Abstract
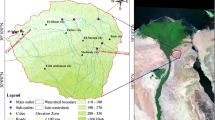
The assessment of hydrometeorological hazards in the mountainous area of Southwestern Sinai area (SWSA) necessitates reliable and accurate information about natural hazards, especially flash floods. Flash floods are the main dangerous hazards that threaten lives and any sustainable development planning in and around the rugged topography areas. The SWSA receives occasional heavy rainstorms every two or four years, triggering destructive floods that runoff towards the Gulf of Suez. The present study aims to extract, evaluate, integrate and map the potential flash flood hazards by applying remote sensing, GIS tools and by statistically analyzing the geomorphometric parameters. Moreover, assessing the flash flood hazard risk ranks was carried for the three main basins (W. Baba, W. Sidri, and W. Nukhul). The drainage networks and basins were extracted from DEM then, delineated into seventy-two sub-basins and then the morphometric parameters of these sub-basins were estimated. The analysis of the various morphometric parameters of the three main basins shows that they have different effects on flash flood hazards. Depending on the statistical analysis of the commutative weights of the important geomorphometric parameters and GIS functions; the studied basins were categorized into three risk ranks; namely: high, moderate and low flash flood risk. The integration of the different controlling parameters revealed that the zones of high flash flood hazard risk are characterized by the low probability of groundwater recharge which should be put into consideration to help the decision makers avoid risks which are considered to be one of the most dangerous obstacles to the sustainable development of the study area.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel Mogheeth S, Abdel Daiem A, Hammad F (1985) Hydrological remarks on Gharandal Basin, Southwest Sinai Peninsula. Desert Inst Bull A.R.E. 35(2):309–329
AbdManap M, Sulaiman WNA, Ramli MF, Pradhan B, Surip N (2013) A knowledge-driven GIS modeling technique for groundwater potential mapping at the upper Langat Basin, Malaysia. Arab J Geosci 6(5):1621–1637
Abou El-Magd AA (2003) Quantitative hydrogeological studies on Wadi Feiran basin, South Sinai, with emphasis on the prevailing environmental conditions. M.Sc. thesis, Geology Dept., Faculty of sciences, Suez Canal University, Ismailia, Egypt, p 353
Aggour TA, Gomaa MA (2008) Hydrogeological and hydrogeochemical studies in Wadi Baba and Sidri, southwestern part of Sinai. Egypt Annals Geol Surv Egypt xxx:497–528
Aglan OShA (1995) Geology of groundwater supplies in the area between Wadi Gharandal and Wadi Sidri, southwestern Sinai. Msc. Thesis, Geol. Dept., Fac. Sci., Ain Shams Univ. p 202
Arnous MO (2004) Geo-environmental assessment of Cairo-Ismailia road area, Egypt, using remote sensing and geographic information system (GIS). Ph.D. thesis, Geology Dept., Fac. of Science, Suez Canal Univ., Ismailia, p 283
Arnous MO (2011) Integrated remote sensing and GIS techniques for landslide hazard zonation: a case study Wadi Watier area, South Sinai, Egypt. J Coast Conserv 15(4):477–497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11852-010-0137-9
Arnous MO (2016) Groundwater potentiality mapping of hard-rock terrain in arid regions using geospatial modelling: example from Wadi Feiran basin, South Sinai, Egypt. Hydrogeol J 24(6):1375–1392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-016-1417-8
Arnous MO, Green DR (2011) GIS and remote sensing as tools for conducting geo-hazards risk assessment along gulf of Aqaba coastal zone, Egypt. J Coast Conserv 15(4):457–475. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11852-010-0136-x
Arnous MO, Green DR (2015) Monitoring and assessing water-logged and salt-affected areas in the eastern Nile Delta region, Egypt, using remotely sensed multi-temporal data and GIS. J Coast Conserv 19(3):369–391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11852-015-0397-5
Arnous MO, Aboulela HA, Green DR (2011) Geo-environmental hazards assessment of the north western gulf of Suez, Egypt. J Coast Conserv 15(1):37–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11852-010-0118-z
Arnous MO, El-Rayes AE, Green DR (2015) Hydrosalinity and environmental land degradation assessment of the East Nile Delta region, Egypt. J Coast Conserv 19(4):491–513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11852-015-0402-z
Arnous MO, El-Rayes AE, Helmy AM (2017) Land-use/land-cover change: a key to understanding land degradation and relating environmental impacts in northwestern Sinai, Egypt. Environ Earth Sci 76:263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6571-3
Bajabaa S, Masoud M, Al-Amri N (2014) Flash flood hazard mapping based on quantitative hydrology, geomorphology and GIS techniques (case study of Wadi Al Lith, Saudi Arabia). Arab J Geosci 7:2469–2481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-0941-2
Ball J (1916) The geography and geology of west central Sinai. Egypt. Surv. Dept, Cairo, p 219
Bapalu VG, Sinha R (2005) GIS in flood hazard mapping: A case study of Kosi River Basin, India; www.gisdevelopment.net, Natural Hazard Management, ESRI
CEOS (2003) The use of earth observing satellites for hazard support: assessments and scenarios, final report of the CEOS Disaster Management Support Group (DMSG). Helen M. Wood, Chair. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) United States Department of Commerce
Climatic Atlas of Egypt (1996) Ministry of transport and communications, Egyptian meteorological authority, Cairo, Egypt
Climatological Normals of The Arab Republic of Egypt (1980) Climatological Normals for the Arab Republic of Egypt up to 1975. Ministry of Civil Aviation, Egyptian Meteorological Authority, Cairo, Egypt
CMDRS (2008) Egypt’s Review: In depth Assessment of Progress in Disaster Risk Reduction
El Nahry AH, Saleh AM (2005) Using remote sensing and GIS techniques for identifying influence of seasonal flashfloods on El-Qaa plain, Egypt. Proc. SPIE 5976, Remote Sensing for Agriculture, Ecosystems, and Hydrology VII, 597604 (October 18, 2005). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.621051
El Shamy IZ (1983) On the hydrogeology of west Central Sinai. Egypt J-Geol 27(1–2):93–105
El-Baz F (1995) Utilizing satellite images for groundwater exploration in fracture zone aquifers. Water resources management in arid condition, Muscal, Sultanate of Oman, p 419–427
El-Rayes AE, Arnous MO (2015) A novel approach in hydrogeochemical exploration for uranium mineralization: example from west central Sinai, Egypt. Acta Geol Sin (English Edition) 89(6):1895–11913. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-6724.12606
EL-Rayes AE, Arnous MO, Aboulela HA (2015) Hydrogeochemical and seismological exploration for geothermal resources in South Sinai, Egypt utilizing GIS and remote sensing. Arab J Geosci 8(8):5631–5647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1667-5
El-Rayes AE, Arnous MO, Aziz AM (2017) Morphotectonic controls of groundwater flow regime and relating environmental impacts in Northwest Sinai, Egypt. Arab J Geosci 10:401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3188-5
Fernandez D, Lutz M (2010) Urban flood hazard zoning in Tucumán Province, Argentina, using GIS and multicriteria decision analysis. Eng Geol 111(1–4):90–99
Gardiner V (1990) Drainage basin morphometry. In: Goudie A (ed) Geomorphological techniques. Unwin Hyman, London, pp 71–81
Geriesh MH (1998) Artificial recharge as an effective tool for augmenting the groundwater resources of Saint Katherine area, South Sinai, Egypt. Proc. 5th Conf. Geol. Sinai develop., Ismailia, Egypt, p 47–67
Hammad FA (1980) Geomorphological and hydrological aspects of Sinai Peninsula. A.R.E. Geol Surv Egypt 10:807–817
Hammad FA, Misak RF (1985) Quantitative geomorphology and groundwater possibilities in the vicinities of Wadi Nasib, Abu Zeneima, Sinai, Egypt. Desert Institute. Bull A.R.E. 35(2):331–351
Horton RF (1932) Drainage basin characteristics. Trans An Geophys Union 13:350–361
Horton RE (1945) Erosional development of streams and their drainage basins, Hydrophysical approach to Quantitative Morphology. Geol Soc Am Bull., 56:275–370
Joji VS, Nair ASK (2014) Terrain characteristics and longitudinal, land use and land cover profiles behavior—a case study from Vamanapuram river basin, southern Kerala, India. Arab J Geosci 7(4):1351–1361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0815-z
Kumar R, Kumar S, Lohani AK, Nema RK, Singh RD (2000) Evaluation of geomorphological characteristics of a catchment using GIS. GIS India, 9(3):13–17
Maidment DR (2002) ArcHydro GIS for water resources. ESRI Press, California
Malczewski J (1996) A GIS-based approach to multiple criteria group decision making. International Journal of Geographical Information System, 10(8):955–971
Martz LW, Garbrechet J (1992) Numerical definition of drainage network and sub catchment areas from digital elevation models. Comput Geosci 18(6):747–761
Mondal T, Gupta S (2015) Evaluation of morphometric parameters of drainage networks derived from topographic map and digital elevation model using remote sensing and GIS. Int J Geomat Geosci 5(4):655–664
Nageswararao K, Swarna LP, Arun KP, Hari KM (2010) Morphometric analysis of Gostani River basin in Andhra Pradesh state, India using spatial information technology. Int J Geom Geosci 1(2):79–187
Omran A, Schroder D, El-Rayes A, Geriesh M (2011) Flood hazard assessment in Wadi Dahab, Egypt based on basin morphometry using GIS techniques. In: Car A, Griesebner G, Strobl J (eds): Geospatial crossroads @ GI_Forum '11. © Herbert Wichmann Verlag, VDE VERLAG GMBH, Berlin/Offenbach ISBN 978-3-87907-509-6
Patton PC (1988) Drainage basin morphometry and floods. In: Baker VR et al (eds) Flood geomorphology. Wiley, New York, pp 51–65
Rai PK, Mohan K, Mishra S, Ahmed A, Mishra VN (2014) A GIS-based approach in drainage morphometric analysis of Kanhar River basin, India. Appl Water Sci 7:217–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-014-0238-y
Saad KF, El Shamy IZ, Sweidan AS (1980) Quantitative analysis of geomorphology and hydrology of Sinai Peninsula, 5th Africa Conference, A.R.E
Sameena M, Krishnamurthy J, Jayaraman V, Ranganna G (2009) Evaluation of drainage networks developed in hard rock terrain. Geocarto Int 24(5):1–24
Shata AA (1955) Some remarks on the distribution of the carboniferous formations in Egypt. Bull Inst Des Egypt 5:241–247
Shawn MM (2011) Geoenvironmental and geophysical evaluation the industrial area south Abu Zeneima, Sinai, Egypt. M.Sc. Thesis, Geol. Dept. Fac. Sci. Suez Canal Univ. Ismailia, Egypt, p. 227
Strahler AN (1954) Quantitative geomorphology of erosional landscapes. C. R. 19th Intern. Geol. Cong., Algiers, 1952, Sec. vol 13, Pt. 3, p 341–354
Strahler AN (1964) Quantitative geomorphology of drainage basins is channel networks. In: Hand Book of Applied Hydrology, Vent Te Chow (ed), McGraw Hill Book Company, New York, p 39-79
Subyani AM (2011) Hydrologic behavior and flood probability for selected arid basins in Makkah area, western Saudi Arabia. Arab J Geosci 4(5):817–824. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-009-0098-1
Taylor AB, Schwarz E (1952) Unit hydrograph lag and peak flow related to basin characteristics. Trans Am Geophys Union 33:235–246
UNISDR (2002) UN International strategy for Disaster Reduction (UN ISDR), Living with Risk - Annex 1, July 2002. http://www.unisdr.org/unisdr/Globalreport.htm
Wang Y, Zhang W, Liu X (2010) Hydrological watersheds model researching based on digital elevation model. 2010 18th International Conference on Geoinformatics, 18-20 June 2010, Beijing, p 1–5, IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/GEOINFORMATICS.2010.5567929l
WMO & UNESCO (1974) International glossary of hydrology. UNESCO publication, Paris, UNESCO;Geneva, WMO, p 393
Xiao, L, Liu H, Zhao X (2010) Impact of digital elevation model resolution on stream network parameters. Environmental Science and Information Application Technology (ESIAT), 2010 International Conference on (vol 3). https://doi.org/10.1109/ESIAT.2010.5568306
Yahaya S, Ahmad N, Abdalla FR (2010) Multicriteria analysis for flood vulnerable areas in Hadejia-Jama’are River Basin, Nigeria. Eur J Sci Res 42(1):71–83
Youssef AM, Pradhan B, Hassan AM (2011) Flash flood risk estimation along the St. Katherine road, southern Sinai, Egypt using GIS based morphometry and satellite imagery. Environ Earth Sci 62(3):611–623
Zerger A, Smith DI (2003) Impediments to using GIS for real-time disaster decision support. Comput Environ Urban Syst 27:123–141
Zhang XU, Zhou T, Zheng J (2009) DEM-based spatial discretization and parameter database design for distributed hydrological model. Proc. SPIE 7498, MIPPR 2009: Remote Sensing and GIS Data Processing and Other Applications, 749831 (October 30, 2009). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.832487
Acknowledgements
The author wishes to express his appreciation and gratitude to Prof. Ahmed E. El-Rayes, Professor of hydrogeology, Geology Department, Faculty of Science, Suez Canal University, Egypt, for his constructive criticism on an earlier draft of the manuscript and his fruitful discussions. The author thanks, reviewers and the editor of Journal of Coastal Conservation for giving constructive comments that also helped improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arnous, M.O., Omar, A.E. Hydrometeorological hazards assessment of some basins in Southwestern Sinai area, Egypt. J Coast Conserv 22, 721–743 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11852-018-0604-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11852-018-0604-2