Abstract
Objective
The purpose of this study is to determine the association between fetal nasal bone length (NBL) and gestational age (GA), biparietal diameter (BPD) and head circumference (HC) in women undergoing prenatal assessments and Down syndrome screening.
Methods
Cross-sectional data were obtained from 3,003 women with singleton pregnancies who underwent a prenatal ultrasound examination at the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Cheng Hsin General Hospital between August 2006 and July 2009.
Results
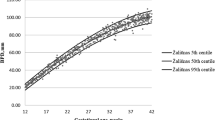
Statistical analyses involved linear regression. NBL with GA, BPD and HC as measured between 14+0 and 35+6 weeks of gestation were linearly related.
Conclusions
Using multiple parameters(GA, BPD and HC) to estimate NBL is more accurate than using than using GA or BPD or HC alone, as indicated by the higher predictive value.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bromley B, Lieberman E, Shipp TD, Benacerraf BR (2002) Fetal nose bone length: a marker for Down syndrome in the second trimester. J Ultrasound Med 21:1387–1394
Bell R, Rankin J, Donaldson LJ (2003) Down’s syndrome: occurrence and outcome in the north of England, 1985–99. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol 17:33–39
Van den Hof MC, Wilson RD (2005) Fetal soft markers in obstetric ultrasound. J Obstet Gynaecol Can 27:592–636
Monni G, Zoppi MA, Ibba RM, Floris M, Manca F, Axiana C (2005) Nuchal translucency and nasal bone for trisomy 21 screening: single center experience. Croat Med J 46:786–791
Bunduki V, Ruano R, Miguelez J, Yoshizaki CT, Kahhale S, Zugaib M (2003) Fetal nasal bone length: reference range and clinical application in ultrasound screening for trisomy 21. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 21:156–160
Otano L, Aiello H, Igarzabal L, Matayoshi T, Gadow EC (2002) Association between first trimester absence of fetal nasal bone on ultrasound and Down syndrome. Prenat Diagn 22:930–932
Cicero S, Bindra R, Rembouskos G, Spencer K, Nicolaides KH (2003) Integrated ultrasound and biochemical screening for trisomy 21 using fetal nuchal translucency, absent fetal nasal bone, free beta-hCG and PAPP-A at 11 to 14 weeks. Prenat Diagn 23:306–310
Collado F, Bombard A, Li V, Julliard K, Aptekar L, Weiner Z (2005) Ethnic variation of fetal nasal bone length between 11–14 weeks’ gestation. Prenat Diagn 25:690–692
Sonek JD, McKenna D, Webb D, Croom C, Nicolaides K (2003) Nasal bone length throughout gestation: normal ranges based on 3537 fetal ultrasound measurements. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 21:152–155
Chen M, Lee CP, Leung KY, Hui PW, Tang MH (2004) Pilot study on the midsecond trimester examination of fetal nasal bone in the Chinese population. Prenat Diagn 24:87–91
Kanagawa T, Fukuda H, Kinugasa Y, Son M, Shimoya K, Murata(ed) Y (2006) Mid-second trimester measurement of fetal nasal bone length in the Japanese population. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 32:403–407
Jung E, Won HS, Lee PR, Kim A (2007) Ultrasonographic measurement of fetal nasal bone length in the second trimester in Korean population. Prenat Diagn 27:154–157
Zelop CM, Milewski E, Brault K, Benn P, Borgida AF, Egan JF (2005) Variation of fetal nasal bone length in second-trimester fetuses according to race and ethnicity. J Ultrasound Med 24:1487–1489
Shin JS, Yang JH, Chung JH, Kim MY, Ryu HM, Han (ed.) JY (2006) The relation between fetal nasal bone length and biparietal diameter in the Korean population. Prenat Diagn 26:321–323
Shohat T, Romano-Zelekha O (2001) Ultrasonographic measurements of fetal femur length and biparietal diameter in an Israeli population. Isr Med Assoc J 3:166–168
Nisbet D, Robinson H, Halliday J, de CL (2002) Australian Society of Ultrasound in Medicine (ASUM) Policy Statement on normal ultrasonic fetal measurements. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 42:101–103
Cicero S, Bindra R, Rembouskos G, Tripsanas C, Nicolaides KH (2002) Fetal nasal bone length in chromosomally normal and abnormal fetuses at 11–14 weeks of gestation. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 11:400–402
Cicero S, Curcio P, Papageorghiou A, Sonek J, Nicolaides K (2001) Absence of nasal bone in fetuses with trisomy 21 at 11–14 weeks of gestation: an observational study. Lancet 358:1665–1667
Guis F, Ville Y, Vincent Y, Doumerc S, Pons JC, Frydman R (1995) Ultrasound evaluation of the length of the fetal nasal bones throughout gestation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 5:304–307
Sonek JD, Nicolaides KH (2002) Prenatal ultrasonographic diagnosis of nasal bone abnormalities in three fetuses with Down syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol 186:139–141
Cusick W, Provenzano J, Sullivan CA, Gallousis FM, Rodis JF (2004) Fetal nasal bone length in euploid and aneuploid fetuses between 11 and 20 weeks’ gestation: a prospective study. J Ultrasound Med 23:1327–1333
Gamez F, Ferreiro P, Salmean JM (2004) Ultrasonographic measurement of fetal nasal bone in a low-risk population at 19–22 gestational weeks. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 23:152–153
Naraphut B, Uerpairojkit B, Chaithongwatthana S, Tannirandorn Y, Tanawattanacharoen S, Manotaya (ed.) S (2006) Nasal bone hypoplasia in trisomy 21 at 15 to 24 weeks’ gestation in A high risk Thai population. J Med Assoc Thai 89:911–917
Schluter PJ, Pritchard G, Gill MA (2007) Using ultrasonic fetal size measurements to estimate gestational age in Brisbane, Australia. Australas Radiol 51:46–52
Merz E, Wellek S (1996) Normal fetal growth profile—a uniform model for calculating normal curves for current head and abdomen parameters and long limb bones. Ultraschall Med 17:153–162
Salomon LJ, Bernard JP, Ville Y (2007) Estimation of fetal weight: reference range at 20–36 weeks’ gestation and comparison with actual birth-weight reference range. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 29:550–555
Odibo AO, Sehdev HM, Sproat L, Parra C, Odibo L, Dunn (ed.) L (2006) Evaluating the efficiency of using second-trimester nasal bone hypoplasia as a single or a combined marker for fetal aneuploidy. J Ultrasound Med 25:437–441 quiz 443
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Grants from the National Science Council (NSC97-2320-B-010-004 and NSC98-2314-B-350-002-MY3).
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiu, WH., Tung, TH., Chen, Ys. et al. Normative curves of fetal nasal bone length for the ethnic Chinese population. Ir J Med Sci 180, 73–77 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-010-0520-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-010-0520-4