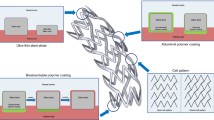
Abstract
Since the advent of percutaneous coronary intervention, enormous advances have been made in the treatment of coronary artery disease. Angioplasty and bare metal stents were plagued by high rates of restenosis leading to repeat revascularization procedures. Examination of the underlying pathophysiology of restenosis led to the development of drug-eluting stents to reduce neointimal hyperplasia. However, as restenosis rates declined, length of dual antiplatelet therapy use and risk of long-term stent thrombosis associated with drug-eluting stents increased. Subsequent generations have improved each facet of stent design. Novel alloys maintain durability and reduce strut thickness to increase deliverability, biocompatible polymers decrease the inflammatory response and improve drug elution kinetics, and new generations of drugs predictably inhibit restenosis. Developments on the horizon include stents with bioabsorbable polymers and platforms. The purpose of this review is to assess the evolution of stent design and the evidence behind each generation and to peer into the future of stent technology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance
Agostoni P, Valgimigli M, Biondi-Zoccai GG, et al. Clinical effectiveness of bare-metal stenting compared with balloon angioplasty in total coronary occlusions: insights from a systematic overview of randomized trials in light of the drug-eluting stent era. Am Heart J. 2006;151:682–9.
Duckers HJ, Nabel EG, Serruys PW. Essentials of restenosis: for the interventional cardiologist. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press; 2007.
Wohrle J, Al-Khayer E, Grotzinger U, et al. Comparison of the heparin coated vs the uncoated Jostent—no influence on restenosis or clinical outcome. Eur Heart J. 2001;22:1808–16.
Mehran R, Nikolsky E, Camenzind E, et al. An Internet-based registry examining the efficacy of heparin coating in patients undergoing coronary stent implantation. Am Heart J. 2005;150:1171–6.
Sousa JE, Serruys PW, Costa MA. New frontiers in cardiology: drug eluting stents. Circulation. 2003;107:2274–9.
Morice MC, Serruys PW, Sousa JE, Fajadet J, Ban Hayashi E, Perin M, et al. Randomized Study with the Sirolimus-Coated Bx Velocity Balloon-Expandable Stent in the Treatment of Patients with de Novo Native Coronary Artery Lesions. A randomized comparison of a sirolimus-eluting stent with a standard stent for coronary revascularization. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1773–80.
Kelbaek H, Thuesen L, Helqvist S, Kløvgaard L, Jørgensen E, Aljabbari S, et al. The Stenting Coronary Arteries in Non-stress/Benestent Disease (SCANDSTENT) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47:449–55.
Moses JW, Leon MB, Popma JJ, et al. Sirolimus-eluting stents versus standard stents in patients with stenosis in a native coronary artery. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:1315–23.
Weisz G, Leon MB, Holmes DR, et al. Five-year follow-up after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation. Results of the SIRIUS (Sirolimus-Eluting Stent in De-Novo Native Coronary Lesions) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53:1488–97.
Stone GW, Ellis SG, Cox DA, et al. A polymer-based, paclitaxel-eluting stent in patients with coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 2004;50:221–31.
Ellis SG, Stone GW, Cox DA, Hermiller J, O’Shaughnessy C, Mann T, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy with paclitaxel-eluting stents: 5-year final results of the TAXUS IV clinical trial (TAXUS IV-SR: Treatment of De Novo Coronary Disease Using a Single Paclitaxel-Eluting Stent). JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2009;2:1248–59.
Windecker S, Remondino A, Eberli FR, Jüni P, Räber L, Wenaweser P, et al. Sirolimus-eluting and paclitaxel-eluting stents for coronary revascularization. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:653–62.
Morice MC, Colombo A, Meier B, Serruys P, Tamburino C, Guagliumi G, et al. Sirolimus- vs paclitaxel-eluting stents in de novo coronary artery lesions: the REALITY trial: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2006;295(8):895–904.
Galløe AM, Thuesen L, Kelbaek H, Thayssen P, Rasmussen K, Hansen PR, et al. Comparison of paclitaxel- and sirolimus-eluting stents in everyday clinical practice: the SORT OUT II randomized trial. JAMA. 2008;299:409–16.
Stone GW, Moses JW, Ellis SG, Schofer J, Dawkins KD, Morice MC, et al. Safety and efficacy of sirolimus- and paclitaxel-eluting coronary stents. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:998–1008.
Daemen J, Wenaweser P, Tsuchida K, Abrecht L, Vaina S, Morger C, et al. Early and late coronary stent thrombosis of sirolimus-eluting and paclitaxel-eluting stents in routine clinical practice: data from a large two-institutional cohort study. Lancet. 2007;369:667–78.
Schömig A, Dibra A, Windecker S, Mehilli J, de Lezo Suárez J, Kaiser C, et al. A meta-analysis of 16 randomized trials of sirolimus-eluting stents versus paclitaxel-eluting stents in patients with coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;50:1373–80.
Stettler C, Wandel S, Allemann S, Kastrati A, Morice MC, Schömig A, et al. Outcomes associated with drug-eluting and bare-metal stents: a collaborative network meta-analysis. Lancet. 2007;370:937–48.
Holmes Jr DR, Kereiakes DJ, Garg S, Serruys PW, Dehmer GJ, Ellis SG, et al. Stent thrombosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;56:1357–65.
Mauri L, Hsieh WH, Massaro JM, Ho KK, D’Agostino R, Cutlip DE. Stent thrombosis in randomized clinical trials of drug-eluting stents. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:1020–9.
Kastrati A, Mehilli J, Dirschinger J, Dotzer F, Schühlen H, Neumann FJ, et al. Intracoronary stenting and angiographic results: strut thickness effect on restenosis outcome (ISAR-STEREO) trial. Circulation. 2001;103:2816–21.
Yoshitomi Y, Kojima S, Yano M, Sugi T, Matsumoto Y, Saotome M, et al. Does stent design affect probability of restenosis? A randomized trial comparing Multilink stents with GFX stents. Am Heart J. 2001;142:445–51.
Pache J, Kastrati A, Mehilli J, Schühlen H, Dotzer F, Hausleiter J, et al. Intracoronary stenting and angiographic results: strut thickness effect on restenosis outcome (ISAR-STEREO-2) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;41:1283–8.
Stone GW, Midei M, Newman W, Sanz M, Hermiller JB, Williams J, et al. Comparison of an everolimus-eluting stent and a paclitaxel-eluting stent in patients with coronary artery disease: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2008;299:1903–13.
Applegate RJ, Yaqub M, Hermiller JB, Sood P, Yu S, Doostzadeh J, et al. Long-term (three-year) safety and efficacy of everolimus-eluting stents compared to paclitaxel-eluting stents (from the SPIRIT III Trial). Am J Cardiol. 2011;107:833–40.
Stone GW, Rizvi A, Newman W, Mastali K, Wang JC, Caputo R, et al. Everolimus-eluting versus paclitaxel-eluting stents in coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1663–74.
Stone GW, Rizvi A, Sudhir K, Newman W, Applegate RJ, Cannon LA, et al. Randomized comparison of everolimus- and paclitaxel-eluting stents. 2-year follow-up from the SPIRIT (Clinical Evaluation of the XIENCE V Everolimus Eluting Coronary Stent System) IV trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58:19–25.
Kedhi E, Joesoef KS, McFadden E, Wassing J, van Mieghem C, Goedhart D, et al. Second-generation everolimus-eluting and paclitaxel-eluting stents in real-life practice (COMPARE): a randomised trial. Lancet. 2010;375:201–9.
Smits PC, Kedhi E, Royaards KJ, Joesoef KS, Wassing J, Rademaker-Havinga TA, et al. 2-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial of everolimus- and paclitaxel-eluting stents for coronary revascularization in daily practice. COMPARE (Comparison of the everolimus eluting XIENCE-V stent with the paclitaxel eluting TAXUS LIBERTÉ stent in all-comers: a randomized open label trial). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58:11–8.
Jensen LO, Thayssen P, Christiansen EH, Tilsted HH, Maeng M, Hansen KN, et al. 2-year patient-related versus stent-related outcomes: the SORT OUT IV (Scandinavian Organization for Randomized Trials With Clinical Outcome IV) Trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60:1140–7.
Jensen LO, Thayssen P, Hansen HS, Christiansen EH, Tilsted HH, Krusell LR, et al. Randomized comparison of everolimus-eluting and sirolimus-eluting stents in patients treated with percutaneous coronary intervention: the Scandinavian Organization for Randomized Trials with Clinical Outcome IV (SORT OUT IV). Circulation. 2012;125:1246–55. Demonstrated that second generation everolimus-eluting stents are noninferior to first generation sirolimus-eluting stents and that first generation stents may have a higher rate of long-term stent thrombosis.
Kimura T, Morimoto T, Natsuaki M, Shiomi H, Igarashi K, Kadota K, et al. Comparison of everolimus-eluting and sirolimus-eluting coronary stents: 1-year outcomes from the Randomized Evaluation of Sirolimus-eluting Versus Everolimus-eluting stent Trial (RESET). Circulation. 2012;126:1225–36.
Räber L, Jüni P, Nüesch E, Kalesan B, Wenaweser P, Moschovitis A, et al. Long-term comparison of everolimus-eluting and sirolimus-eluting stents for coronary revascularization. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57:2143–51. Demonstrated that everolimus-eluting stents likely have a long-term benefit over sirolimus-eluting stents driven by decreased incidence of stent thrombosis.
de Waha A, Dibra A, Byrne RA, Ndrepepa G, Mehilli J, Fusaro M, et al. Everolimus-eluting versus sirolimus-eluting stents: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2011;4:371–7.
Jensen L, Thayssen P, Maeng M, et al. Three-year outcomes after revascularization with everolimus- and sirolimus-eluting stents from the SORT OUT IV trial. J Am Coll Cardiol Intv. 2014;7:840–8.
Di Lorenzo E, Sauro R, Varricchio A, et al. Randomized comparison of everolimus-eluting stents and sirolimus-eluting stent in patients with ST elevation myocardial infarction: RACES-MI trial. J Am Coll Cardiol Intv. 2014;7:849–56. Demonstrated that everolimus-eluting stents are as effective as sirolimus-eluting stents but safer due to associated decreased risk of ST.
Kandzari DE, Leon MB, Popma JJ, Fitzgerald PJ, O’Shaughnessy C, Ball MW, et al. Comparison of zotarolimus-eluting and sirolimus-eluting stents in patients with native coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48:2440–7.
Moussa ID, Klein LW, Shah B, Mehran R, Mack MJ, Brilakis ES, et al. Consideration of a new definition of clinically relevant myocardial infarction after coronary revascularization procedures: an expert consensus document from the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:1563–70.
Eisenstein EL, Leon MB, Kandzari DE, Mauri L, Edwards R, Kong DF, et al. Long-term clinical and economic analysis of the Endeavor zotarolimus-eluting stent versus the cypher sirolimus-eluting stent: 3-year results from the ENDEAVOR III trial (Randomized Controlled Trial of the Medtronic Endeavor Drug [ABT-578] Eluting Coronary Stent System Versus the Cypher Sirolimus-Eluting Coronary Stent System in De Novo Native Coronary Artery Lesions). JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2009;2:1199–207.
Maeng M, Tilsted HH, Jensen LO, Kaltoft A, Kelbæk H, Abildgaard U, et al. 3-year clinical outcomes in the randomized SORT OUT III superiority trial comparing zotarolimus- and sirolimus-eluting coronary stents. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2012;5:812–8.
Stone GW, Teirstein PS, Meredith IT, et al. The PLATINUM (A Prospective, Randomized, Multicenter Trial to Assess an Everolimus-Eluting Coronary Stent System [PROMUS Element] for the Treatment of up to Two De Novo Coronary Artery Lesions) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57:1700–8.
Williams P, Mamas M, Morgan K, El-Omar M, Clarke B, Bainbridge A, et al. Longitudinal stent deformation: a retrospective analysis of frequency and mechanisms. Euro Interv. 2012;8:267–74.
Orrniston JA et al. JACC: Cardiovasc Interv. 2011;4:1310–7.
Chalet Y, Panes F, Chevalier B, Monassier JP, Spaulding C, Lancelin B, et al. Should we avoid ostial implantations of Wiktor stents? Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn. 1994;32:376–9.
Leibundgut G, Gick M, Toma A, et al. Longitudinal compression of the platinum-chromium everolimus-eluting stent during coronary implantation: predisposing mechanical properties, incidence, and predictors in a large patient cohort. Cathet Cardiovasc Interv. 2013;81:E206–14.
Tada T, Byrne RA, Cassese S, King L, Schulz S, Mehilli J, et al. Comparative efficacy of 2 zotarolimus-eluting stent generations: resolute versus endeavor stents in patients with coronary artery disease. Am Heart J. 2013;165:80–6. Demonstrated that Resolute zotarolimus-eluting stents are superior with regards to restenosis rates compared to Endeavor zotarolimus-eluting stents due to improved drug release kinetics.
Park KW, Lee JM, Kang SH, Ahn HS, Yang HM, Lee HY, et al. Safety and efficacy of second-generation everolimus-eluting Xience V stents versus zotarolimus-eluting resolute stents in real-world practice: patient-related and stent-related outcomes from the multicenter prospective EXCELLENT and RESOLUTE-Korea registries. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;61:536–44. Demonstrated that everolimus-eluting stents and Resolute zotarolimus-eluting stents have similar safety and efficacy over 1 year follow up.
von Birgelen C, Basalus MW, Tandjung K, van Houwelingen KG, Stoel MG, Louwerenburg JH, et al. A randomized controlled trial in second-generation zotarolimus-eluting Resolute stents versus everolimus-eluting Xience V stents in real-world patients: the TWENTE trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;59:1350–61. Demonstrated that Resolute zotarolimus-eluting stents are noninferior to everolimus-eluting stents in a real world population of patients with complex lesions.
Serruys PW, Silber S, Garg S, van Geuns RJ, Richardt G, Buszman PE, et al. Comparison of zotarolimus-eluting and everolimus-eluting coronary stents. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:136–46.
von Birgelen C, Sen H, Lam MK, Danse PW, et al. Third-generation zotarolimus-eluting and everolimus-eluting stents in all-comer patients requiring a percutaneous coronary intervention (DUTCH PEERS): a randomised, single-blind, multicentre, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2014;383:413–23. Demonstrated, again, that Resolute zotarolimus-eluting stents and everolimus-eluting stents perform comparably with regards to safety and efficacy with no significant difference in rates of stent thrombosis.
Palmerini T, Biondi-Zoccai G, Della Riva D, Stettler C, Sangiorgi D, D’Ascenzo F, et al. Stent thrombosis with drug-eluting and bare-metal stents: evidence from a comprehensive network meta-analysis. Lancet. 2012;379:1393–402. Demonstrated that colbalt chromium everolimus-eluting stents have the lowest rate of stent thrombosis in this comparison of bare metal stent and various drug-eluting stents.
Palmerini T, Biondi-Zoccai G, Della Riva D, Mariani A, Sabaté M, Valgimigli M, et al. Clinical outcomes with drug-eluting and bare-metal stents in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: evidence from a comprehensive network meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:496–504.
Bangalore S, Kumar S, Fusaro M, Amoroso N, et al. Short- and long-term outcomes with drug-eluting and bare-metal coronary stents: a mixed-treatment comparison analysis of 117 762 patient-years of follow-up from randomized trials. Circulation. 2012;125:2873–91. This metaanalysis evaluating the safety and efficacy of various drug-eluting stents and bare metal stents demonstrated that everolimus-eluting stents, sirolimus-eluting stents, and Resolute zotarolimus-eluting stents have the greatest efficacy and everolimus-eluting stents may be the safest.
Finn AV, Joner M, Nakazawa G, Kolodgie F, Newell J, John MC, et al. Pathological correlates of late drug-eluting stent thrombosis: strut coverage as a marker of endothelialization. Circulation. 2007;115:2435–41.
Serruys PW, Farooq V, Kalesan B, de Vries T, Buszman P, Linke A, et al. Improved safety and reduction in stent thrombosis associated with biodegradable polymer-based biolimus-eluting stents versus durable polymer-based sirolimus-eluting stents in patients with coronary artery disease: final 5-year report of the LEADERS (Limus Eluted From A Durable Versus ERodable Stent Coating) randomized, noninferiority trial. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2013;6:777–89. Demonstrated that biodegradable polymers may reduce the risk of very late stent thrombosis associated with first generation drug-eluting stents.
Smits PC, Hofma S, Togni M, Vázquez N, Valdés M, Voudris V, et al. Abluminal biodegradable polymer biolimus-eluting stent versus durable polymer everolimus-eluting stent (COMPARE II): a randomised, controlled, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2013;381:651–60.
Natsuaki M, Kozuma K, Morimoto T, Kadota K, Muramatsu T, Nakagawa Y, et al. Biodegradable polymer biolimus-eluting stent versus durable polymer everolimus-eluting stent: a randomized, controlled, noninferiority trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:181–90.
Byrne RA, Kastrati A, Kufner S, Massberg S, Birkmeier KA, Laugwitz KL, et al. Randomized, non-inferiority trial of three limus agent-eluting stents with different polymer coatings: the Intracoronary Stenting and Angiographic Results: Test Efficacy of 3 Limus-Eluting Stents (ISAR-TEST-4) Trial. Eur Heart J. 2009;30:2441–9.
Meredith IT, Verheye S, Dubois CL, Dens J, Fajadet J, Carrié D, et al. Primary endpoint results of the EVOLVE trial: a randomized evaluation of a novel bioabsorbable polymer-coated, everolimus-eluting coronary stent. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;59:1362–70.
Christiansen EH, Jensen LO, Thayssen P, Tilsted HH, Krusell LR, Hansen KN, et al. Biolimus-eluting biodegradable polymer-coated stent versus durable polymer-coated sirolimus-eluting stent in unselected patients receiving percutaneous coronary intervention (SORT OUT V): a randomised non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2013;381:661–9.
Krucoff MW, Kereiakes DJ, Petersen JL, Mehran R, Hasselblad V, Lansky AJ, et al. A novel bioresorbable polymer paclitaxel-eluting stent for the treatment of single and multivessel coronary disease: primary results of the COSTAR (Cobalt Chromium Stent With Antiproliferative for Restenosis) II study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;51:1543–52.
Bangalore S, Toklu B, Amoroso N, Fusaro M, Kumar S, Hannan EL, et al. Bare metal stents, durable polymer drug eluting stents, and biodegradable polymer drug eluting stents for coronary artery disease: mixed treatment comparison meta-analysis. BMJ. 2013;347:f6625. This meta-analysis evaluating bare metal stents, drug-eluting stents, and drug-eluting stents with bioresorbable polymers demonstrated that everolimus-eluting stents and Resolute zotarolimus-eluting stents have the best combination of safety and efficacy.
Navarese EP, Tandjung K, Claessen B, Andreotti F, Kowalewski M, Kandzari DE, et al. Safety and efficacy outcomes of first and second generation durable polymer drug eluting stents and biodegradable polymer biolimus eluting stents in clinical practice: comprehensive network meta-analysis. BMJ. 2013;347:f6530. Demonstrated that bioresorbable polymers have a significantly higher rate of myocardial infarction when compared to everolimus-eluting stents and Resolute zotarolimus-eluting stents.
Palmerini T, Biondi-Zoccai G, Della Riva D, Mariani A, Sabaté M, Smits PC, et al. Clinical outcomes with bioabsorbable polymer- versus durable polymer-based drug-eluting and bare-metal stents: evidence from a comprehensive network meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63:299–307.
Nishio S, Kosuga K, Igaki K, Okada M, Kyo E, Tsuji T, et al. Long-term (>10 years) clinical outcomes of first-in-human biodegradable poly-l-lactic acid coronary stents: Igaki-Tamai stents. Circulation. 2012;125:2343–53. This 10 year investigation of bioresorbable stents demonstrated a good safety and efficacy profile with the stent struts mostly disappearing by 3 years follow-up.
Diletti R, Serruys PW, Farooq V, Sudhir K, Dorange C, Miquel-Hebert K, et al. ABSORB II randomized controlled trial: a clinical evaluation to compare the safety, efficacy, and performance of the Absorb everolimus-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffold system against the XIENCE everolimus-eluting coronary stent system in the treatment of subjects with ischemic heart disease caused by de novo native coronary artery lesions: rationale and study design. Am Heart J. 2012;164:654–63.
Capodanno D, Gori T, Nef H, Latib A, Mehilli J, Lesiak M, Caramanno G, Naber C, Di Mario C, Colombo A, Capranzano P, Wiebe J, Araszkiewicz A, Geraci S, Pyxaras S, Mattesini A, Naganuma T, Münzel T, Tamburino C. Percutaneous coronary intervention with everolimus-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffolds in routine clinical practice: early and midterm outcomes from the European multicentre GHOST-EU registry. EuroIntervention. 2014 Jul 18. [Epub ahead of print]
Rasmussen K, Maeng M, Kaltoft A, Thayssen P, Kelbaek H, Tilsted HH, et al. Efficacy and safety of zotarolimus-eluting and sirolimus-eluting coronary stents in routine clinical care (SORT OUT III): a randomised controlled superiority trial. Lancet. 2010;375:1090–9.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
ᅟ
Conflict of Interest
Gregory Katz, Bhisham Harchandani, and Binita Shah declare that they have no conflict of interest. Binita Shah was partially funded by an NIH grant (UL1 TR000038).
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Coronary Heart Disease
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katz, G., Harchandani, B. & Shah, B. Drug-Eluting Stents: the Past, Present, and Future. Curr Atheroscler Rep 17, 11 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-014-0485-2
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-014-0485-2