Abstract
Background
Spontaneous rapid resolution of acute subdural hematoma (ASDH) is a rare phenomenon for this severe insult after head trauma.
Case report
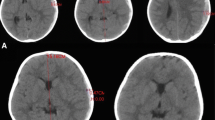
We present a 22-year-old patient who developed ASDH with a moderate midline shift and compression of lateral ventricle after a truncal collision but without a direct beat on the head. Conservative management was performed under close monitoring because of unexpected improvement of clinical signs and symptoms. Unexpectedly, the ASDH resolved spontaneously within 13 h after the trauma, and he was discharged 1 week later without any neurological deficit. In addition, similar cases reported in literature were reviewed.
Conclusion
Because most of the patients developing ASDH underwent emergent surgical intervention, the incidence of this phenomenon may be underestimated. Although emergent surgical removal remains the first choice for the treatment of ASDH, conservative management with careful monitoring may also work out in selected patients who show neurologic and radiologic improvements.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Matsuyama T, Shimomura T, Okumura Y et al (1997) Rapid resolution of symptomatic acute subdural hematoma: case report. Surg Neurol 48:193–196
Cohen JE, Eger K, Montero A et al (1998) Rapid spontaneous resolution of acute subdural hematoma and HIV related cerebral atrophy: case report. Surg Neurol 50:241–244
Niikawa S, Sugimoto S, Hattori T et al (1989) Rapid resolution of acute subdural hematoma—report of four cases. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 29:820–824
Kuroiwa T, Tanabe H, Takatsuka H et al (1993) Rapid spontaneous resolution of acute extradural and subdural hematomas. Case report. J Neurosurg 78:126–128
Juran V, Smrcka M (1997) Rapid resolution of acute subdural hematoma. Case report. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 99(supplement(1)):S73
Tsui EY, Fai Ma K, Cheung YK et al (2000) Rapid spontaneous resolution and redistribution of acute subdural hematoma in a patient with chronic alcoholism: a case report. Eur J Radiol 36:53–57
Kato N, Tsunoda T, Matsumura A et al (2001) Rapid spontaneous resolution of acute subdural hematoma occurs by redistribution—two case reports. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 41:140–143
Inamasu J, Nakamura Y, Saito R et al (2002) Rapid resolution of traumatic acute subdural hematoma by redistribution. Am J Emerg Med 20:376–377
Imai K (2003) Rapid spontaneous resolution of signs of intracranial herniation due to subdural hematoma—case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 43:125–129
Berker M, Gulsen S, Ozcan OE (2003) Ultra rapid spontaneous resolution of acute posttraumatic subdural hematomas in patient with temporal linear fracture. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 145:715–717
Erol FS, Kaplan M, Topsakal C et al (2004) Coexistence of rapidly resolving acute subdural hematoma and delayed traumatic intracerebral hemorrhage. Pediatr Neurosurg 40:238–240
Kundra SN, Kundra R (2005) Extracranial redistribution causing rapid spontaneous resolution of acute subdural hematoma. Neurol India 53:124
Huang SH, Lee HM, Lin CK et al (2005) Rapid resolution of infantile acute subdural hematoma: a case report. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 21:291–294
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, L., Liu, W.G., Ma, L. et al. Spontaneous rapid resolution of acute subdural hematoma after head trauma: Is it truly rare?. Ir J Med Sci 178, 367–371 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-008-0168-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-008-0168-5