Abstract
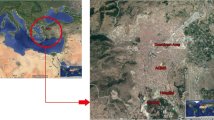
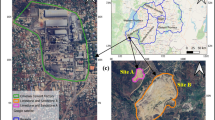
Hot-dip galvanizing (HDG) plants are a major source of particulate matter (PM) and, as a result, the areas around the plants can be affected by these emissions. The primary objective of this study was to evaluate the dispersion of PM with an aerodynamic diameter of less than 10 μm (PM10) released from an HDG plant located in Sohar, Oman. Two PM10 emission sources were considered: the off-gases resulting from the combustion of fuel used to generate the required heat for melting the zinc and the fumes generated from dipping the steel in the molten zinc bath. Supported by CALPUFF dispersion modeling software, the study analyses were based on selected modeling days representing winter and summer—the predominant seasons experienced in the region. CALPUFF simulation results revealed that winter’s top PM10 concentration level at 27.968 μg/m3 was slightly greater than the summer’s maximum recorded level at 27.207 μg/m3. However, that being said, the concentration levels for both seasons were far below the allowable concentration limit set by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (U.S. EPA) at 365.21 μg/m3.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Wahab SA, Fgaier H, Elkamel A, Chan K (2014) Air quality assessment for the proposed Miller Braeside quarry expansion in Canada: TSP. Air Qual Atmos Health 8(6):573–589
Abdul-Wahab S, Al-Rawas G, Charabi Y, Al-Wardy M, Fadlallah S (2017) A study to investigate the key sources of odors in Al-Multaqa Village, Sultanate of Oman. Environ Forensic 18(1):15–35
Abdul-Wahab S, Fadlallah S, Al-Rashdi M (2018) Evaluation of the impact of ground-level concentrations of SO2, NOx, CO, and PM10 emitted from a steel melting plant on Muscat, Oman. Sustain Cities Soc 38:675–683
Al-Rawas G, Abdul-Wahab S, Charabi Y, Al-Wardy M, Fadlallah S (2018) modeling the trends of vehicle-emitted pollutants in Salalah, Sultanate of Oman, over a 10-year period. Stoch Env Res Risk A 32(5):1355–1373
American Galvanizers Association (2012) Hot-dip galvanizing for corrosion protection: a specifier’s guide. https://galvanizeit.org/uploads/publications/Galvanized_Steel_Specifiers_Guide.pdf. Accessed 01 Feb 2019
Asif Z, Chen Z, Han Y (2018) Air quality modeling for effective environmental management in the mining region. Int J Environ Waste Manag 68(9):1001–1014
Charabi Y, Abdul-Wahab S, Al-Rawas G, Al-Wardy M, Fadlallah S (2018) Investigating the impact of monsoon season on the dispersion of pollutants emitted from vehicles: a case study of Salalah City, Sultanate of Oman. Transp Res Part D: Transp Environ 59:108–120
Drivas P (1976) Emissions from hot-dip galvanizing processes. EPA Report No. (EPA-905/4-76-002). Pacific Environmental Services, Inc, Santa Monica
El Safty A, El Mahgoub K, Helal S, Maksoud NA (2008) Zinc toxicity among galvanization workers in the iron and steel industry. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1140(1):256–262
Gaigl C, Mensinger M (2017) Hot dip galvanized steel constructions under fire exposure. Presented at 2nd International Fire Safety Symposium Naples, Italy, June 7-9, p 2017
Kragie SX, Ryan PB, Bergin MH, Wang S (2011) Airborne trace metals from coal combustion in Beijing. Air Qual Atmos Health 6(1):157–165
Otero-Pregigueiro D, Hernández-Pellón A, Borge R, Fernández-Olmo I (2018) Estimation of PM10-bound manganese concentration near a ferromanganese alloy plant by atmospheric dispersion modeling. Sci Total Environ 627:534–543
Prueksakorn K, Kim T, Vongmahadlek C (2013) Applications of WRF/CALPUFF modeling system and multi-monitoring methods to investigate the effect of seasonal variations on odor dispersion: a case study of Changwon City, South Korea. Air Qual Atmos Health 7(1):13–27
Rola MC, Dorado RM, de Moraes MR, Bodmann B (2016) Air quality assessment and dispersion of pollutants in the region of the Thermoelectric Plant President Médici using WRF/CALMET/CALPUFF models. J Environ Eng Sci 6(4A):143–155
Scire JS, Strimaitis DG, Yamartino RJ (2000) A User’s Guide for the CALPUFF Model (Version 5.0). Earth Techn Inc, Concord http://www.src.com/calpuff/download/CALPUFF_UsersGuide.pdf. Accessed 01 Feb 2019
Song Y, Zhang M, Cai X (2006) PM10 modeling of Beijing in the winter. Atmos Environ 40(22):4126–4136
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (2012) Air and radiation: National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS)
Wages PA, Silbajoris R, Speen A, Brighton L, Henriquez A, Tong H, Brombergc PA, Simmons SO, Samet JM (2014) Role of H2O2 in the oxidative effects of zinc exposure in human airway epithelial cells. Redox Biol 3:47–55
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdul-Wahab, S.A., Charabi, Y., Osman, I.I. et al. Impact of the ambient air quality due to the dispersion of PM10 from a hot-dip galvanizing plant located in the Sultanate of Oman. Air Qual Atmos Health 12, 1279–1289 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-019-00738-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-019-00738-0