Abstract
Background
Non-convulsive seizures and status epilepticus are common in brain-injured patients in intensive care units. Continuous electroencephalography (cEEG) monitoring is the most sensitive means of their detection. In centres where cEEG is unavailable, routine EEG is often utilized for diagnosis although its sensitivity is lower.
Aims
To establish the rate of electrographic seizure detection in ICU using routine EEG.
Methods
We identified all routine EEGs performed within a general adult ICU in Ireland over 3 years, and analyzed the clinical and EEG data.
Results
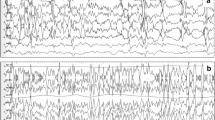
Fifty-two patients underwent single or repeated EEG evaluation during the time period. Epileptiform abnormalities were evident in 15%, periodic abnormalities in 14%, and electrographic seizures in just one patient (2%) in their first or only routine EEG recording.
Conclusion
The rate of electrographic seizure detection by routine EEG in a general ICU is lower than anticipated. Earlier and more prolonged recordings are needed in this setting.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Towne AR, Waterhouse EJ, Boggs JG, Garnett LK, Brown AJ, Smith JR, DeLorenzo RJ (2000) Prevalence of nonconvulsive status epilepticus in comatose patients. Neurology 54:340–345
Young GB, Doig GS (2005) Continuous EEG monitoring in comatose intensive care patients: epileptiform activity in etiologically distinct groups. Neurocrit Care 2:5–10. doi:10.1385/NCC:2:1:005
Young BG, Jordan KG, Doig GS (1996) An assessment of nonconvulsive seizures in the intensive care unit using continuous EEG monitoring: an investigation of variables associated with mortality. Neurology 47:83–89
Claassen J, Mayer MD, Kowalski RG, Emerson RG, Hirsch LJ (2004) Detection of electrographic seizures with continuous EEG monitoring in critically ill patients. Neurology 62:1743–1748
Pandian JD, Cascino GD, So EL, Manno E, Fulgham JR (2004) Digital video-electroencephalographic monitoring in the neurological-neurosurgical intensive care unit: clinical features and outcome. Arch Neurol 61:1090–1094. doi:10.1001/archneur.61.7.1090
Narayanan JT, Murthy JM (2007) Nonconvulsive status epilepticus in a neurological intensive care unit: profile in a developing country. Epilepsia 48:900–906. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2007.01099.x
Privitera M, Hoffman M, Moore JL, Jester D (1994) EEG detection of nontonic-clonic status epilepticus in patients with altered consciousness. Epilepsy Res 18:155–166. doi:10.1016/0920-1211(94)90008-6
Vespa PM, O’Phelan K, Shah M, Mirabelli J, Starkman S, Kidwell C, Saver J, Nuwer MR, Frazee JG, McArthur DA, Martin NA (2003) Acute seizures after intracerebral hemorrhage: a factor in progressive midline shift and outcome. Neurology 60:1441–1446
Carrera E, Michel P, Despland PA, Maeder-Ingvar M, Ruffieux C, Debatisse D, Ghika J, Devuyst G, Bogousslavsky J (2006) Continuous assessment of electrical epileptic activity in acute stroke. Neurology 67:99–104. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000223361.90278.ca
Claassen J, Jette N, Chum F, Green R, Schmidt M, Choi H, Jirsch J, Frontera JA, Connolly ES, Emerson RG, Mayer SA, Hirsch LJ (2007) Electrographic seizures and periodic discharges after intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurology 69:1356–1365. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000281664.02615.6c
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McHugh, J.C., Downey, T., Murphy, R.P. et al. Analysis of routine EEG usage in a general adult ICU. Ir J Med Sci 178, 263–266 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-009-0317-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-009-0317-5