Abstract
Background
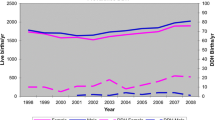
The incidence of developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) in the Republic of Ireland is unknown. It has been shown by previous Irish studies that effective screening methods for DDH are not widely practiced. The effect of this on treatment outcomes is unknown.
Aims
The aim of this study was to estimate the incidence and treatment outcomes of DDH in the Southeast of Ireland.
Methods
In a retrospective study, all cases of DDH in children born in 2009 were identified using the outpatient clinic database. We defined an early and late diagnosis as those treated before and after three months, respectively. We defined the operative incidence as those who required open surgery.
Results
Fifty-six cases of DDH were diagnosed giving an incidence of 6.73 per 1,000 live births. 58.9 % (n = 33) were referred to the clinic and began treatment early, while 41.1 % (n = 23) presented late. The incidence of operative procedures was 1.08 per 1,000 live births. The incidence of those requiring surgery was higher in the late diagnosis group.
Conclusion
Our overall incidence rate of 6.73 per 1,000 live births in 2009 is similar to other international studies. Worryingly our incidence of 2.77 per 1,000 having late diagnosis and 1.08 per 1,000 live births requiring open surgery was higher. Despite screening with clinical examination, the percentage of late diagnosis remains high. There is a need for the development of a national screening policy with greater use of ultrasound screening to improve current practices.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Engesaeter IO, Lehmann T, Laborie LB, Lie SA, Rosendahl K, Engesaeter LB (2011) Total hip replacement in young adults with hip dysplasia: age at diagnosis, previous treatment, quality of life, and validation of diagnoses reported to the Norwegian Arthroplasty Register between 1987 and 2007. Acta Orthop 82(2):149–154. doi:10.3109/17453674.2011.566146
Leck I (2000) Screening for congenital dislocation of the hip. Lancet 355:232–233. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)72105-X (author reply)
Bialik V, Bialik GM, Blazer S, Sujov P, Wiener F, Berant M (1999) Developmental dysplasia of the hip: a new approach to incidence. Pediatrics 103(1):93–99
Marks DS, Clegg J, al-Chalabi AN (1994) Routine ultrasound screening for neonatal hip instability. can it abolish late-presenting congenital dislocation of the hip? J Bone Joint Surg Br 76(4):534–538
Dezateux C, Rosendahl K (2007) Developmental dysplasia of the hip. Lancet 369(9572):1541–1552. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60710-7
Mahan ST, Katz JN, Kim YJ (2009) To screen or not to screen? A decision analysis of the utility of screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am 91(7):1705–1719. doi:10.2106/JBJS.H.00122
Schwend RM, Schoenecker P, Richards BS, Flynn JM, Vitale M (2007) Screening the newborn for developmental dysplasia of the hip: now what do we do? J Pediatr Orthop 27(6):607–610. doi:10.1097/BPO.0b013e318142551e
Leck I (1986) An epidemiological assessment of neonatal screening for dislocation of the hip. J R Coll Physicians Lond 20(1):56–62
Sharpe P, Mulpuri K, Chan A, Cundy PJ (2006) Differences in risk factors between early and late diagnosed developmental dysplasia of the hip. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 91(3):F158–F162. doi:10.1136/adc.2004.070870
Gul R, Coffey JC, Khayyat G, McGuinness AJ (2002) Late presentation of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Ir J Med Sci 171(3):139–140
O’Grady MJ, Mujtaba G, Hanaghan J, Gallagher D (2010) Screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip: current practices in Ireland. Ir J Med Sci 179(2):279–283. doi:10.1007/s11845-009-0339-z
Central Statistics Office (2009) Report on vital statistics 2009, Table 2.17 Births in 2009 showing place of occurrence and area of normal residence. http://www.cso.ie/en/media/csoie/releasespublications/documents/vitalstats/2009/annualreport2009.pdf. Accessed 10 August 2012
Clarke NM, Reading IC, Corbin C, Taylor CC, Bochmann T (2012) Twenty years experience of selective secondary ultrasound screening for congenital dislocation of the hip. Arch Dis Child 97(5):423–429. doi:10.1136/archdischild-2011-301085
Maxwell SL, Ruiz AL, Lappin KJ, Cosgrove AP (2002) Clinical screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip in Northern Ireland. BMJ 324(7344):1031–1033
Lisle R, Boekelaar M, Stannage K, Whitewood C (2012) Delayed diagnosis of developmental dislocation of the hip: the Western Australian experience. ANZ J Surg 82(9):612–615. doi:10.1111/j.1445-2197.2012.06110.x
Grill F, Muller D (1997) Results of hip ultrasonographic screening in Austria. Der Orthopade 26(1):25–32
Clinical practice guideline: early detection of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Committee on Quality Improvement, Subcommittee on Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. American Academy of Pediatrics for DDH (2000). Pediatrics 105(4 Pt 1):896–905
Patel H (2001) Preventive health care, 2001 update: screening and management of developmental dysplasia of the hip in newborns. CMAJ 164(12):1669–1677
Shorter D, Hong T, Osborn DA (2011) Screening programmes for developmental dysplasia of the hip in newborn infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 9:CD004595. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004595.pub2
Graf R (1980) The diagnosis of congenital hip-joint dislocation by the ultrasonic combound treatment. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 97(2):117–133
Standing Medical Advisory Committee and the Standing Nursing and Midwifery Advisory Committee (1986) Screening for the detection of congenital dislocation of the hip. Arch Dis Child 61(9):921–926
Elbourne D, Dezateux C, Arthur R, Clarke NM, Gray A, King A, Quinn A, Gardner F, Russell G (2002) Ultrasonography in the diagnosis and management of developmental hip dysplasia (UK Hip Trial): clinical and economic results of a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 360(9350):2009–2017
Thaler M, Biedermann R, Lair J, Krismer M, Landauer F (2011) Cost-effectiveness of universal ultrasound screening compared with clinical examination alone in the diagnosis and treatment of neonatal hip dysplasia in Austria. J Bone Joint Surg Br 93(8):1126–1130. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.93B8.25935
Bialik V, Bialik GM, Wiener F (1998) Prevention of overtreatment of neonatal hip dysplasia by the use of ultrasonography. J Pediatr Orthop B 7(1):39–42
Wilson JM, Jungner YG (1968) Principles and practice of mass screening for disease. Bol Oficina Sanit Panam 65(4):281–393
Atrey A, Gupte CM, Corbett SA (2010) Review of successful litigation against english health trusts in the treatment of adults with orthopaedic pathology: clinical governance lessons learned. J Bone Joint Surg Am 92(18):e36. doi:10.2106/JBJS.J.00277
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phelan, N., Thoren, J., Fox, C. et al. Developmental dysplasia of the hip: incidence and treatment outcomes in the Southeast of Ireland. Ir J Med Sci 184, 411–415 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-014-1133-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-014-1133-0