Abstract
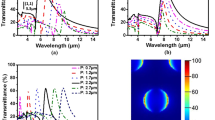
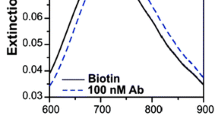
Noble metal nanoparticles with localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) properties are widely used as optical sensors in biochemical detection and medical diagnosis. In this paper, we propose an effective determination method to measure the LSPR absorption intensity of gold nanorods (GNRs). A near-infrared (NIR) imaging system is established, and an NIR absorption image of the multiple samples of the colloidal GNRs is captured. Then, the LSPR absorption intensities of these samples are obtained by calculating the average grayscale of the target areas based on the NIR image processing technology. By using this method, the LSPR absorption intensities of the multiple samples are determined all at once, and their accuracy is as high as that obtained by using spectrophotometry. These results suggest that this method is an efficient multi-channel determination technique with high-throughput sensing applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anker J N, Hall W P, Lyandres O, et al. Biosensing with plasmonic nanosensors [J]. Nature Materials, 2008, 7: 442–453.
Haes A J, Van Duyne R P. A unified view of propagating and localized surface plasmon resonance biosensors [J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2004, 379: 920–930.
Medley C D, Smith J E, Tang Z W, et al. Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric assay for the direct detection of cancerous cells [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2008, 80(4): 1067–1072.
Liu J M, Wang H F, Yan X P. A gold nanorod based colorimetric probe for the rapid and selective detection of Cu2+ ions [J]. Analyst, 2011, 136: 3904–3910.
Mayer K M, Hafner J H. Localized surface plasmon resonance sensors [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2011, 111(6): 3828–3857.
Wang C G, Chen Y, Wang T T, et al. Biorecognition-driven self-assembly of gold nanorods: a rapid and sensitive approach toward antibody sensing [J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2007, 19(24): 5809–5811.
Wang C G, Ma Z F, Wang T T, et al. Synthesis, assembly, and biofunctionalization of silica-coated gold nanorods for colorimetric biosensing [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2006, 16: 1673–1678.
Huang H W, Liu X Y, Hu T, et al. Ultra-sensitive detection of cysteine by gold nanorod assembly [J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2010, 25(9): 2078–2083.
Aslan K, Geddes C D. Wavelength-ratiometric plasmon light scattering-based immunoassays [J]. Plasmonics, 2009, 4: 267–272.
Wang G Q, Chen Z P, Wang W H, et al. Chemical redox-regulated mesoporous silica-coated gold nanorods for colorimetric probing of Hg2+ and S2-[J]. Analyst, 2011, 136: 174–178.
Huang H W, Qu C T, Liu X Y, et al. Amplification of localized surface plasmon resonance signals by a gold nanorod assembly and ultra-sensitive detection of mercury [J]. Chemical Communications, 2011, 47: 6897–6899.
Clarke F. Extracting process-related information from pharmaceutical dosage forms using near infrared microscopy [J]. Vibrational Spectrocopy, 2004, 34(1): 25–35.
Cruz J, Bautista M, Amigo J M, et al. Nir-chemical imaging study of acetylsalicylic acid in commercial tablets [J]. Talanta, 2009, 80(2): 473–478.
Tsuta M, Sugiyama J, Sagara Y. Near-infrared imaging spectroscopy based on sugar absorption band for melons [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2002, 50: 48–52.
Li J B, Rao X Q, Ying Y B. Detection of common defects on oranges using hyperspectral reflectance imaging [J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2011, 78: 38–48.
Brooksby B A, Dehghani H, Pogue B W, et al. Near-infrared (NIR) tomography breast image reconstruction with a priori structural information from MRI: algorithm development for reconstructing heterogeneities [J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronic, 2003, 9(2): 199–209.
Ni W H, Kou X S, Yang Z, et al. Tailoring longitudinal surface plasmon wavelengths, scattering and absorption cross sections of gold nanorods [J]. Acs Nano, 2008, 2(4): 677–686.
Sau T K, Murphy C J. Seeded high yield synthesis of short Au nanorods in aqueous solution [J]. Langmuir, 2004, 20(15): 6414–6420.
Shen Y F, Krusienski D, Li J, et al. A hierarchical horizon detection algorithm [J]. Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(1): 111–114.
Wang B, Fan S S. An improved Canny edge detection algorithm [EB/OL]. [2013-03-02]. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5403419&tag=1.
Zhang Y, Li T, Li Q L. Defect detection for tire laser shearography image using curvelet transform based edge detector [J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2013, 47: 64–71.
Brethorst A Z, Desai N, Enright D P, et al. Performance evaluation of Canny edge detection on a tiled multicore architecture [EB/OL]. [2013-03-05]. http://ebooks.spiedigi-tallibrary.org/data/Conferences/SPIEP/2643/78720F_1.pdf.
Maini R, Aggarwal H. Study and comparison of various image edge detection techniques [J]. International Journal of Image Processing (IJIP), 2009, 3(1): 1–11.
Bai X Z. Morphological image fusion using the extracted image regions and details based on multi-scale top-hat transform and toggle contrast operator [J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2013, 23(2): 542–554.
Duda R O, Hart P E. Use of the Hough transformation to detect lines and curves in pictures [J]. Communications of the ACM, 1972, 15(1): 11–15.
Jošth R, Dubská MarkMta, Herout A, et al. Real-time line detection using accelerated high-resolution Hough transform [J]. Image Analysis, 2011, 6688: 784–793.
Ball G R, Kasiviswanathan H, Srihari S N, et al. Analysis of line structure in handwritten documents using the Hough transform [EB/OL]. [2013-03-05]. http://ebooks.spiedigital-library.org/data/Conferences/SPIEP/10562/75340Z_1.pdf.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (SBK201240182).
Biography: LI Qian, female, Master candidate, research direction: detection of biological signal.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Huang, H., Li, Z. et al. Near-infrared absorption imaging and processing technologies based on gold nanorods. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 18, 307–312 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11859-013-0933-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11859-013-0933-9
Key words
- gold nanorods (GNRs)
- localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR)
- near-infrared (NIR) absorption image
- image processing