Abstract
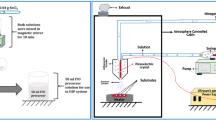
GeSi:H films are prepared by hot-wire chemical vapor deposition (CVD) with high hydrogen dilution, DH=98%. Effects of hot wire temperature (Tw) on deposition rate, structural properties and bandgap of GeSi:H films are studied with surface profilemeter, Raman spectroscopy, Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy, and UV-VIS-NIR spectrophotometer. It is found that the deposition rate (Rd) goes up with increasing of Tw, but increasing rate of Rd declines when Tw⩾1 550 °C. High Tw is beneficial to the formation of Ge-Si, but it has little effect on relative contents of the hydrogen bonds (Ge-H, Si-H, etc.) in the films. In the Tw range of 1 400–1 850 °C, the maximum bandgap of the GeSi:H films is 1.39 eV at Tw =1 450 °C and the band gap decreases with Tw increasing when Tw⩾1 450 °C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dominguez M, Rosales P, Torres A, et al. Effects of germane flow rate in electrical properties of a-SiGe:H films for ambipolar thin-film transistors [J]. Thin Solid Films, 2014, 562(26): 260–263.
Han S Y, Jeon K S, Cho B, et al. Characteristics of a-SiGe:H thin film transistor infrared photosensor for touch sensing displays [J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2012, 48(7): 952–959.
Ducros C, Szambolics H, Emieux F, et al. Back reflectors with periodic gratings for light trapping in a-SiGe:H solar cells [J]. Thin Solid Films, 2016, 620: 10–16.
Doyle J R, Xu Y, Reedy R, et al. Film stoichiometry and gas dissociation kinetics in hot-wire chemical vapor deposition of a-SiGe:H [J]. Thin Solid Films, 2008, 516(5): 526–528.
Jadkar S R, Sali J V, Kshirsagar S T, et al. The effect of substrate temperature on HW-CVD deposited a-SiGe:H films [J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2002, 299(2): 168–173.
Yusoff A R M, Syahrul M N, Henkel K. Retracted article: Hydrogenated nanocrystalline silicon germanium thin films [J]. Pramana, 2007, 69(2): 285–300.
Xu Y, Mahan A H, Gedvilas L M, et al. Deposition of photosensitive hydrogenated amorphous silicon-germanium films with a tantalum hot wire [J]. Thin Solid Films, 2006, 501(1): 198–201.
Xu Y, Nelson B P, Gedvilas L M, et al. Improving narrow bandgap a-SiGe:H alloys grown by hot-wire chemical vapor deposition [J]. Thin Solid Films, 2003, 430(1): 197–201.
Karthik M, Gohil J M, Suresh A K. Probing the thickness and roughness of the functional layer in thin film composite membranes [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(42): 26464–26474.
Xie D, Qiu Z R, Wan L, et al. Spectroscopic ellipsometry and X-ray diffraction studies on Si1-xGex/Si epifilms and superlattices [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 421: 748–754.
Kamesaki K, Masuda A, Izumi A, et al. Proposal of catalytic chemical sputtering method and its application to prepare large grain size poly-Si [J]. Thin Solid Films, 2001, 395(1): 169–172.
Werf C H M V, Veenendaal P A T T, Veen M K V, et al. The influence of the filament temperature on the structure of hot-wire deposited silicon [J]. Thin Solid Films, 2003, 430(1): 46–49.
Alonso M I, Winer K. Raman spectra of c-Si1−xGex alloys [J]. Physical Review B Condensed Matter, 1989, 39(14): 10056–10062.
Isomura M, Nakahata K, Shima M, et al. Microcrystalline silicon-germanium solar cells for multi-junction structures [J]. Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells, 2002, 74(1): 519–524.
Veenendaal P A T T, Schropp R E I. Processes in silicon deposition by hot-wire chemical vapor deposition[J]. Current Opinion in Solid State & Materials Science, 2002, 6(5): 465–470.
Soukup R J, Ianno N J, Pribil G, et al. Deposition of high quality amorphous silicon, germanium and silicongermanium thin films by a hollow cathode reactive sputtering system [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2004, 177: 676–681.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFB1500400-2018YFB1500403), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61741404, 61464007), and the Jiangxi Provincial Key Research and Development Foundation (2016BBH80043)
Biography: TAI Xin, male, Master candidate, research direction: crystallized silicon solar cell.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tai, X., Li, X., Zhen, H. et al. Effects of Hot Wire Temperature on Properties of GeSi:H Films with High Hydrogen Dilution by Hot-Wire Chemical Vapor Deposition. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 24, 405–408 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11859-019-1413-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11859-019-1413-7
Key words
- GeSi:H films
- hot-wire chemical vapor deposition (CVD)
- deposition rate
- structural properties
- band gap
- hot wire temperature