Abstract
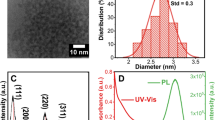
Bright Cu-doped ternary ZnCdS quantum dots (ZnCdS: Cu QDs) with varied Cd concentrations were synthesized in aqueous solution by using a convenient microwave method. These ternary QDs could be directly dispersed in water solution. By regulating the Cd2+ concentration from 0 to 50% (mole fraction of the cations), the photoluminescence excitation (PLE) peak of such ZnCdS:Cu QDs could be continuously redshifted from 320 nm to 380 nm, while their photoluminescence (PL) peak was redshifted from 490 nm to 580 nm, exhibiting multicolor Cu-related emissions. Furthermore, the quantum yield of the ZnCdS:Cu QDs could reach as high as 12% by regulating the Cu doping concentration. These ZnCdS:Cu ternary QDs with kind surface conditions and good composition-controllable optical properties may have potential application in many areas such as sensing, bioimaging, and light-emitting diodes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wood V, Halpert J E, Panzer M J, et al. Alternating current driven electroluminescence from ZnSe/ZnS: Mn/ZnS nanocrystals [J]. Nano Letters, 2009, 9(6): 2367–2371.
Stouwdam J W, Janssen R A J. Electroluminescent Cu-doped CdS quantum dots [J]. Advanced Materials, 2009, 21(28): 2916–2920.
Schlamp M C, Peng Xiaogang, Alivisatos A P. Improved efficiencies in light emitting diodes made with CdSe(CdS) core/shell type nanocrystals and a semiconducting polymer[ J]. J Appl Phys, 1997, 82: 5837–5842.
Dubertret B, Skourides P, Norris D J, et al. In vivo imaging of quantum dots encapsulated in phospholipid micelles [J]. Science, 2002, 298(5599): 1759.
Medintz I L, Uyeda H T, Goldman E R, et al. Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging, labelling and sensing [J]. Nature Materials, 2005, 4(6): 435–446.
Parak W J, Pellegrino T, Plank C. Labelling of cells with quantum dots [J]. Nanotechnology, 2005, 16: R9–R25.
Yu Xuefeng, Li Kaiyang, Xiao Si, et al. Immunofluorescence detection with quantum dot bioconjugates for hepatoma in vivo [J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2007, 12(1): 014008.
Aroutiounian V, Petrosyan S, Khachatryan A, et al. Quantum dot solar cells [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2001, 89:2268.
Robel I, Subramanian V, Kuno M, et al. Quantum dot solar cells: Harvesting light energy with CdSe nanocrystals molecularly linked to mesoscopic TiO2 films [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2006, 128(7): 2385–2393.
Mueller A H, Petruska M A, Achermann M, et al. Multicolor light-emitting diodes based on semiconductor nanocrystals encapsulated in GaN charge injection layers [J]. Nano Letters, 2005, 5(6): 1039–1044.
Nizamoglu S, Ozel T, Sari E, et al. White light generation using CdSe/ZnS core-shell nanocrystals hybridized with In-GaN/GaN light emitting diodes [J]. Nanotechnology, 2007, 18: 065709.
Medintz I, Konnert J H, Clapp A R. A fluorescence resonance energy transfer-derived structure of a quantum dot-protein bioconjugate nanoassembly [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2004, 101(26): 9612–9617.
Chan W C W, Nie S. Quantum dot bioconjugates for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection [J]. Science, 1998, 281(5385): 2016–2018.
Wu Xingyong, Liu Hongjian, Liu Jianquan, et al. Immunofluorescent labeling of cancer marker Her2 and other cellular targets with semiconductor quantum dots [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2002, 21: 41–46.
Mandal P, Talwar S, Major S. Orange-red luminescence from Cu doped CdS nanophosphor prepared using mixed Langmuir-Blodgett multilayers [J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2008, 128: 114703.
Chen Zhenqian, Lian Chao, Zhou Dong, et al. Greatly enhanced and controlled manganese photoluminescence in water-soluble ZnCdS: Mn/ZnS core/shell quantum dots [J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2010, 488(1–3): 73–76.
Yu Xuefeng, Peng Xiaoniu, Chen Zhenqian, et al. High temperature sensitivity of manganese-assisted excitonic photoluminescence from inverted core/shell ZnSe:Mn/CdSe nanocrystals [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2010, 96: 123104.
Zheng Y, Yang Z, Ying J Y, et al. Aqueous synthesis of glutathione-capped ZnSe and Zn1−x CdxSe alloyed quantum dots [J]. Advanced Materials, 2007, 19(11): 1475–1479.
Zhong X H, Feng Y Y, Knoll W, et al. Alloyed ZnxCd1−x S nanocrystals with highly narrow luminescence spectral width [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2003, 125(44): 13559–13563.
Sakly A, Safta N, Mejri H, et al. The electronic band parameters calculated by the Kronig-Penney method for Cd1-x ZnxS quantum dot superlattices [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 476(1–2): 648–652.
Bailey R E, Nie S. Alloyed semiconductor quantum dots: Tuning the optical properties without changing the particle size [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2003, 125(23): 7100–7106.
Ali M, Chattopadhyay S, Nag A, et al. White-light emission from a blend of CdSeS nanocrystals of different Se: S ratio [J]. Nanotechnology, 2007, 18: 075401.
Chen Zhen, Chen Hu, Meng Huan, et al. Bio-distribution and metabolic paths of silica coated CdSeS quantum dots [J]. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 2008, 230(3): 364–371.
Zhong Xinhua, Han Mingyong, Dong Zhili, et al. Composition-Tunable ZnxCd1−x Se nanocrystals with high luminescence and stability [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2003, 125(28): 8589–8594.
Ali Azam K, Manisha K, Lalita J, et al. Green luminescence from copper doped zinc sulphide quantum particles [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2009, 67(18): 2702–2704.
Norris D J, Efros A L, Erwin S C. Doped nanocrystals [J]. Science, 2008, 319(5871): 1776–1779.
Zheng Jinju, Zheng Zhuhong, Gong Weiwei, et al. Stable, small, and water-soluble Cu-doped ZnS quantum dots prepared via femtosecond laser ablation [J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2008, 465(4–6): 275–278.
Bowers R, Melamed N. Luminescent centers in ZnS: Cu: Cl phosphors [J]. Physical Review, 1955, 99(6): 1781–1787.
Jayanthi K, Chawla S, Chander H, et al. Structural, optical and photoluminescence properties of ZnS: Cu nanoparticle thin films as a function of dopant concentration and quantum confinement effect [J]. Crystal Research and Technology, 2007, 42(10): 976–982.
Huang Jinman, Yang Yi, Xue Shanhua, et al. Photoluminescence and electroluminescence of ZnS: Cu nanocrystals in polymeric networks [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1997, 70: 2335–2337.
Stouwdam J W, Janssen R A J. Electroluminescent Cu-doped CdS quantum dots [J]. Advanced Materials, 2009, 21(28): 2916–2920.
Nien Y T, Chen P W, Chen I G. Synthesis and characterization of Zn1−x CdxS: Cu, Cl red electroluminescent phosphor powders [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 462(1–2): 398–403.
Kumar C, Sonal S, Sandeep N. Study of composition dependent structural, optical, and magnetic properties of Cu-doped Zn1-x CdxS nanoparticles [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 108(12): 123519.
Pradhan N, Goorskey D, Thessing J, et al. An alternative of CdSe nanocrystal emitters: Pure and tunable impurity emissions in ZnSe nanocrystals [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2005, 127: 17586–17587.
Wang Mingwen, Sun Lingdong, Fu Xuefeng, et al. Synthesis and optical properties of ZnS:Cu(II) nanoparticles [J]. Solid State Communications, 2000, 115: 493–496.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (10904119)
Biography: YANG Yuezhou, male, Master candidate, research direction: quantum optics.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Liang, S., Yu, X. et al. Microwave synthesis of Cu-doped ternary ZnCdS quantum dots with composition-controllable photoluminescence. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 17, 217–222 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11859-012-0831-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11859-012-0831-6