Abstract
Background
Although microvascular decompression (MVD) has become the best surgical treatment for trigeminal neuralgia, it does not achieve 100 % cure rate. Re-exploration of the posterior fossa may carry increased risk over first-time MVD and is not always successful, so other treatments are needed.
Aims
In this study, we evaluate the effectiveness of the patients with recurrent trigeminal neuralgia after MVD treated with percutaneous balloon compression (PBC).
Methods
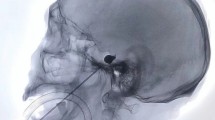
The clinical data of 52 recurrent trigeminal neuralgia patients after MVD who underwent PBC between November 2007 and March 2012 were retrospectively reviewed and analyzed.
Results
After the PBC, 50 patients (96.2 %) experienced immediate pain relief; 1 patient had occasional pain, and did not require medication; and 1 patient had no pain relief. The total efficiency was 98.1 %. With a mean length of follow-up of 37.6 months, ranging from 12 to 64 months after surgery, 43 (82.7 %) patients remained pain-free, 4 patients (7.7 %) had mild recurrence, and 3 patients (5.8 %) had severe recurrence. The mean time to recurrence was 25.1 months (5–60 months). PBC was repeated a second time in three patients, a third time in one patient. Postoperative complications included facial numbness in 51 patients (98.1 %), masseter muscle weakness in 31 patients (59.6 %), paresthesia in 5 patients (9.6 %), and diplopia secondary to abducens nerve palsy in 1 patient (1.9 %). None of the patients had serious surgical morbidities.
Conclusions
PBC is a minimally invasive, safe and effective procedure which can be regarded as an optimized choice for recurrent trigeminal neuralgia after MVD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jannetta PJ (1967) Arterial compression of the trigeminal nerve at the pons in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 26:159–162
Sekula RF Jr, Frederickson AM, Jannetta PJ, Quigley MR, Aziz KM, Arnone GD (2011) Microvascular decompression for elderly patients with trigeminal neuralgia: a prospective study and systematic review with meta-analysis. J Neurosurg 114:172–179
Tatli M, Satici O, Kanpolat Y, Sindou M (2008) Various surgical modalities for trigeminal neuralgia:literature study of respective long-term outcomes. Aeta Neuraehir (Wien) 150:243–255
Matsushima T, Yamaguchi T, Inoue TK, Matsukado K, Fukui M (2000) Recurrent trigeminal neuralgia after microvascular decompression using an interposing technique. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 142:557–561
Tyler-Kabara EC, Kassam AB, Horowitz MH, Urqo L, Hadjipanayis C, Levy EI, Chang YF (2002) Predictors of outcome in surgically managed patients with typical and atypical trigeminal neuralgia: comparison of results following microvascular decompression. J Neurosurg 96:527–531
Barker FG 2nd, Jannetta PJ, Bissonette DJ, Larkins MV, Jho HD (1996) The long-term outcome of microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. N Engl J Med 334:1077–1083
Mullan S, Lichtor T (1983) Percutaneous microcompression of the trigeminal ganglion for trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 59:1007–1012
LichtorT Mullan JF (1990) A 10-year follow-up review of percutaneous microcompression of the trigeminal ganglion. J Neurosurg 72:49–54
Skirving DJ, Dan NG (2001) A 20-year review of percutaneous balloon compression of the trigeminal ganglion. J Neurosurg 94:913–917
Rath SA, Klein HJ, Richter H (1996) Findings and long-term results of subsequent operation after failed microdecompression for trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery 39:933–940
Lee SH, Levy EI, Scarrow AM, Kassam A, Jannetta PJ (2000) Recurrent trigeminal neuralgia attributable to veins after microvascular decompression. Neurosurgery 46:356–361 (discussion 361-2)
Amador N, Pollock BE (2008) Repeat posterior fossa exploration for patients with persistent or recurrent idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 108:916–920
Kureshi SA, Wilkins RH (1998) Posterior fossa reexploration for persistent or recurrent trigeminal neuralgia or hemifacial spasm: surgical findings and therapeutic implications. Neurosurgery 43:1111–1117
Uqwuanyi UC, Kitchen ND (2010) The operative findings in re-do microvascular decompression for recurrent trigeminal neuralgia. Br J Neurosurg 24:26–30
Cho DY, Chang CG, Wang YC, Wang FH, Shen CC, Yang DY (1994) Repeat operations in failed microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery 35:665–669
Park SS, Lee MK, Kim JW, Jung JY, Kim IS, Ghang GG (2008) Percutaneous balloon compression of trigeminal ganglion for the treatment of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia: experience in 50 patients. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 43:186–189
Omeis I, Smith D, Kim S, Murali R (2008) Percutaneous balloon compression for the treatment of recurrent trigeminal neuralgia: long-term outcome in 29 patients. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 86:259–265
Chen JF, Lee ST (2003) Comparison of percutaneous trigeminal ganglion compression and microvascular decompression for the management of trigeminal neuralgia. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 105:203–208
Kouzounias K, Lind G, Schechtmann G, Winter J, Linderoth B (2010) Comparison of percutaneous balloon compression and glycerol rhizotomy for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 113:486–492
Frank F, Fabrizi AP (1989) Percutaneous surgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 97:128–130
Brisman R (2007) Microvascular decompression vs. gamma knife radiosurgery for typical trigeminal neuralgia: preliminary findings. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 85:94–98
Sindou M, Leston J, Howeidy T, Decullier E, Chapuis F (2006) Micro-vascular decompression for primary trigeminal neuralgia (typical or atypical). Long-term effectiveness on pain; prospective study with survival analysis in a consecutive series of 362 patients. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 148:1235–1245
Li ST, Wang X, Pan Q, Hai J, Liu N, Shen F, Liu Z, Guan Y (2005) Studies on the operative outcomes and mechanisms of microvascular decompression in treating typical and atypical trigeminal neuralgia. Clin J Pain 21:311–316
Brown JA, Chittum CJ, Sabol D, Gouda JJ (1996) Percutaneous balloon compression of the trigeminal nerve for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurg Focus 1:e4
Stomal-Slowinska M, Slowinski J, Lee TK, Uitti RJ, Deen HG, Reimer R, Cheshire WP Jr, Herzog-Bryan G, Wharen RE Jr (2011) Correlation of clinical findings and results of percutaneous balloon compression for patients with trigeminal neuralgia. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 11:14–21
Chen JF, Tu PH, Lee ST (2012) Repeated percutaneous balloon compression for recurrent trigeminal neuralgia: a long-term study. World Neurosurg 77:352–356
Campos WK, Linhares MN (2011) A prospective study of 39 patients with trigeminal neuralgia treated with percutaneous balloon compression. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 69:221–226
Correa CF, Teixeira MJ (1998) Balloon compression of the Gasserian ganglion for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 71:83–89
Lobato RD, Rivas JJ, Sarabia R, Lamas E (1990) Percutaneous microcompression of the gasserian ganglion for trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 72:546–553
Asplund P, Linderoth B, Bergenheim AT (2010) The predictive power of balloon shape and change of sensory functions on outcome of percutaneous balloon compression for trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 113:498–507
Lee ST, Chen JF (2003) Percutaneous trigeminal ganglion balloon compression for treatment of trigeminal neuralgia, part II: results related to compression duration. Surg Neurol 60:149–153 (discussion 153-4)
Brown JA, McDaniel MD, Weaver MT (1993) Percutaneous trigeminal nerve compression for treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: results in 50 patients. Neurosurg 32:570–573
Urculo E, Alfaro R, Arrazola M, Astudilio E, Rejas G (2004) Trochlear nerve palsy after repeated percutaneous balloon compression for recurrent trigeminal neuralgia: case report and pathogenic considerations. Neurosurgery 54:505–508 (discussion 508–9)
Broggi G, Franzini A, Lasio G, Giorqi C, Servello D (1990) Long-term results of percutaneous retrogasserian thermorhizotomy for “essential” trigeminal neuralgia: considerations in 1000 patients. Neurosurgery 26:783–787
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, Y., Yang, D., Dong, X. et al. Percutaneous balloon compression (PBC) of trigeminal ganglion for recurrent trigeminal neuralgia after microvascular decompression (MVD). Ir J Med Sci 184, 745–751 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-014-1163-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-014-1163-7