Abstract
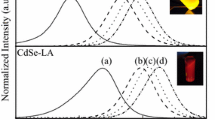
We report a facile aqueous phase synthesis for preparing water-soluble inverted core/shell ZnSe/CdSe semiconductor nanocrystals. The samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and their optical properties were investigated by using UV-vis-NIR spectrophotometer and fluorescence spectrophotometer. The results indicate that the synthesized ZnSe/CdSe nanocrystals are inverted core/shell structure with diameter of about 5 nm. Furthermore, their absorption band-edge is red-shifted with the growth of CdSe shell; correspondingly, their emission wavelength can be tuned from 460 nm to 604 nm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruchez M, Moronne M, Gin P, et al. Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels[J]. Science, 1998, 281: 2013–2016.
Peng X G, Manna L, Yang W D, et al. Shape control of CdSe nanocrystals[J]. Nature, 2000, 404(6773): 59–61.
Nie S, Emory S R. Probing single molecules and single nanoparticles by surface-enhanced Raman scattering[J]. Science, 1997, 275: 1102–1106.
Gao X, Cui Y, Levenson R M, et al. In Vivo cancer targeting and imaging with semiconductor quantum dots[J]. Nat Biotechnol, 2004, 22(8): 969–976.
Chan W C W, Nie S. Quantum dot bioconjugates for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection[J]. Science, 1998, 281: 2016–2018.
Han M, Gao X, Su J Z, et al. Quantum-dot-tagged microbeads for multiplexed optical coding of biomolecules[J]. Nat Biotechnol, 2001, 19: 631–635.
Alivisatos A P. Semiconductor clusters, nanocrystals, and quantum dots[J]. Science, 1996, 271: 933–937.
Gaponenko S V. Optical Properties of Semiconductor Nanocrystals[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1998.
Larson D R, Zipfel W R, Williams R M, et al. Water-soluble quantum dots for multiphoton fluorescence imaging in vivo[J]. Science, 2003, 300: 1434–1436.
Coe S, Woo W K, Bawendi M, et al. Electroluminescence from single monolayers of nanocrystals in molecular organic devices[J]. Nature, 2002, 420: 800–803.
Tessler N, Medvedev V, Kazes M, et al. Efficient near-infrared polymer nanocrystal light-emitting diodes[J]. Science, 2002, 295: 1506–1508.
Yu X F, Chen L D, Li K Y, et al. Immunofluorescence detection with quantum dot bioconjugates for hepatoma in vivo[J]. J Biomed Opt, 2007, 12(1): 014008.
Chen Z Q, Lian C, Zhou D, et al. Greatly enhanced and controlled manganese photoluminescence in water-soluble ZnCdS: Mn/ZnS core/shell quantum dots[J]. Chem Phys Lett, 2010, 488: 73–76.
Pandey A, Guyot-Sionnest P. Slow electron cooling in colloidal quantum dots[J]. Science, 2008, 322: 929–932.
Hines M A, Guyot-Sionnest P. Synthesis and characterization of strongly luminescing ZnS-capped CdSe nanocrystals[J]. J Phys Chem, 1996, 100: 468–471.
Dabbousi B O, Rodriguez-Viejo J, Mikulec F V, et al. (CdSe) ZnS core-shell quantum dots: synthesis and characterization of a size series of highly luminescent nanocrystallits[J]. J Phys Chem B, 1997, 101: 9463–9475.
Chen Y, Vela J, Htoon H, et al. “Giant” multishell CdSe nanocrystal quantum dots with suppressed blinking[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2008, 130: 5026–5027.
Mahler B, Spinicelli P, Buil S, et al. Towards non-blinking colloidal quantum Dots[J]. Nat Mater, 2008, 7: 659–664.
Kim S, Fisher B, Eisler H, et al. Type-II quantum dots: CdTe/CdSe (core/shell) and CdSe/ZnTe (core/shell) heterostructures [J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2003, 125: 11466–11467.
Nanda J, Ivanov S A, Htoon H, et al. Absorption cross sections and auger recombination lifetimes in inverted core/shell nanocrystals: implications for lasing performance[J]. J Appl Phys, 2006, 99: 034309.
Klimov V I, Ivanov S A, Nanda J, et al. Single-exciton optical gain in semiconductor nanocrystals[J]. Nature, 2007, 447: 441–446.
Balet L P, Ivanov S A, Piryatinski A, et al. Inverted core/shell nanocrystals continuously tunable between type-I and type-II localization regimes[J]. Nano Lett, 2004, 4(8): 1485–1488.
Ivanov S A, Nanda J, Piryatinski A, et al. Light amplification using inverted core/shell nanocrystals: Towards lasing in the single-exciton regime[J]. J Phys Chem B, 2004, 108: 10625–10630.
Li J J, Wang Y A, Guo W Z, et al. Large-scale synthesis of nearly monodisperse CdSe/CdS core/shell nanocrystals using air-stable reagents via successive ion layer adsorption and reaction[ J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2003, 125: 12567–12575.
Cao Y W, Banin U. Synthesis and characterization of InAs/InP and InAs/CdSe core/shell nanocrystals[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 1999, 38: 3692–3694.
Zhong Xinhua, Xie Renguo, Zhang Ying, et al. High-Quality violet- to red-emitting ZnSe/CdSe core/shell nanocrystals[J]. Chem Mater, 2005, 17: 4038–4042.
Bussian D A, Crooker S A, Yin M, et al. Tunable magnetic exchange interactions in manganese-doped inverted core/shell ZnSe-CdSe nanocrystals[J]. Nat Mater, 2009, 8: 35–40.
Hao E, Zhang H, Yang B. Preparation of luminescent polyelectrolyte/Cu-doped ZnSe nanoparticle multilayer composite films[J]. J Collolid Interface Sci, 2001, 238: 285–290.
Xie R G, Zhong X H, Basche T. Synthesis, characterization, and spectroscopy of type-II core/shell semiconductor nanocrystals with ZnTe cores[J]. Adv Mater, 2005, 17: 2741–2745.
Han J, Zhang H, Tang Y, et al. Role of redox reaction and electrostatics in transition-metal impurity-promoted photoluminescence evolution of water-soluble ZnSe nanocrystals[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2009, 113(18): 7503–7510.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (10874134) and the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (20060486031)
Biography: ZHOU Jing, male, Master candidate, research direction: synthesis and optical properties of nanomaterials.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Jiang, L., Guo, W. et al. Aqueous phase synthesis and fluorescence properties of inverted core/shell ZnSe/CdSe nanocrystals. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 15, 320–324 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11859-010-0659-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11859-010-0659-x