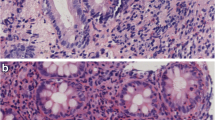
Abstract
Eosinophilic esophagitis has become a diagnosis familiar to allergists and immunologists who treat pediatric patients presenting with complaints of recurrent vomiting, feeding difficulty, abdominal pain, dysphagia, and food impaction. Over the past 3 years, published research has addressed several clinically important issues, including incidence among special patient populations, adult patients and familial cases, diagnostic features, natural history and complications, therapies with topical steroids, and pathogenesis with distinct genetic markers of the disorder.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Collins MH, et al.: Eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults: a systematic review and consensus recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology 2007, 133:1342–1363.
Noel RJ, Putnam PE, Rothenberg ME: Eosinophilic esophagitis. N Engl J Med 2004, 351:940–941.
Gill R, Durst P, Rewalt M, et al.: Eosinophilic esophagitis disease in children from West Virginia: a review of the last decade (1995–2004). Am J Gastroenterol 2007, 102:2281–2285.
Wang FY, Gupta SK, Fitzgerald JF: Is there a seasonal variation in the incidence or intensity of allergic eosinophilic esophagitis in newly diagnosed children? J Clin Gastroenterol 2007, 41:451–453.
Vanderheyden AD, Petras RE, DeYoung BR, et al.: Emerging eosinophilic (allergic) esophagitis: increased incidence or increased recognition? Arch Pathol Lab Med 2007, 131:777–779.
Martin de Carpi J, Gomez Chiari M, Castejon Ponce E, et al.: [Increasing diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis in Spain]. An Pediatr (Barc) 2005, 62:333–339.
Konikoff MR, Noel RJ, Blanchard C, et al.: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of fluticasone propionate for pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2006, 131:1381–1391.
Assa’ad A: Eosinophilic esophagitis: association with allergic disorders. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 2008, 18:119–132.
Roy-Ghanta S, Larosa DF, Katzka DA: Atopic characteristics of adult patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008, 6:531–535.
Pentiuk SP, Miller CK, Kaul A: Eosinophilic esophagitis in infants and toddlers. Dysphagia 2007, 22:44–48.
Kerlin P, Jones D, Remedios M, et al.: Prevalence of eosinophilic esophagitis in adults with food bolus obstruction of the esophagus. J Clin Gastroenterol 2007, 41:356–361.
Lee GS, Craig PI, Freiman JS, et al.: Intermittent dysphagia for solids associated with a multiringed esophagus: clinical features and response to dilatation. Dysphagia 2007, 22:55–62.
Byrne KR, Panagiotakis PH, Hilden K, et al.: Retrospective analysis of esophageal food impaction: differences in etiology by age and gender. Dig Dis Sci 2007, 52:717–721.
Prasad GA, Talley NJ, Romero Y, et al.: Prevalence and predictive factors of eosinophilic esophagitis in patients presenting with dysphagia: a prospective study. Am J Gastroenterol 2007, 102:2627–2632.
Schoepfer AM, Gschossmann J, Scheurer U, et al.: Esophageal strictures in adult eosinophilic esophagitis: dilation is an effective and safe alternative after failure of topical corticosteroids. Endoscopy 2008, 40:161–164.
Schaefer ET, Fitzgerald JF, Molleston JP, et al.: Comparison of oral prednisone and topical fluticasone in the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis: a randomized trial in children. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008, 6:165–173.
Aceves SS, Bastian JF, Newbury RO, et al.: Oral viscous budesonide: a potential new therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis in children. Am J Gastroenterol 2007, 102:2271–2279; quiz 2280.
Zink DA, Amin M, Gebara S, et al.: Familial dysphagia and eosinophilia. Gastrointest Endosc 2007, 65:330–334.
Collins MH, Blanchard C, Abonia JP, et al.: Clinical, pathologic, and molecular characterization of familial eosinophilic esophagitis compared with sporadic cases. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008, 6:621-629.
Straumann A, Bussmann C, Zuber M, et al.: Eosinophilic esophagitis: analysis of food impaction and perforation in 251 adolescent and adult patients. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008, 6:598–600.
Chehade M, Sampson HA, Morotti RA, et al.: Esophageal subepithelial fibrosis in children with eosinophilic esophagitis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2007, 45:319–328.
Blanchard C, Wang N, Stringer KF, et al.: Eotaxin-3 and a uniquely conserved gene-expression profile in eosinophilic esophagitis. J Clin Invest 2006, 116:536–547.
Blanchard C, Mingler MK, Vicario M, et al.: IL-13 involvement in eosinophilic esophagitis: transcriptome analysis and reversibility with glucocorticoids. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007, 120:1292–1300.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Assa’ad, A. Gastrointestinal eosinophil-mediated disorders and their treatment. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 9, 26–29 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-009-0004-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-009-0004-7