. 2017;10:43–50.
Heuvelman HJ, van Geldorp MW, Kappetein AP, Geleijnse ML, Galema TW, Bogers AJ, et al. Clinical course of patients diagnosed with severe aortic stenosis in the Rotterdam area: insights from the AVARIJN study. Neth Heart J. 2012;20:487–93.
• Lim WY, Ramasamy A, Lloyd G, Bhattacharyya S. Meta-analysis of the impact of intervention versus symptom-driven management in asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis. Heart. 2017;103:268–72 Meta-analysis of available non-randomized studies comparing conservative management versus early AVR for asymptomatic patients with severe aortic stenosis. This meta-analysis showed no clear benefit from early AVR.
Banovic M, Lung B, Bartunek J, Penicka M, Vanderheyden M, Casselman F, et al. The Aortic Valve replAcemenT versus conservative treatment in Asymptomatic seveRe aortic stenosis (AVATAR trial): protocol update. Am Heart J. 2018;195:153–4.
Ledwoch J, Thiele H. Treatment of asymptomatic aortic stenosis: watchful waiting or early intervention? Heart. 2017;42:528–35.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Andrés M. Pineda and Todd L. Kiefer declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Valvular Heart Disease
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pineda, A.M., Kiefer, T.L. Asymptomatic Severe Aortic Valve Stenosis—When to Intervene: a Review of the Literature, Current Trials, and Guidelines. Curr Cardiol Rep 20, 129 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11886-018-1072-x
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11886-018-1072-x