Abstract
Introduction
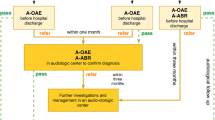
Hearing screening programmes aim to detect hearing loss in the neonate. The Health Service Executive (HSE) South was the first phase of a national roll-out of a neonatal hearing screening programme in Ireland, going live on 28 April 2011.
Results
Over 11,738 babies have been screened for permanent childhood hearing impairment (PCHI) during the first 12 months. The percentage of eligible babies offered hearing screening was 99.2 %. Only 0.2 % (n = 25) of those offered screening declined. 493 (4 %) were referred for immediate diagnostic audiological assessment. The average time between screen and diagnostic audiology appointment was 2 weeks. 15 (1.3/1,000) babies have been identified with a PCHI over the 12-month period. 946 (4 %) babies screened were admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) for >48 h. The prevalance of PCHI is 7.3/1,000 in the NICU population compared to 0.6/1000 in the well baby population. 214 (1.8 % of total babies screened) had a clear response in the screening programmes, but were deemed to be at risk of an acquired childhood hearing impairment. These babies will be reassessed with a diagnostic audiology appointment at 8–9 months of age. To date, there is one case of acquired hearing impairment through this targeted follow-up screen. Of the 15 cases of PCHI identified, 8 (53 %) of these had one or more risk factors for hearing loss and 7 (37 %) were admitted to the NICU for >48 h. Four babies were referred for assessment at the National Cochlear Implant Centre.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Northgate eScreener Plus (eSP).
References
Fortum HM, Summerfield AQ, Marshall DH, Davis AC, Bamford JM (2001) Incidence of permanent childhood hearing impairment in the United Kingdom and implications for universal neonatal hearing screening: questionnaire based assessment study. BMJ 323(7312):536–540
Yoshinaga-Itano C, Sedey AL (1998) Language of early and late identified children with hearing loss. Paediatrics 102:1161–1171
National Rehabilitation Board (1996) The epidemiology of childhood hearing impairment in South-East Ireland: implications for service providers. National Rehabilitation Board, Dublin
American academy of pediatrics (2007) Position statement: principles and guidelines for early hearing detection and intervention programs. Pediatrics 106(4):798
Census (2011) Central Statistics Office, Dublin, Ireland
National Audiology Review (2011) HSE publication. www.hse.ie/Eng/Services/Publications/corporate/AudiologyReview.pdf
Wood S, Davis A, Sutton G (2011) NHS publications, Newborn hearing screening programme (NHSP): recommendations for changes in targeted follow up procedures. http://hearing.screening.nhs.uk/audiology
Nikolopoulous TP, Archbold SM (1999) The development of auditory perception in children following cochlear implantation. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 49:189–191
Sutton G, Gravel J, Hood L (2008) Assessment of auditory neuropathy/auditory dys-synchrony: a recommended protocol, NHSP, NHS Publication. http://hearing.screening.nhs.uk/audiologypublic
Wilson JM (1968) The evaluation of the worth of early disease detection. J R Coll Gen Pract 16(Suppl 2):48–57
Health service executive (2011) A practical guide to newborn bloodspot screening in Ireland, National newborn bloodspot screening laboratory, 5th edn. Children’s University Hospital, Dublin
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O’Connor, A., O’Sullivan, P.G., Behan, L. et al. Initial results from the newborn hearing screening programme in Ireland. Ir J Med Sci 182, 551–556 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-013-0924-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-013-0924-z