Abstract
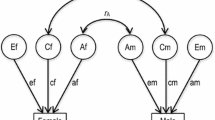
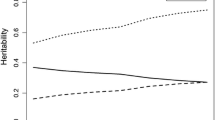
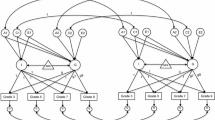
Identical and fraternal twins (N = 540, age 8 to 18 years) were tested on three different measures of writing (Woodcock-Johnson III Tests of Achievement—Writing Samples and Writing Fluency; Handwriting Copy from the Group Diagnostic Reading and Aptitude Achievement Tests), three different language skills (phonological awareness, rapid naming, and vocabulary), and three different reading skills (word recognition, spelling, and reading comprehension). Substantial genetic influence was found on two of the writing measures, writing samples and handwriting copy, and all of the language and reading measures. Shared environment influences were generally not significant, except for Vocabulary. Non-shared environment estimates, including measurement error, were significant for all variables. Genetic influences among the writing measures were significantly correlated (highest between the speeded measures writing fluency and handwriting copy), but there were also significant independent genetic influences between copy and samples and between fluency and samples. Genetic influences on writing were significantly correlated with genetic influences on all of the language and reading skills, but significant independent genetic influences were also found for copy and samples, whose genetic correlations were significantly less than 1.0 with the reading and language skills. The genetic correlations varied significantly in strength depending on the overlap between the writing, language, and reading task demands. We discuss implications of our results for education, limitations of the study, and new directions for research on writing and its relations to language and reading.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berninger, V. W., Abbott, R. D., Abbott, S. P., Graham, S., & Richards, T. (2002). Writing and reading: Connections between language by hand and language by eye. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 35, 39–56.
Berninger, V., & Fuller, F. (1992). Gender differences in orthographic, verbal, and compositional fluency: Implications for diagnosis of writing disabilities in primary grade children. Journal of School Psychology, 30, 363–382. Berninger and Fuller.
Berninger, V. W., Nielsen, K. H., Abbott, R. D., Wijsman, E., & Raskind, W. (2008). Gender differences in severity of writing and reading disabilities. Journal of School Psychology, 46, 151–172.
Betjemann, R. S., Keenan, J. M., Olson, R. K., & DeFries, J. C. (2011). Choice of reading comprehension test influences the outcomes of genetic analyses. Scientific Studies of Reading, 15(4), 363–382. doi:10.1080/10888438.2010.493965.
Betjemann, R. S., Willcutt, E. G., Olson, R. K., Keenan, J. M., DeFries, J. C., & Wadsworth, S. J. (2008). Word reading and reading comprehension: Stability, overlap and independence. Reading and Writing, 21, 539–558.
Byrne, B., Coventry, W. L., Olson, R. K., Hulslander, J., Wadsworth, S., DeFries, J. C., et al. (2008). A behavior-genetic analysis of orthographic learning, spelling, and decoding. Journal of Research in Reading, 31, 8–21.
Byrne, B., Coventry, W. L., Olson, R. K., Samuelsson, S., Corley, R., Willcutt, E. G., et al. (2009). Genetic and environmental influences on aspects of literacy and language in early childhood: Continuity and change from preschool to grade 2. Journal of Neurolinguistics, 22, 219–236.
Camarata, S., & Woodcock, R. (2006). Sex differences in processing speed: Developmental effects in males and females. Intelligence, 34, 231–252. doi:10.1016/jintell.2005.12.001.
Compton, D. L., Olson, R. K., DeFries, J. C., & Pennington, B. F. (2002). Are all RAN created equal? Comparing the relationships among two different formats of alphanumeric RAN and various word reading skills in normally achieving and reading disabled individuals. Scientific Studies of Reading, 6(4), 343–368.
DeFries, J. C., Filipek, P. A., Fulker, D. W., Olson, R. K., Pennington, B. F., & Smith, S. D. (1997). Colorado learning disabilities research center. Learning Disabilities, 8, 7–19.
DeFries, J. C., & Fulker, D. W. (1985). Multiple regression analysis of twin data. Behavior Genetics, 15, 467–478.
DeFries, J. C., & Fulker, D. W. (1988). Multiple regression analysis of twin data: Etiology of deviant scores versus individual differences. Acta Geneticae Medicae et Gemellologiae: Twin Research, 37, 205–216.
Denckla, M. B., & Rudel, R. G. (1976). Rapid “automatized” naming (R.A.N.): Dyslexia differentiated from other learning disabilities. Neuropsychologia, 14, 471–479.
Dunn, L. M., & Dunn, M. (1997). Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test-III. Circle Pines: American Guidance Service.
Fitzgerald, J., & Shanahan, T. (2000). Reading and writing relations and their development. Educational Psychologist, 35, 39–50.
Friend, A., DeFries, J.C., & Olson, R.K. (2008). Parental education moderates genetic influences on reading disability. Psychological Science, 19, 1124–1130. PubMed Central ID# NIHMSID63472.
Gayán, J., & Olson, R. K. (2001). Genetic and environmental influences on orthographic and phonological skills in children with reading disabilities. Developmental Neuropsychology, 20(2), 487–511.
Gayán, J., & Olson, R. K. (2003). Genetic and environmental influences on individual differences in printed word recognition. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 84, 97–123.
Graham, S., Berninger, V., Weintraub, N., & Schafer, W. (1998). The development of handwriting fluency and legibility in grades l through 9. Journal of Educational Research, 92, 42–52.
Graham, S., Harris, K. R., & Fink, B. (2002). Contributions of spelling instruction to the spelling, writing, and reading of poor spellers. Journal of Educational Psychology, 94, 669–686.
Harlaar, N., Cutting, L., Deater-Deckard, K., DeThorne, L. S., Justice, L. M., Schatschneider, C., et al. (2010). Predicting individual differences in reading comprehension: A twin study. Annals of Dyslexia, 60, 265–288. doi:10.1007/s11881-010-0044-7.
Harlaar, N., Spinath, F. M., Dale, P. S., & Plomin, R. (2005). Genetic influences on early word recognition abilities and disabilities: A study of 7-year-old twins. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 46, 373–384.
Harris, K.R., & Graham, S. (2011). “An adjective is a word hanging down from a noun”: Learning to write and students with learning disabilities. Annals of Dyslexia. doi:10.1007/s11881-011-0057-x.
Hooper, S.R., Costa, L., McBee, M., Porter, F., Anderson, K.L., Yerby, D.C., Childress, A., & Knuth, S.B. (2011). A written language intervention for at-risk second grade students: A randomized controlled trial of the process assessment of the learner lesson plans in a tier 2 response-to-intervention (RtI) model. Annals of Dyslexia. doi:10.1007/s11881-011-0056-y.
Jastak, S., & Wilkinson, G. S. (1984). The Wide Range Achievement Test-Revised: Administration manual. Wilmington: Jastak Associates, Inc.
Jenkins, J. R., Johnson, E., & Hileman, J. (2004). When is reading also writing: Sources of individual differences on the new reading performance assessments. Scientific Studies of Reading, 8, 125–151.
Keenan, J. M., Betjemann, R., Wadsworth, S. J., DeFries, J. C., & Olson, R. K. (2006). Genetic and environmental influences on reading and listening comprehension. Journal of Research in Reading, 29, 75–91.
Kovas, Y., Haworth, C. M. A., Dale, P. S., & Plomin, R. (2007). The genetic and environmental origins of learning abilities and disabilities in the early school years. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 72, 1–144.
Markwardt, F. C., Jr. (1998). Peabody Individual Achievement Test—Revise-Normative Update. Circle Pines: American Guidance Service.
McGue, M., & Bouchard, T. J., Jr. (1984). Adjustment of twin data for the effects of age and sex. Behavior Genetics, 14, 325–343.
Miller, B., & McCardle, P. (2011a). Reflections on the need for continued research on writing. Reading and Writing, 24(2), 121–132.
Miller, B., & McCardle, P. (2011b). Moving closer to a public health model of language and learning disabilities: The role of genetics and the search of etiologies. Behavior Genetics, 41, 1–5. doi:10.1007/s10519-010-9439-9.
Neale, M.C., Boker, S.M., Xie, G., & Maes, H.H. (2002). Mx: Statistical Modeling. VCU Box 900126, Richmond, VA 23298: Department of Psychiatry. 6th Edition.
Nichols, R. C., & Bilbro, W. C. (1966). The diagnosis of twin zygosity. Acta Genetica, 16, 265–275.
Olson, R. K. (2004). SSSR, environment, and genes. Scientific Studies of Reading, 8(2), 111–124.
Olson, R., Forsberg, H., Wise, B., & Rack, J. (1994). Measurement of word recognition, orthographic, and phonological skills. In G. R. Lyon (Ed.), Frames of Reference for the Assessment of Learning Disabilities: New Views on Measurement Issues (pp. 243–277). Baltimore: Paul H. Brookes Publishing Co.
Olson, R.K., Keenan, J.M., Byrne, B., Samuelsson, S., Coventry, W.L., Corley, R., Wadsworth, S.J., Willcutt, E.G., DeFries, J.C., Pennington, B.F., & Hulslander, J. (2011). Genetic and environmental influences on vocabulary and reading development from pre-kindergarten through grade 4. Scientific Studies of Reading, 15(1), 26–46. doi:10.1080/10888438.2011.536128.
Olson, R. K., Wise, B., Conners, F., Rack, J., & Fulker, D. (1989). Specific deficits in component reading and language skills: Genetic and environmental influences. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 22, 339–348.
Schmitz, S., Cherny, S. S., & Fulker, D. W. (1998). Increase in power through multivariate analyses. Behavior Genetics, 28, 357–364.
Plomin, R., DeFries, J. C., McClearn, G. E., & McGuffin, P. (2008). Behavioral Genetics (5th ed.). New York: Worth Publishers.
Shanahan, T. (2006). Relations among oral language, reading, and writing. In C. A. MacArthur, S. Graham, & J. Fitzgerald (Eds.), Handbook of Writing Research. New York: Guilford Press.
Wechsler, D. (2003). Examiners’ Manual: Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children-Fourth Edition. San Antonio: The Psychological Corporation.
Wolf, M., & Bowers, P. G. (1999). The double-deficit hypothesis for the developmental dyslexias. Journal of Educational Psychology, 91, 415–438.
Woodcock, R. W., McGrew, K. S., & Mather, N. (2001). Woodcock-Johnson III Tests of Achievement. Itasca: Riverside Publishers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funding was provided by the Eunice Kennedy Schriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, grant number HD027802. We thank the twins and their families who participated in the study. We also thank the many cooperating school districts that initially contacted the twins’ families for participation in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olson, R.K., Hulslander, J., Christopher, M. et al. Genetic and environmental influences on writing and their relations to language and reading. Ann. of Dyslexia 63, 25–43 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-011-0055-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-011-0055-z