Abstract
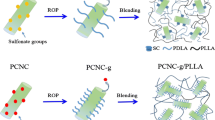
A polycaprolactone-grafted cellulose nanocrystal (PCL-g-CN) was prepared in ionic liquid and characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectrum (FT-IR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). A peak assigned to the carbonyl group appears at 1 730 cm−1 in the FT-IR of PCL-g-CN, which confirms that the grafting reaction is successfully completed. The morphologies of PCL-g-CNs still maintain rod-like structure according to the TEM images. XRD results show that the crystal type of the PCL-g-CNs changed from cellulose I to cellulose II. The reasons for crystal transition of CNs turn out to be combined effects of anion and cation in ionic liquid with CNs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dufresne A. Processing of polymer nanocomposites reinforced with polysaccharide nanocrystals [J]. Molecules, 2010, 15(6): 4111–4128.
Youssef H, Lucian A L, Orlando J R. Cellulose nanocrystals: Chemistry, self-Assembly, and applications [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2010, 110(6): 3479–3500.
Muhammad N, Man Z, Khalil M A B. Ionic liquid-A future solvent for the enhanced uses of wood biomass [J]. European Journal of Wood and Wood Products, 2012, 70(1–3): 125–133.
Swatloski R P, Spear S K, Holbrey J D, et al. Dissolution of cellose with ionic liquids [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2002, 124(18): 4974–4975.
Kubisa P. Ionic liquids as solvents for polymerization processes-Progress and challenges [J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2009, 34(12): 1333–1347.
Kubisa P. Application of ionic liquids as solvents for polymerization processes [J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2004, 29(1): 3–12.
Lu J, Yan F, Texter J. Advanced applications of ionic liquids in polymer science [J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2009, 34(5): 431–448.
Liu D T, Xia K F, Cai W H, et al. Investigations about dissolution of cellulose in the 1-allyl-3-alkylimidazolium chloride ionic liquids [J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2012, 87(2): 1058–1064.
Cai T, Yang G S, Zhang H H, et al. A new process for dissolution of cellulose in ionic liquids [J]. Polymer Engineering and Science, 2012, 52(8): 1708–1714.
Wang H, Gurau G, Rogers R D. Ionic liquid processing of cellulose [J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2012, 41(4): 1519–1537.
Xu Q, Kennedy J F, Liu L J. An ionic liquid as reaction media in the ring opening graft polymerization of ɛ-caprolactone onto starch granules [J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2008, 72(1): 113–121.
Xu Q, Wang Q R, Liu L J. Ring-opening graft polymerization of L-lactide onto starch granules in an ionic liquid [J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2008, 107(4): 2704–2713.
Wilpiszewska K, Spychaj T. Ionic liquids: Media for starch dissolution, plasticization and modification [J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2011, 86(2): 424–428.
Kadokawa J, Takegawa A, Mine S, et al. Preparation of chitin nanowhiskers using an ionic liquid and their composite materials with poly(vinyl alcohol) [J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2011, 84(4): 1408–1412.
Jaworska M M, Kozlecki T, Gorak A. Review of the application of ionic liquids as solvents for chitin [J]. Journal of Polymer Engineering, 2012, 32(2): 67–69.
Mine S, Izawa H, Kaneko Y, et al. Acetylation of alpha-chitin in ionic liquids [J]. Carbohydrate Research, 2009, 344(16): 2263–2265.
Gibril M E. Current status of applications of ionic liquid for cellulose dissolution and modifications: review [J]. International Journal of Engineering Science and Technology, 2012, 4(7): 3556–3571.
Barthel S, Heinze T. Acylation and carbanilation of cellulose in ionic liquids [J]. Green Chemistry, 2006, 8(3): 301–306.
Wu J, Zhang J, Zhang H, et al. Homogeneous acetylation of cellulose in a new ionic liquid [J]. Biomacromolecules, 2004, 5(2): 266–268.
Liu C F, Zhang A P, Li W Y, et al. Homogeneous modification of cellulose in ionic liquid with succinic anhydride using N-bromosuccinimide as a catalyst [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2009, 57(5): 1814–1820.
Han J Q, Zhou C J, French A D, et al. Characterization of cellulose II nanoparticles regenerated from 1-butyl-3-methy-limidazolium chloride [J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2013, 94(2): 773–781.
Liu C F, Zhang A P, Li W Y, et al. Dissolution of cellulose in novel green solvent ionic liquids and its application [J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2009, 21(9): 1800–1806.
Liu C F, Sun R C, Zhang A P, et al. Homogeneous modification of sugarcane bagasse cellulose with succinic anhydride using a ionic liquid as reaction medium [J]. Carbohydrate Research, 2007, 342(7): 919–926.
Lin N, Huang J, Chang P R, et al. Preparation, modification, and application of starch nanocrystals in nanomaterials: A review [EB/OL]. [2012-08-13]. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2011/573687.
Lin N, Chen G J, Huang J, et al. Effects of polymer-grafted natural nanocrystals on the structure and mechanical properties of poly(1actic acid): A case of cellulose whisker-graft-polycaprolactone [J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2009, 113(5): 3417–3425.
Liu D G, Zhong T H, Chang P R, et al. Starch composites reinforced by bamboo cellulosic crystals [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(7): 2529–2536.
Ren Q, Wu J, Zhang J, et al. Synthesis of 1-allyl-3-methy-limidazolium-based room-temperature ionic liquid and preliminary study of its dissolving cellulose [J]. Acta Polymerica Sinica, 2003, 1(3): 448–451.
Zhang H, Wu J, Zhang J, et al. 1-Allyl-3-methylimidazolium Chloride Room Temperature Ionic liquid: A new and powerful nonderivatizing solvent for cellulose [J]. Macromolecules, 2005, 38(20): 8272–8277.
Pinkert A, Marsh K N, Pang S, et al. Ionic liquids and their interaction with cellulose [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2009, 109(12): 6712–6728.
Liu Z, Wang H, Li Z X, et al. Characterization of the regenerated cellulose films in ionic liquids and rheological properties of the solutions [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2011, 128(1–2): 220–227.
Zhu S, Wu Y, Chen Q, et al. Dissolution of cellulose with ionic liquids and its application: A mini-review [J]. Green Chemistry, 2006, 8(4): 325–327.
Zhao W, Chen H Z, Ma R Y. Structural characteristics of cellulose after dissolution and regeneration from the ionic liquid [BMIM]Cl [J]. Journal of Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2007, 34(2): 138–141(Ch).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Supported by Supporting Project of New Century Excellent Talents of Ministry of Education of China (NCET-11-0686), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Self-Determined and Innovative Research Funds of WUT 2012-Ia-006), ecoENERGY Innovation Initiative of Canada, Program of Energy Research and Development (PERD) of Canada, and State Key Laboratory of Pulp and Paper Engineering, South China University of Technology (201212)
Biography: HUANG Qing, female, Master, research direction: biomass nanocomposites.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Q., Huang, J. & Chang, P.R. Polycaprolactone grafting of cellulose nanocrystals in ionic liquid [BMIM]Cl. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 19, 117–122 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11859-014-0987-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11859-014-0987-3