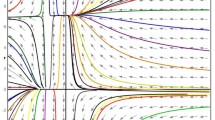
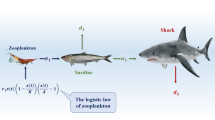
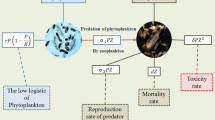
Abstract
This work seeks to demonstrate how light pollution impacts fishing activities, including catch rates and the profits of fishermen. Our goal is to examine how light pollution affects the fishing dynamics of sardines and anchovies in the Casablanca-Rabat region of Morocco, within a bioeconomic framework involving these two marine populations. In this article, we show that our model is well posed by studying the positivity and the boundedness of our system, and then we show the local stability of the interior equilibrium point. Then, we move on to calculating the fishing effort that maximizes fishermen’s profits and catches under two main constraints: The influence of light pollution on the sustained viability of the sardine and anchovy populations. Using data reported by the National Fisheries Research Institute (INRH), we obtain detailed results in numerical simulations.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agmour I, Bentounsi M, Baba N et al (2020) Impact of wind speed on fishing effort. Model Earth Syst Environ 6:1007–1015. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-00736-7
Baba Nossaiba, Agmour Imane, El Foutayeni Yousef, Achtaich Naceur (2021) Bioeconomic-Epidemiological Model of Scomber colias Population in the Moroccan Coasts. J Appl Math 2021(8892388):22. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8892388
Baba N, Agmour I, El Foutayeni Y et al (2022) The Tide Effects on Bioeconomic Model of Sardina pilchardus, Engraulis encrasicolus and Xiphias gladius in Atlantic Moroccan Zone. Earth Syst Environ 6:295–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-021-00227-4
Bendahou FE, Baba N, El Foutayeni Y, Achtaich N (2023) Impact of pollution on sardine, sardinella, and mackerel fishery: a bioeconomic approach, Commun Math Biol Neurosci, 2023, Article ID 55
Busson S, Verny P (2017) Etude AUBE. Aménagement Urbain Biodiversité et Eclairage. Ile-de-la-Réunion. Etude et rapport. Cerema. Centre d’études et d’expertise sur les risques, l’environnement, la mobilité et l’aménagement 48
Cinzano P, Falchi F, Elvidge CD (2001) The world atlas of the artificial night sky brightness. Mon Not R Astron; Soc 328:689–707
Clark CW, Gordon RM (1975) The economics of Fishing and Modern Cap-ital Theory. Simplified Approach J Environ Econ Manag 2:92–106
Ding Q, Huang Y, Zhu C (2023) Entropy-TOPSIS Method to Study the Factors Affecting Light Pollution. Highl Sci Eng Technol 64. https://doi.org/10.54097/hset.v64i.11246
Fang L, Wu Z, Tao Y, Gao J (2023) Light Pollution Index System Model Based on Markov Random Field. Mathematics 11:3030
Gliwicz ZM (1986) A lunar cycle in zooplankton. Ecology 67:883–897
INRH/DRH (2016) Rapport annuel de l’état des stocks et des pêcheries marocaines
Kolber R (2002) Die Lichtverschmutzung in der Schweiz. Mogliche Auswirkungen und praktische Losungsansatze, Diplomarbeit, Institut fur Umwelttechnik, Fachhochschule Basel
Kumlien HF (1888) Observations on bird migration in Milwaukee. Auk 5:325–328
Larinier M, Boyer-Bernard S (1991) Downstream migration of smolts and effectiveness of a fish bypass structure at halsou hydroelectric powerhouse on the nive river. Bulletin Francais de la Peche et de la Pisciculture 321:72–92
Lewis HF (1927) Destruction of birds by lighthouse in the provinces of Ontario and Quebec. Can Field-Nat 41:55–58
Longcore T, Rich C (2004) Ecological light pollution. Front Ecol Environ 2004(2):191–198
Moore MV, Kohler SJ (2002) Measuring light pollution in urban lakes and its effects on lake invertebrates. Part of the conference Ecological Consequences of Artificial Night Lighting. http://www.urbanwildlands.org/abstracts.html
Moore MV, Pierce SM, Walsh HM et al (2000) Urban light pollution alters the diel vertical migration of Daphnia. Verh Internat Verein Limnol 27:779–782
Munro JA (1924) A premiminary report in the destruction of birds at lighthouse on the coast of British Columbia. Can Field-Nat 38:171–175
Murty KG (1971) On a characterization of P-matrices. SIAM J Appl Math 20:378–383
Nemeth RS, Anderson JJ (1992) Response of juvenile coho and chinook salmon to strobe and mercury vapor lights. N Am J Fish Manag 12(4):684–692
Perkin EK, Holker F, Richardson JS, Sadler JP, Wolter C, Tockner K (2011) The influence of artificial light on stream and riparian ecosystems: questions, challenges, and perspectives. Ecosphere 2(11):122. https://doi.org/10.1890/ES11-00241.1
Pierce SM, Moore MV (1998). Light pollution affects the diel vertical migration of freshwater zooplankton. Annual Meeting of the Ecological Society of America, Baltimore, MD
Ramirez R, Johnson ER, Gido KB (2006) Effects of artificial lighting and presence of Menidia beryllina on growth and diet of Lamesthes sicculus. Southwest Nat 51(4):510–513
Rapport D’activité 2019. Royaume Du Maroc Ministère de l’agriculture, de la Pêche Maritime, du Développement Rural et des Eaux et Forêts Département de la Pêche Maritime
Rapport d’activité du Département de la Pêche Maritime (2021) Année
Su R, Chen Y, Huang Z (2023) Evaluating Light Pollution: An IES Model for Intervention Strategies. Environ Pollut 13(1). https://doi.org/10.5539/ep.v13n1p1
Teyssèdre A (1996) L’orientation des animaux : Méthodes et mécanismes. Nathan 234
Widder EA, Robison BH, Reisenbichler KR, Haddock SHS (2005) Using red light for in situ observations of deep-sea fishes
Zhang Y, Cheng L, (2023) Evaluation Model of Location Light Pollution Level based on Analytic Hierarchy Process and Entropy Weight Method. E3S Web of Conf. Volume 393. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202339303035
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors affirm that there are no conflicts of interest related to the publication of this paper
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Baba, N., Hafdane, M., Agmour, I. et al. Investigating the influence of light pollution on the bioeconomic dynamics of fisheries. J Coast Conserv 28, 23 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11852-023-01027-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11852-023-01027-w