Abstract
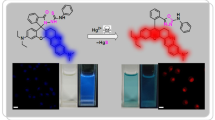
A rhodamine-benzimidazole conjugate (RB) as a probe was investigated. UV-Vis analysis showed that a strong absorption band at 552 nm was formed with the addition of Cu2+, while other transition metal ions induced a little more absorption. The absorption value of RB solution at 552 nm has a linear correlation with Cu2+ concentration between 35–70 μmol/L; the detection limit reached 6.82×10−2 μmol/L, which is lower than the settled limitation for copper in the drinking water (∼30 μmol/L) standardized by World Health Organization (WHO). Moreover, FL analysis showed that only Fe3+ could induce large fluorescence intensity enhancement at 582 nm; other common metal ions including Cu2+ cannot induce the enhancement. There was a good linear correlation between relative fluorescence intensity and Fe3+ concentration ranging from 2 μmol/L to 20 μmol/L, and the detection limit reached 1.70×10−2 μmol/L. The results showed that RB could detect Cu2+ and Fe3+ simultaneously, with the UV-Vis and fluorescence spectroscopy, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Silva A P, Gunaratne H Q N, Gunnlaugsson T, et al. Higher generation luminescent PET (photoinduced electron transfer) sensors [J]. Chemosensors of Ion and Molecule Recognition, 1997, 492: 143–157.
Thomas S W, Joly G D, Swager T M. Chemical sensors based on amplifying fluorescent conjugated polymers [J]. Chemical Review, 2007, 107(4): 1339–1386.
Han W S, Lee H Y, Jung S H, et al. Silica-based chromogenic and fluorogenic hybrid chemosensor materials [J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2009, 38(7): 1904–1915.
Yuan M J, Li Y L, Li J B, et al. A colorimetric and fluorometric dual-modal assay for mercury ion by a molecule [J]. Organic Letters, 2007, 9(12): 2313–2316.
Mizukami S, Nagano T, Urano Y, et al. A fluorescent anion sensor that works in neutral aqueous solution for bioanalytical application [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2002, 124(15): 3920–3925.
Zhu M, Yuan M J, Liu X F, et al. Visible near-infrared chemosensor for mercury ion [J]. Organic Letters, 2008, 10(7): 1481–1484.
He X R, Liu H B, Li Y L, et al. Gold nanoparticle-based fluorometric and colorimetric sensing of copper (II) ions [J]. Advanced Materials, 2005, 17(23): 2811–2815.
Li J B, Zeng Y, Hu Q H, et al. A fluorescence “turn-on” chemodosimeter for Cu2+ in aqueous solution based on the ion promoted oxidation [J]. Dalton Transactions, 2012, 41(13): 3623–3626.
Li J B, Hu Q H, Zeng Y, et al. Rhodamine-based fluorescent probes for cations [J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2012, 24(05): 823–833.
Xu H X, Wang X Q, Zhang C L, et al. Coumarin-hydrazone based selective fluorescence sensor for copper(II) detection in aqueous solution [J]. Inorganic Chemistry Communications, 2013, 34: 8–11.
Goswami S, Sen D, Das A K, et al. A new rhodamine-coumarin Cu2+ selective colorimetric and “off-on” fluorescence probe for effective use in chemistry and bioimaging along with its bound X-ray crystal structure [J]. Sensors and Acuators B-Chemical, 2013, 183: 518–525.
Kumar V, Kumar A, Diwan U, et al. A Zn2+ responsive highly sensitive fluorescent probe and 1D coordination polymer based on a coumarin platform [J]. Dalton Transcations, 2013, 42(36): 13078–13083.
Chen Y C, Zhu C C, Cen J J, et al. A reversible ratiometric sensor for intracellular imaging: Metal coordination-altered FRET in a dual fluorophore hybrid [J]. Chemical Communications, 2013, 49(69): 7632–7634.
Schmittel M, Lin H W. Quadruple-channel sensing: A molecular sensor with a single type of receptor site for selective and quantitative multi-ion analysis [J]. Angewandte Chime-international Edition, 2007, 46(6): 893–896.
Singh N, Mulrooney R C, Kaur N, et al. A nanoparticle based chromogenic chemosensor for the simultaneous detection of multiple analytes [J]. Chemical Communications, 2008, 40: 4900–4902.
Singh N, Kaur N, Choitir C N, et al. A dual detecting polymeric sensor: chromogenic naked eye detection of silver and ratiometric fluorescent detection of manganese [J]. Tetrahedron Letters, 2009, 50(29): 4201–4204.
Lee D Y, Singh N, Jang D O. A benzimidazole-based single molecular multianalyte fluorescent probe for the simultaneous analysis of Cu2+ and Fe3+ [J]. Tetrahedron Letters, 2010, 51(7): 1103–1106.
Kaur P, Sareen D. The synthesis and development of a dual-analyte colorimetric sensor simultaneous estimation of Hg2+ and Fe3+ [J]. Dyes and Pigments, 2011, 88(3): 296–300.
Dong M, Wang Y W, Peng Y. Highly selective ratiometric fluorescent sensing for Hg2+ and Au3+, respectively, in aqueous media [J]. Organic Letters, 2010, 12(22): 5310–5313.
Yu F B, Zhang W S, Li P, et al. Cu2+-selective naked-eye and fluorescent probe: Its crystal structure and application in bioimaging [J]. Analyst, 2009, 134(9): 1826–1833.
Li J B, Yu X L, Liu X W, et al. New rhodamine-based colorimetric chemosensor: Simple synthesis and rapid Cu2+ detection [J]. Sensor Letters, 2011, 9(4): 1331–1341.
Huang L, Chen F J, Xi P X, et al. A turn-on fluorescent chemosensor for Cu2+ in aqueous media and its application to bioimaging [J]. Dyes and Pigments, 2011, 90(3): 265–268.
Wang H H, Xue L, Fang Z J, et al. A colorimetric and fluorescent chemosensor for copper ions in aqueous media and its application in living cells [J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2010, 34(7): 1239–1242.
Wolfbeis O S. Materials for fluorescence-based optical chemical sensors [J]. Journal of Material Chemistry, 2005, 15(27–28): 2657–2669.
Yuan M J, Zhou W D, Liu X F, et al. A multianalyte chemosensor on a single molecule: Promising structure for an integrated logic gate [J]. Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2008, 73(13): 5008–5014.
Zhou Y, You X Y, Fang Y, et al. A thiophen-thiooxorhodamine conjugate fluorescent probe for detecting mercury in aqueous media and living cells [J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2010, 8(21): 4819–4822.
Wang B D, Hai J, Liu Z C, et al. Selective detection of iron(III) by rhodamine-modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles [J]. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 2010, 49(27): 4576–4579.
Kim S K, Swamy K M K, Chung S Y, et al. New fluorescent and colorimetric chemosensors based on the rhodamine and boronic acid groups for the detection of Hg2+ [J]. Tetrahedron Letters, 2010, 51(25): 3286–3289.
Jun M E, Ahn K H. Fluorogenic and chromogenic detection of palladium species through a catalytic conversion of a rhodamine B derivative [J]. Organic Letters, 2010, 12(12): 2790–2793.
Hu Z Q, Lin C S, Wang X M, et al. Highly sensitive and selective turn-on fluorescent chemosensor for Pb2+ and Hg2+ based on a rhodamine-phenylurea conjugate [J]. Chemical Communications, 2010, 46(21): 3765–3767.
Tang L J, Li F F, Liu M H. Single sensor for two metal ions: colorimetric recognition of Cu2+ and fluorescent recognition of Hg2+ [J]. Spectrochimica Acta part A-molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2011, 78(3): 1168–1172.
Li J B, Hu Q H, Yu X L, et al. A novel rhodamine-benzimidazole conjugate as a highly selective turn-on fluorescent probe for Fe3+ [J]. Journal of Fluorescence, 2011, 21(5): 2005–2013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (20901063, 51203127), Wuhan Chenguang Scheme (Grant 201050231049) established under Wuhan Science and Technology Bureau, Outstanding youth project of Hubei Provincial Department of Education (20121509).
Biography: YU Xianglin, female, Ph.D., Associate professor, research direction: organic/inorganic compound functional materials.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, X., Qu, H., Hu, Q. et al. A rhodamine-based sensor for chromogenic detection of Cu2+ and fluorescent detection of Fe3+ . Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 19, 129–136 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11859-014-0989-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11859-014-0989-1