Abstract
Background
Essential hypertension is a chronic pathology that causes long-term complications due to late diagnosis of patients, the inability to control the disease through medication, or due to the complexity of associated risk factors.
Aims
Our study sets out to identify specific patterns of response to arterial hypertension treatment, by taking into consideration the multiple connections between risk factors in a relevant population of hypertensive patients.
Methods
Network science is an emerging paradigm, branching over multiple aspects of physical, biological and social phenomena. One such branch, which has brought significant contributions to medical science, is the field of network medicine. To apply this methodology, we create a complex network of hypertensive patients based on their common medical conditions. Consequently, we obtain a community-based representation which pinpoints specific—and previously uncharted—patterns of hypertension development. This approach creates incentives for evaluating patient’s treatment efficacy, by considering its network topological position.
Results
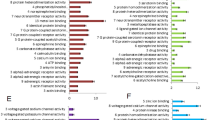
Distinct clusters of patients with common properties have emerged for each study group (group A—treated with nebivolol, group B—treated with perindopril and group C—treated with candesartan cilexetil). Therefore, our network-based clustering allows for a better treatment assessment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cortez-Diaz N, Martins SR, Belo A, VALSIM Study investigators et al (2013) Association of metabolic risk factors with uncontrolled hypertension: comparison of the several definitions of metabolic syndrome. J Hypertens 31(10):1991–1997. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e32836342f7
Elperin DT, Pelter MA, Deamer RL et al (2014) A large cohort study evaluating risk factors associated with uncontrolled hypertension. J Clin Hypertens. 16(2):149–154. doi:10.1111/jch.12259
Marotta T, Liccardo M, Schettini F et al (2015) Association of hyperuricemia with conventional cardiovascular risk factors in elderly patients. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwhich). 17(1):27–32. doi:10.1111/jch.12434
Newman MEJ (2003) The structure and function of complex networks. SIAM Rev 45(2):167–256. doi:10.1137/S003614450342480
Wang XF, Chen G (2003) Complex networks: small-world, scale-free and beyond. Circuits Syst Mag IEEE 3(1):6–20. doi:10.1109/MCAS.2003.1228503
Papo D, Buldú JM, Boccaletti S et al (2014) Complex network theory and the brain. The Royal Society publishing, Philosophical transactions B. doi:10.1098/rstb.2013.0520
Barabási AL (2013) Network science. Phil Trans Royal Soc A Math Phys Eng Sci 371(1987):20120375. doi:10.1098/rsta.2012.0375
Barabási AL, Gulbahce N, Loscalzo J (2011) Network medicine: a network-based approach to human disease. Nat Rev Genet 12(1):56–68. doi:10.1038/nrg2918
Loscalzo J, Barabasi AL (2011) Systems biology and the future of medicine. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med 3(6):619–627. doi:10.1002/wsbm.144
Goh KI, Choi IG (2012) Exploring the human diseasome: the human disease network. Brief Funct Genomics 11(6):533–542. doi:10.1093/bfgp/els032
Silverman EK, Loscalzo J (2012) Network medicine approaches to the genetics of complex diseases. Discov Med 14(75):143–152
Cho D-Y, Kim Y-A, Przytycka TM (2012) Network Biology Approach to Complex Diseases. PLoS Comput Biol 8(12):e1002820. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002820
Udrescu M, Topirceanu A, Avram R, Mihaicuta S (2014) AER score: a social-network-inspired predictor for sleep apnea syndrome. Chest 145(3):609. doi:10.1378/chest.1824353
Wang K, Sun J, Zhou S et al (2013) Correction: prediction of drug-target interactions for drug repositioning only based on genomic expression similarity. PLoS Comput Biol 9:11. doi:10.1371/annotation/958d4c23-4f1e-4579-b6ef-8ae1f828b1dd.10.1371/annotation/958d4c23-4f1e-4579-b6ef-8ae1f828b1dd
Mancia G et al (2007) The task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension, the task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the european society of cardiology. Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the european society of hypertension (ESH) and of the european society of cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 28(12):1462–1536
Mancia G et al (2013) Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 34(28):2159–2219
American Diabetes Association (2010) Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2010. Diabetes Care 33(Suppl1):S11–S61
Jacomy M, Venturini T, Heymann S, Bastian M (2014) ForceAtlas2, a Continuous Graph Layout Algorithm for Handy Network Visualization Designed for the Gephi Software. PLoS One 9(6):e98679
Barabási AL (2007) Network medicine—from obesity to the “diseasome”. N Engl J Med 357(4):404–407. doi:10.1056/NEJMe078114
Heart Score Program available at http://www.heartscore.org/ro/Pages/Welcome.aspx, Accessed: 12-01-2015
Cooney MT, Dudina A, D’Agostino R, Graham IM (2010) Cardiovascular risk-estimation systems in primary prevention: do they differ? Do they make a difference? Can we see the future? Circulation 122(3):300–310. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.852756
Ulusoy S (2013) Assessment of cardiovascular risk in hypertensive patients: a comparison of commonly used risk scoring programs. Kidney Int Suppl 3(4):340–342. doi:10.1038/kisup.2013.72
Poldervaart JM, Reitsma JB, Koffijberg H et al (2013) The impact of the HEART risk score in the early assessment of patients with acute chest pain: design of a stepped wedge, cluster randomised trial. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 13:77. doi:10.1186/1471-2261-13-77
Noack A (2009) Modularity clustering is force-directed layout. Phys Rev E 79(2):026102. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.79.026102
Newman ME, Girvan M (2004) Finding and evaluating community structure in networks. Phys Rev E 69(2):026113. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.69.026113
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical committee approval
The present study has been approved by the Ethical Committee at “Victor Babes” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Timisoara, Romania (no.10/2013). Furthermore, all the patients included in the study have signed the informed consent, thus agreeing to participate in this research.
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suciu, L., Cristescu, C., Topîrceanu, A. et al. Evaluation of patients diagnosed with essential arterial hypertension through network analysis. Ir J Med Sci 185, 443–451 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-015-1342-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-015-1342-1