Abstract
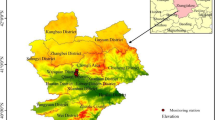
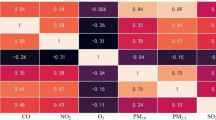
Advances in urbanization and industrialization and increase in human activities have caused significant ecological and environmental effects in the recent past. Various prediction methods and techniques have been for early detection and reduction of air pollution. In this study, air quality data from Sichuan Province, China were collected from March 2015 to March 2020. EWM algorithm was used to determine the weights of factors that affect air quality such as PM2.5, PM10, SO2, CO, NO2, O3, monthly average precipitation, and relative humidity. EWM-BP, EWM-RNN, EWM-GRU and EWM-LSTM air quality information entropy prediction models were constructed based on the data from Sichuan Province. The accuracy of the models was evaluated using RMSE, MAE, MAPE and r (correlation coefficient) as the parameters. The spatio-temporal evolution characteristics of Sichuan air quality information entropy were evaluated through Mann–Kendall nonparametric test, and calculation of individual influence index, closeness centrality index, betweenness centrality index and eigenvector centrality index. The results can be summarized as follows: (1) The weights of the factors that affect air quality were: PM2.5, PM10, SO2, CO, NO2, O3, monthly average precipitation, and relative humidity, in a descending order; (2) The EWM-LSTM model had the highest accuracy in predicting air quality, with RMSE, MAE, MAPE and r values of 0.012, 0.011, 1.400 and 0.942, respectively. (3) The air quality of the 21 cities in Sichuan Province exhibited significant seasonal variation with high air quality observed in winter and low air quality observed in summer. The Mann–Kendall non-parametric test results showed a significant increase in air quality in 2017. (4) The air quality information entropy in Sichuan Province increased from southwest to northeast with Liangshan Prefecture, Meishan, Ziyang, Zigong, Luzhou, and Guangyuan cities (individual impact index was above 0.490) having the highest impact on air quality. The present findings provide a basis for air quality prediction and provide information for development of strategies to minimize and manage air pollution.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data available on request from the authors.
References
Ass A, Ss B, Rk B (2022) Bibliometric analysis of entropy weights method for multi-objective optimization in machining operations. Mater Today: Proc 50(5):1248–1255
Bai X, Tian H, Liu X, Bobo W, Liu S, Hao Y, Luo L, Liu W, Zhao S, Lin S, Hao J, Guo Z, Lv Y (2020) Spatial-temporal variation characteristics of air pollution and apportionment of contributions by different sources in Shanxi province of China. Atmos Environ 244:117926
Beddows VA (2016) Sensitivity and uncertainty analysis of episodic ozone predictions from the community multiscale air quality model, University of London, King's College
Das S, Dayal V, Murugesan A, Rajarathnam U (2021) Air pollution trade-offs in developing countries: an empirical model of health effects in goa, India. Environ Dev Econ 27(2):145–166
Dyer C, Ballesteros M, Ling W, Matthews A, Smith NA (2015) Transition-based dependency parsing with stack long short-term memory. Comput Sci 37(2):321–332
Elmi I, Zampolli S, Dori L, Cardinali GC, Nicoletti S, Giovanelli G, Severi M (2005) A low cost transportable instrument based on microsystem technologies for benzene monitoring in outdoor air: a comparative in-field test using a standard GC tool. Trans Ecol Environ 85:425–434
Festus MA (2022) Air quality and management in petroleum refining industry: A review. Environ Chem Ecotoxicol 4:89–96
Holian MJ (2014) The effect of social and economic development on air pollution in Indian cities. Environ Urban ASIA 5(1):1–15
Lin CJ (2022) Pollution characteristics and source analysis of atmospheric particulates and water-soluble ions in rainfall in Mianyang suburbs, Southwest University of Science and Technology (in Chinese)
Mikhailov EF, Mironov GN, Pöhlker C, Chi X, Andreae MO (2015) Chemical composition, microstructure, and hygroscopic properties of aerosol particles at the Zotino tall tower observatory (ZOTTO), Siberia, during a summer campaign. Atmos Chem Phys 15(6):7837–7893
Ong BT, Sugiura K, Zettsu K (2016) Dynamically pre-trained deep recurrent neural networks using environmental monitoring data for predicting PM2.5. Neural Comput Appl 27(6):1553–1566
Pak U, Ma J, Ryu U, Ryom K, Juhyok U, Pak K, Pak C (2020) Deep learning-based pm2.5 prediction considering the spatiotemporal correlations: a case study of Beijing, China. Sci Total Environ 699(Jan.10):133561.1-133561.11
Pawan, Gupta, Maudood N, Khan, Arlindo et al (2013) Modis aerosol optical depth observations over urban areas in Pakistan: quantity and quality of the data for air quality monitoring. Atmos Pollut Res 4(1):43–52
Shamsuddin SA, Awal WRN, Dahalan MRM, Shamsuddin AS, Dahalan WM (2022) Monitoring air quality using an IOT-Enabled air pollution system on smartphones. Adv Maritime Technol Appl 166:249–264
Shen FX, Zhu TL, Niu MT (2018) Advances in research on proinflammatory effects of biochemical components of atmospheric particulate matter. Chin Sci Bull 63:968–978 (in Chinese)
Stewart C, Damby DE, Horwell CJ et al (2022) Volcanic air pollution and human health: recent advances and future directions. Bull Volcanol 84(1):1–25
Suryowati K, Bekti RD, Fajiriyah R, Siswoyo E (2021) The effect of regional characteristics and relationship among locations in air pollution using spatial autoregressive (SAR) and spatial durbin models (SDM). J Phys: Conf Ser 1776(1):012051 (10pp)
Sutskever I, Vinyals O, Le QV (2014) Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. Advances in neural information processing systems. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1409.3215
Tao H, Xing J, Pan G, Pleim J, Ran L, Wang S et al (2022) Impact of anthropogenic heat emissions on meteorological parameters and air quality in Beijing using a high-resolution model simulation. Front Environ Sci Eng China 16(4):44
Tk A, Sk A, Kk B, Mo A (2014) Time series forecasting using a deep belief network with restricted Boltzmann machines - ScienceDirect. Neurocomputing 137:47–56
Volkamer R, Jimenez JL, Martini FS, Dzepina K, Qi Z, Salcedo D, Molina TL, Worsnop RD, Molina JM (2006) Secondary organic aerosol formation from anthropogenic air pollution: rapid and higher than expected. Geophys Res Lett 33(17). https://doi.org/10.1029/2006gl026899
Walna B, Kurzyca I, Bednorz E, Kolendowicz L (2013) Fluoride pollution of atmospheric precipitation and its relationship with air circulation and weather patterns (Wielkopolski National Park, Poland). Environ Monit Assess 185:5497–5514
Wang J, Du P, Hao Y, Ma X, Niu T, Yang W (2020) An innovative hybrid model based on outlier detection and correction algorithm and heuristic intelligent optimization algorithm for daily air quality index forecasting. J Environ Manage 255(Feb.1):109855.1-109855.11
Wei W, Wang Z (2021) Impact of industrial air pollution on agricultural production. Atmosphere 12(5):639
Xja B, Nra B, Jv B, Cw B (2021) On the minimal wind directions required to assess mean annual air pollution concentration based on CFD results. Sustain Cities Soc 71:102920
Yu Z, Yi X, Ming L, Li R, Shan Z (2015) Forecasting fine-grained air quality based on big data. the 21th ACM SIGKDD International Conference. ACM
Zhou GB, Wu J, Zhang CL, Zhou ZH (2016) Minimal gated unit for recurrent neural networks. Int J Autom Comput 13(003):226–234
Funding
This work was supported by Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2023NSFSC0807), Opening Fund of Sichuan Mineral Resources Research Center (SCKCZY2022-YB017) and the General Program of Sichuan Center for Disaster Economy Research (ZHJJ2022-YB002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publication
Not applicable.
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, K., Liu, B., Yang, X. et al. Spatial and temporal evolution characteristics of air quality based on EWM-LSTM model: A case study of Sichuan Province, China. Air Qual Atmos Health 17, 191–202 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-023-01437-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-023-01437-7